Prelims

Typhoid Fever
About the disease
- Typhoid is a life-threatening bacterial infection caused by Salmonella Typhi.
- It spreads mainly through the faecal–oral route via contaminated food and water.
- After ingestion, bacteria multiply and enter the bloodstream.
- Common symptoms include prolonged fever and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Severe cases may cause complications or death, confirmed through blood testing.
Disease Burden and Risk
- In 2019, an estimated 9.24 million cases and ~1.1 lakh deaths occurred globally.
- Majority of cases and deaths occurred in South-East Asia and Africa.
- Risk is higher in areas with unsafe water and poor sanitation, especially among children.
Treatment and Resistance
- Antibiotics are the primary treatment for typhoid fever.
- Antimicrobial resistance has reduced effectiveness of standard antibiotics.
Prevention and Vaccination
- Prevention depends on safe water, sanitation and hygiene.
- World Health Organization recommends typhoid conjugate vaccines in endemic countries.
- Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance supports vaccine rollout in eligible nations.
- Gavi was established in 2000 as a global health partnership.
Venezuela Crisis and India’s Energy Security

India–Venezuela Oil Trade
- India imported $255.3 million worth of oil from Venezuela till November 2025.
- This constituted only 0.3% of India’s total oil imports during the period.
- In 2013, India imported nearly $13 billion worth of Venezuelan crude oil.
- Since 2019, India has steadily reduced imports due to U.S. sanctions.
- Fear of secondary sanctions constrained commercial engagement with Venezuela.
Venezuela in Global Oil Markets
- Venezuela is a member of Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
- It contributes about 3.5% of OPEC oil exports.
- Venezuela accounts for roughly 1% of global oil supply.
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
- OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organisation of 12 oil-exporting developing countries created at the Baghdad Conference in 1960.
- Headquarters of OPEC is located in Vienna, Austria.
- Founding members were Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
- India is not a member of OPEC.
- Objective is to coordinate and unify petroleum policies of member countries.
- OPEC aims to ensure fair and stable petroleum prices for producers.
OPEC+
- OPEC+ was formed in 2016 through partnership between OPEC and non-OPEC producers.
- It consists of OPEC members plus 10 additional oil-producing countries.
- OPEC members include Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria and UAE.
- Non-OPEC members include Russia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei and Kazakhstan.
- Other non-OPEC participants are Mexico, Malaysia, Oman, South Sudan and Sudan.
Chenab River
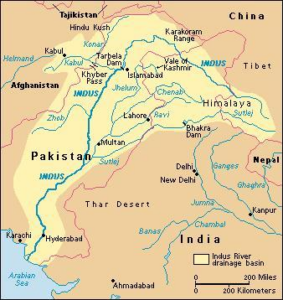
Origin and Course
- Chenab River originates at Tandi, Himachal Pradesh, from Chandra–Bhaga confluence.
- It flows through Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The river enters Pakistan after flowing northwest.
- Chenab joins the Sutlej River in Pakistan, which later joins the Indus.
- Major tributaries include Marusudar, Jhelum and Sohan rivers.
Important Dams on Chenab River
- Salal Dam
- Located in Reasi district, commissioned 1987–1995.
- It is a run-of-the-river project with 690 MW capacity.
- Baglihar Dam
- Located in Ramban district.
- It is a run-of-the-river with storage project, commissioned in 2009.
- Has an installed capacity of 450 MW (Stage-I).
- Dul Hasti Dam
- Located in Kishtwar district.
- It is a run-of-the-river project with 390 MW capacity.
Important Upcoming Projects on Chenab
- Pakal Dul Project
- Located in Kishtwar district.
- Itis a storage-cum-hydropower project with 1,000 MW capacity.
- Kiru Project
- It is a run-of-the-river project of 624 MW in Kishtwar.
- Ratle Project
- It is a run-of-the-river project with 850 MW capacity.
White-bellied Heron

Context: Environmental clearance recommended for Kalai-II Hydropower Project on Lohit River. The river forms part of the species’ natural habitat.
Species Profile
- White-bellied heron (Ardea insignis) is a large heron species.
- It is the second largest living heron.
- Also called imperial heron or great white-bellied heron.
Habitat and Distribution
- Inhabits wetlands in tropical and subtropical forests.
- Found along eastern Himalayan foothills.
- Distribution spans northeast India, Bhutan and northern Myanmar.
Ecology
- Prefers free-flowing rivers with minimal disturbance.
- Diet consists mainly of fish from river rapids.
Threats
- Threatened by habitat loss and degradation.
- Impacted by wetland conversion and settlement expansion.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.
Rani Velu Nachiyar

Core Profile
-
- Rani Velu Nachiyar lived from 1730 to 1796.
- She was the queen of Sivaganga in present-day Tamil Nadu.
- She belonged to the Ramnad (Ramanathapuram) kingdom.
- Also known by the title Veeramangai.
- Family and Marriage
-
- Daughter of Raja Chellamuthu Vijayaragunatha Sethupathy.
- Married Muthuvadugananthur Udaiyathevar, prince of Sivaganga, at age 16.
Skills and Learning
- Trained in weapon handling, horse riding and archery.
- Skilled in Silambam and Valari martial traditions.
- Proficient in Tamil, English, French and Urdu.
Resistance and Administration
- Formed alliances with Hyder Ali of Mysore and Gopala Nayaker.
- Organised an army including a women’s battalion named “Udaiyaal”.
- Regarded as the first Indian queen to resist British rule.
- Delegated administrative authority to the Marudu brothers in 1780.

