
Ayushman Arogya Mandir (AAM)

Overview
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir aims to shift India’s healthcare from selective care to comprehensive primary healthcare.
- Delivers preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care at community level.
Components (Two-Pillar Structure)
- Component 1: Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC)
- 1.5 lakh Ayushman Arogya Mandirs to be established nationwide.
- Provides universal, free primary healthcare services.
- Focus on wellness, disease prevention and early diagnosis close to communities.
- Component 2: Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
- Provides ₹5 lakh per family per year health insurance cover.
- Covers secondary and tertiary hospitalisation.
- Targets over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families.
Ayushman Bharat – PM-JAY
- Flagship health scheme of Government of India, launched as per National Health Policy 2017.
- Aims to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- World’s largest health assurance scheme.
- Covers ₹5 lakh per family per year for hospitalisation.
- Beneficiaries: Over 12 crore families (~55 crore people), bottom 40% of population.
Responsible Nations Index (RNI)

Context:
- World Intellectual Foundation (WIF) to launch Responsible Nations Index (RNI).
- Collaborators: Jawaharlal Nehru University, IIM Mumbai, Dr Ambedkar International Centre.
What it is?
- Global ranking framework assessing how responsibly nations govern society, environment, and global conduct.
Aim:
- Shift benchmarking from GDP/power-centric metrics to values-based governance, dignity, sustainability, and international responsibility.
Key Features:
- Covers 154 countries worldwide.
- Uses transparent, globally sourced datasets.
- Three core dimensions:
- Internal Responsibility: citizen dignity, justice, welfare.
- Environmental Responsibility: climate action, resource stewardship.
- External Responsibility: peace, cooperation, global stability.
- Comparable, objective, policy-relevant design.
Significance:
- Adds an ethical lens beyond economic or military power.
- Incentivises human development, sustainability, and peace.
- Aligns with SDGs, climate commitments, and human rights.
BRICS India 2026 Logo

What is the BRICS India 2026 Logo?
- Official visual identity of India’s BRICS Chairship (2026).
- Reflects India’s vision, values and priorities for leading BRICS.
India’s BRICS Chairship 2026
- Host country: India
- Chairship period: Calendar year 2026
- Milestone: 20th anniversary of BRICS (2006–2026)
Theme & Symbolism
- Inspired by India’s national flower – Lotus.
- Symbolises:
- Resilience and renewal
- Unity in diversity
- Cultural and spiritual harmony
- Core message: “Togetherness for global welfare”
- Aligns with India’s philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (One Earth, One Family).
Key Features of the Logo
- Lotus shape: Represents India’s civilisational identity and growth through adversity.
- Namaste hands at the centre: Symbolise respect, dialogue and cooperation.
- Five coloured petals: Represent the founding BRICS nations – Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Balanced design: Reflects unity among diverse cultures, economies and political systems.
- Digital platform: Dedicated BRICS India 2026 website for meetings, initiatives, outcomes and public engagement.
Significance
- Projects India’s leadership role in the Global South.
- Reinforces BRICS as a people-centric, development-oriented platform.
- Aligns with India’s four priorities for BRICS 2026:
- Resilience
- Innovation
- Cooperation
- Sustainability
Catastrophe Bonds (CAT Bonds)

