Prelims

Polavaram Project

Basic Profile
- Polavaram is a multi-purpose irrigation project.
- Constructed on the Godavari River.
- Located in West and East Godavari districts, Andhra Pradesh.
- Accorded National Project status by the Union Government.
Structural Features
- Dam length is about 1.2 km.
- Pier height measures 54 metres.
- Equipped with 48 radial gates.
- Each gate measures 16 m × 20 m.
- Spillway Capacity
- Designed for once-in-1000-year flood events.
- Spillway discharge capacity is 50 lakh cusecs.
- Claimed to be highest spillway capacity globally.
- Exceeds spillway capacity of Three Gorges Dam, China.
- Irrigation and Water Transfer
- Creates 4,36,825 hectares of gross irrigation potential.
- Diverts 80 TMC water to the Krishna River basin.
- Supplies drinking water to 28.50 lakh people.
- Covers 611 villages.
- Power Generation
-
- Planned hydropower capacity of 960 MW.
- Planned hydropower capacity of 960 MW.
DPDP Act and RTI Act Interface

Context
- The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 amended provisions of the RTI Act, 2005. Civil society groups argued that amendments weakened transparency and accountability. The issue centres on changes to Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act.
Attorney-General’s Opinion
-
- Attorney-General stated DPDP Act does not dilute the RTI Act.
- He argued the Act balances privacy and transparency, consistent with constitutional principles.
- The opinion emphasised harmony between data protection and public accountability.
- Key Legal Reasoning
-
- Although Section 8(1)(j) was amended, Section 8(2) of RTI Act remains unchanged.
- Section 8(2) mandates disclosure of exempt information when public interest outweighs harm.
- Therefore, disclosure of personal information is still possible under larger public interest.
- According to the opinion, accountability mechanisms under RTI remain legally intact.
Concerns Raised by Critics
- Critics argue amendment converts a conditional exemption into a total exemption.
- Earlier, personal information could be disclosed if linked to public activity or interest.
- The previous proviso ensured information shared with Parliament could not be denied to citizens.
- Transparency advocates fear reduced access to information about public authorities.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDP Act)
- Applicability
-
- Applies to digital personal data processed within India, including digitised offline data.
- Extends to extra-territorial processing if goods or services are offered in India.
- Excludes personal data used for personal purposes or made public legally by the individual.
- Consent Framework
-
- Data processing permitted only for lawful purposes with consent of the Data Principal.
- Consent can be withdrawn at any time.
- Children defined as below 18 years; verifiable parental or guardian consent mandatory.
- Section 9 prohibits harmful processing and targeted advertising towards children.
- Consent exemption allowed for government services, medical emergencies, and legitimate uses.
- Rights and Duties of Data Principals
-
- Rights include access, correction, erasure, grievance redressal, and nomination of representatives.
- Duty to avoid false or frivolous complaints, with penalties up to ₹10,000.
Gold Exchange-Traded Funds (Gold ETFs)

Core Features
- Gold ETFs are commodity-based exchange-traded funds.
- Underlying asset is physical gold bullion.
- Structured as passive investment instruments tracking gold prices.
- ETF units represent physical gold in demat or paper form.
- One unit equals 1 gram of gold.
- Backed by high-purity physical gold.
Trading and Transparency
- Listed and traded on National Stock Exchange of India.
- Also traded on Bombay Stock Exchange.
- Offer full transparency of holdings due to direct gold pricing.
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)
-
- ETF is a basket of securities traded like a stock.
- Can include equities, bonds, or commodities.
- Cost Aspect
-
- ETFs generally have lower fees than mutual funds.
- Gold ETFs have lower expenses than physical gold investments.
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)

