Prelims Pinpointer
Parliamentary Privileges & Immunities

Core Concept
- Parliamentary privileges are special rights, freedoms and immunities.
- Available to MPs and State Legislature members.
- Aim is independent and obstruction-free functioning of legislatures.
Historical Origin
- Rooted in the Charter Act, 1833.
- Expanded under Government of India Act, 1935.
Sources
| Article | Provision |
| Article 105 | Freedom of speech, immunity for MPs, power to define privileges |
| Article 122 | Courts barred from examining Parliamentary procedure |
| Article 194 | Same privileges for State Legislatures |
| Article 212 | Courts barred from State Legislature procedural scrutiny |
- Other Sources
-
- British Parliamentary conventions (as in 1947)
- Statutory laws enacted by Parliament
- Rules of Procedure of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
- Judicial interpretations
Legal Position
- No Act of Parliament defines privileges.
- Privileges currently follow British conventions.
- Lok Sabha Privileges Committee (2008) rejected codification.
Nature of Privileges
- Available to individual members and the House.
- Co-terminus with membership.
- Cease after member leaves office.
- Individual Privileges of MPs & MLAs
| Right | Source |
| Freedom of speech in legislature | Article 105(1) |
| Immunity for speech and votes | Article 105(2) |
| Protection for authorised publications | Article 105(2) |
| Courts barred from procedural inquiry | Article 122(1) |
| Freedom from civil arrest during session + 40 days before & after | Section 135A, CPC 1908 |
-
- Power to publish and restrict parliamentary reports
- 44th Constitutional Amendment (1978) allows press reporting except secret sittings
- Power to hold secret sittings
- Authority to make internal rules
- Power to punish for breach or contempt
- Right to information on member arrest or detention
- Power to summon witnesses and demand records
- Judicial immunity for proceedings
- No arrest inside Parliament without Presiding Officer’s consent
Breach of Privilege
- Violation of House or Member rights
- Includes disobedience of House orders
- Includes defamatory acts against House, members, committees
Contempt of the House
- Any act obstructing legislative functioning
- Includes:
- Defamatory publications
- Questioning Chair’s impartiality
- Publishing expunged proceedings
| Step | Authority |
| Motion moved with consent | Speaker (LS) / Chairman (RS) |
| Committee referral | 10 members (RS), 15 members (LS) |
| Committee role | Determines breach, submits report |
| House decision | Accepts or rejects report |
| Chairman’s power | Suo-motu reference or inquiry |
| Restriction | One issue per sitting, must be recent |
Punishments
- Reprimand
- Warning
- Imprisonment (only during House session)
- Suspension
- Expulsion
Supreme Court Judgments
| Case | Principle |
| P.V. Narasimha Rao (1998) | MPs immune if vote linked to bribe |
| K. Ajith (2021) | Privileges do not override criminal law |
| Sita Soren (2024) | Bribery not protected by Articles 105 & 194 |
Aditya-L1 and Solar Storm Impact

Mission & Source
- Aditya-L1 is India’s first solar observatory.
- Operated by Indian Space Research Organisation.
- Study published in The Astrophysical Journal (December 2024).
Space-Weather Event
- A major solar storm hit Earth in October 2024.
- Event involved massive solar plasma eruption.
- Analysis used Aditya-L1 and international mission data.
Key Observations
- Turbulent region caused the strongest effects.
- Earth’s magnetic field was strongly compressed.
- Magnetosphere was pushed unusually close to Earth.
- Geostationary satellites were briefly exposed to harsh space conditions.
- Such exposure occurs only during severe space-weather events.
Auroral & Atmospheric Effects
- Auroral-region currents intensified at high latitudes.
- This led to upper-atmosphere heating.
- Resulted in enhanced atmospheric escape.
Space Weather Definition (ISRO)
- Caused by solar transient activity.
- Includes solar plasma eruptions.
- Can affect satellites, navigation, communications, power grids.
National Improvised Explosive Device Data Management System (NIDMS)

In News: Inaugurated by the Union Home Minister at NSG Garrison, Manesar.
System Profile
- NIDMS is a secure national digital IED database platform.
- Stores IED and bomb-blast data since 1999.
- Provides single-window access to investigation agencies.
Institutional Framework
- Policy authority: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Operational host: National Security Guard (NSG).
- Technical backbone: National Bomb Data Centre (NBDC), NSG.
User Agencies
- State Police Forces.
- Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs).
- National Investigation Agency (NIA).
- Anti-Terrorism Squads (ATS).
Core Objective: Create “One Nation, One IED Data Repository”.
Database Features
- Pan-India IED archive since 1999.
- Two-way system: upload and retrieval of data.
- Signature-based linking of incidents.
- Parameters include location, device type, circuit, timer, explosive.
Analytics Capability
- AI-enabled pattern detection.
- Supports modus-operandi analysis.
- Enables predictive threat mapping.
Inter-Operable Systems
- Integrated with
-
-
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS)
- Interoperable Criminal Justice System – Phase II (ICJS-2)
- National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS)
- e-Prisons
- e-Prosecution
- Forensics databases
-
- Data Standards
-
- Uses uniform data formats.
- Includes evidence tagging.
- Ensures secure data sharing.
Zehanpora Stupa Site