Legal Status
- IRDAI is a statutory regulatory body.
- Established under the IRDAI Act, 1999.
- Functions as an autonomous authority.
- Works under the Ministry of Finance.
- Head office located at Hyderabad.
Core Mandate
- Protects policyholders’ interests.
- Regulates and develops the insurance sector.
- Ensures fair conduct and transparency in insurance business.
- Enforces financial prudence and solvency norms.
Composition
- Consists of a Chairperson.
- Includes five full-time members.
- Includes four part-time members.
- Members appointed by the Government of India.
Regulatory Powers
- Registers and licenses insurers and intermediaries.
- Prescribes capital and eligibility requirements.
- Regulates premium pricing and policy conditions.
- Approves insurance products.
- Regulates investment of insurance funds.
- Specifies financial reporting standards.
- Conducts inspection, audit and investigation.
Entities Regulated
- Life insurance companies (public and private).
- General insurance companies.
- Standalone health insurance companies.
- Reinsurance companies.
- Insurance intermediaries.
Intermediaries Covered
- Corporate agents.
- Insurance brokers.
- Third-party administrators (TPAs).
- Surveyors and loss assessors.
District-Led Textiles Transformation (DLTT) Plan

Context: Ministry of Textiles announced DLTT to develop district-level textile hubs.
Scheme Profile
- DLTT is a district-centric textiles transformation strategy.
- Implemented by the Ministry of Textiles.
- Targets 100 Global Export Champion districts.
- Upgrades 100 Aspirational Districts into self-reliant hubs.
Core Objective
- Promote export-oriented and inclusive growth in textiles.
- Strengthen MSMEs and formalise workforce at district level.
District Categorisation
- Districts assessed using data-driven scoring.
- Scoring parameters include exports, MSMEs and workforce presence.
Two-Pronged Strategy
- Champion Districts focus on scale and sophistication.
- Support includes Mega CFCs and Industry 4.0 adoption.
- Aspirational Districts focus on foundation and formalisation.
- Support includes skilling, certification and Raw Material Banks.
Regional Focus
- Emphasises Purvodaya convergence.
- Targets Eastern and North-Eastern India.
- Includes tribal belt development and GI tagging.
Implementation Model
- Based on convergence of schemes.
- Involves government, industry and academia collaboration.
Dust EXperiment (DEX)

Context: ISRO confirmed one IDP enters Earth’s atmosphere every ~16 minutes using DEX data.
About DEX
-
- DEX is India’s first indigenous cosmic dust detector.
- Detects interplanetary and orbital dust in Earth’s upper atmosphere.
- Developers and Platform
-
-
- Developed by Indian Space Research Organisation.
- Built by Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad.
- Flown on POEM of PSLV-C58 mission.
-
- Mission Aim
-
- Measures cosmic dust flux in near-Earth space.
- Generates data for space environment monitoring and satellite safety.
- Key Technical Features
-
- Detects hypervelocity impacts (>4 km/s).
- Payload mass ~3 kg; power ~4.5 W.
- 140° field of view for higher hit probability.
- Operated in LEO ~350 km, ~9.5° inclination.
- Measurements
-
- Detection rate ~1 particle per 1,000 seconds.
- Measured flux ~6.5 × 10⁻³ particles m⁻² s⁻¹.
Interplanetary Dust Particles (IDPs)
- IDPs are microscopic fragments from comets, asteroids and meteoroids.
-
- Continuously enter planetary atmospheres.
- Origins: From cometary debris, asteroidal collisions, and cosmic erosion.
- Relevance
-
- Pose risk to spacecraft at hypervelocity.
- Inform near-Earth space environment assessments.
Spina Bifida
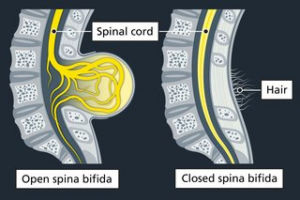
Core Concept
- Spina bifida is a congenital neural tube defect.
- Occurs due to incomplete spinal cord development.
- Develops within the first 28 days after conception.
Nature of Condition
- It is a non-communicable birth defect.
- Strongly associated with maternal folate deficiency.
Primary Causes
- Inadequate folic acid intake during early pregnancy.
- Poor maternal nutrition or anaemia.
- Unplanned pregnancies without supplementation.
- Possible genetic and environmental interaction.
Key Clinical Features
- Sac-like swelling on the back at birth.
- Weakness or paralysis of lower limbs.
- Hydrocephalus due to impaired CSF drainage.
- Urinary and bowel incontinence.
- Orthopaedic deformities, including club foot.
Management
- Early surgical closure of spinal defect.
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt for hydrocephalus.
- Long-term rehabilitation therapy.
- Orthopaedic correction using surgery or braces.