Context: Kushan-period Buddhist complex excavated at Zehanpora, Baramulla.
Location
- Situated in Zehanpora village, Baramulla district, Jammu & Kashmir.
- Lies on the ancient Silk Route corridor.
- Route linked Kashmir with Gandhara (Afghanistan–Pakistan).
Chronology
- Dated to Kushan period (1st–3rd century CE).
- Kashmir was a Buddhist centre under Kanishka and Huvishka.
- Buddhism in Kashmir began under Ashoka (3rd century BCE).
- Region associated with Mahayana Buddhism.
Cultural Network
- Zehanpora was part of the Gandhara Buddhist network.
- Network connected monasteries, trade routes and learning centres.
Site Components
- Contains multiple stupas.
- Includes apsidal chaityas (prayer halls).
- Includes viharas (monk residences).
- Includes urban-type settlements.
- Spread over nearly 10 acres.
Structural Evidence
- Presence of stupa-base mounds.
- Clustered mounds indicate multiple stupas.
- Evidence of wooden super-structures.
- Shows layered construction.
Survey Methods
- Used drones.
- Used remote sensing.
- Used aerial photography.
- Used ground mapping.
Kashmir Markhor

In News: The Kashmir markhor population is estimated at 200–300 individuals, mainly confined to the Kazinag range of Jammu & Kashmir.
About the Species
- Taxonomy
-
- Subspecies of markhor (Capra falconeri).
- Classified as a wild mountain goat.
-
- Endemism: Occurs in India only in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Etymology
-
-
- “Markhor” derived from Persian meaning “snake-killer”.
-
- Habitat Range
-
-
- Found in Pir Panjal range of Jammu & Kashmir.
-
- Recorded in:
-
-
- Kazinag National Park
- Hirpora Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tattakuti Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khara Gali Conservation Reserve
-
- Habitat Type
-
-
- Lives in rocky cliffs, open forests and alpine meadows.
-
- Physical Traits
-
- Body weight up to 100 kg.
- Male horn length up to 160 cm.
- Has long hair for cold-climate insulation.
- Capable of nearly vertical cliff movement.
- Diet
-
-
- Feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, leaves and twigs.
-
- Ecological Role
-
- Serves as indicator of mountain ecosystem health.
- Acts as prey for snow leopards, leopards and wolves.
Weimar Triangle
Context: India participated for the first time in the Weimar Triangle format.
About Weimar Triangle
- Basic Profile
-
- A trilateral diplomatic grouping.
- Members: France, Germany and Poland.
- Origin
-
- Established in 1991.
- Named after Weimar city, Germany.
- First meeting held by foreign ministers.
- Purpose
-
- Promotes European integration.
- Supports political and security coordination.
- Focused on Eastern Europe and Russia-related issues.
- Key Functions
-
- Coordinates EU foreign and security policy positions.
- Acts on Russia–Ukraine security matters.
- Holds pre-summit consultations before EU and NATO meetings.
- Supports trilateral cooperation in diplomacy, defence and economy.
- Historical Role
-
- Supported Poland’s NATO entry (1999), Poland’s EU accession (2004).
- Geopolitical Role
-
- Serves as a link between Western and Central/Eastern Europe.
- Influences EU policy on Russia and Ukraine.
New Frog Species from Arunachal Pradesh

Discovery
- Two new frog species discovered in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Discovery led by S. D. Biju (Frogman of India).
- Genus: Leptobrachium.
Soman’s Slender Arm Frog (Leptobrachium somani)
- A new slender-armed frog species.
- Found at Tiwarigaon, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Named after E. Somanath (journalist).
- Body length ~55 mm.
- Colour: greyish-brown with light-grey markings.
- Eye colour: silver-grey to light-blue.
- Habitat: evergreen forests.
- Males call from stream banks.
Mechuka Slender Arm Frog (Leptobrachium mechuka)
- A new slender-armed frog species.
- Named after Mechuka town, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Body length ~60 mm.
- Habitat: evergreen forests and grasslands.
- Colour: uniform brown with reddish tinge.
- Eye colour: silvery-white.
Ratapani Tiger Reserve
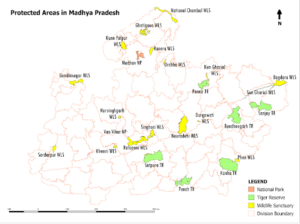
Context: Newly notified Ratapani Tiger Reserve named after Dr. Vishnu Shridhar Wakankar.
Location
- Located in Raisen and Sehore districts, Madhya Pradesh.
- Lies in the Vindhya Range hills.
- Runs along the northern bank of the Narmada River.
- Kolar River forms the western boundary.

Area & Landscape
- Total area 1,271 sq km.
- Terrain includes hills, plateaus, valleys and plains.
Water Bodies
- Barna Reservoir.
- Ratapani Dam (Barrusot Lake).
Heritage Sites
- Contains Bhimbetka rock shelters.
- Bhimbetka is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Includes Ginnourgarh Fort, POW camp, Keri Mahadeo, Ratapani Dam, Jholiyapur Dam.
Vegetation
- Forest type: dry deciduous and moist deciduous.
- Dominant tree: Teak (Tectona grandis).
- Teak covers about 55% of the area.
- Tiger is the apex predator.
- Tiger population ~40 individuals.
- Chinkara present (endangered).
- Other fauna: Panther, Hyena, Jackal, Indian Fox, Wild Dog, Jungle Cat, Small Indian Civet, Nilgai, Blackbuck, Chausingha, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer.