What are Catastrophe Bonds?
- Insurance-linked securities that transfer natural disaster risk from governments/insurers to capital markets.
- Hybrid financial instrument combining insurance + debt features.
- Converts disaster insurance coverage into a tradable bond.
- Used to manage low-probability, high-impact risks like earthquakes, cyclones and floods.
Why CAT Bonds are Needed
- Traditionally, financial risk of disasters is fully borne by State/Central governments.
- CAT bonds help:
- Reduce fiscal burden after disasters
- Ensure quick liquidity for relief and reconstruction
- Diversify risk globally
Key Stakeholders
- Sponsor: Sovereign governments (pay insurance premium).
- Intermediaries: Multilateral institutions like World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
- Investors: Pension funds, hedge funds, family offices, institutional investors.
How CAT Bonds Work
- Government pays premium → bond issued via intermediary.
- Investors receive regular coupons.
- If no disaster occurs → investors get principal + interest.
- If specified disaster occurs → investors may lose part/all principal, which is used for disaster relief.
Pricing and Risk
- Coupon rate depends on:
- Probability of disaster
- Severity and frequency
- Earthquake bonds: Lower premiums (~1–2%).
- Cyclone/hurricane bonds: Higher premiums due to greater frequency and uncertainty.
- Risks are non-correlated with financial markets, making them attractive for diversification.
Global Examples
- Mexico: Pioneer in sovereign CAT bonds for earthquake and cyclone risks.
- Philippines: Uses CAT bonds for typhoon and earthquake protection.
Key Advantages
- Transfers disaster risk to global capital markets.
- Provides pre-arranged, rapid funding after disasters.
- Reduces post-disaster borrowing and fiscal stress.
- Encourages disaster risk management and preparedness.
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)

Context:
- 16th Assembly of International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) concluded in Abu Dhabi, urging faster global renewable energy transition.
What is IRENA?
- World’s only intergovernmental organisation dedicated exclusively to renewable energy.
- Serves as a global hub for policy advice, data, technology cooperation, and investment support.
Establishment & Membership
- Founded: 26 January 2009, Bonn (Germany)
- Statute in force: 8 July 2010
- Headquarters: Masdar City, Abu Dhabi (UAE)
- India: Founding member
Aim
- Accelerate global energy transition through sustainable and equitable renewable energy use.
- Supports climate mitigation, energy access, energy security, and green growth.
Key Functions
- Policy guidance: National renewable policies and transition roadmaps.
- Data & analysis: Global datasets on costs, investments, and deployment.
- Technology support: Solar, wind, bioenergy, geothermal, hydro, ocean energy.
- Capacity building: Training for governments and utilities.
- Investment facilitation: Mobilises green finance, especially for developing countries.
- Global cooperation: Platform for renewable energy diplomacy.
Significance
- Central pillar of global clean-energy transition.
- Supports SDG-7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and Net-Zero targets.
- Reduces fossil-fuel dependence, enhancing energy security and climate resilience.
Menkes Disease
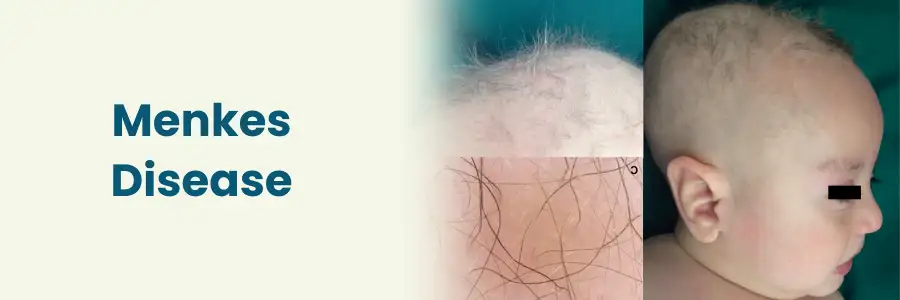
What is Menkes Disease?
- Rare genetic disorder affecting the body’s ability to absorb, transport and utilise copper.
- Also known as “Kinky Hair Disease”.
Genetic Basis
- Caused by mutation in ATP7A gene.
- Gene location: X chromosome.
- Inheritance pattern: X-linked recessive.
- Therefore, mostly affects male infants.
Role of Copper (Normal Physiology)
- Required in very small amounts, but essential for:
- Brain and nervous system development
- Blood vessel and blood cell formation
- Iron metabolism (conversion into usable form)
- Immune function
- Wound healing and metabolism
- Copper is naturally present in food and supplements.
Pathophysiology
- Impaired copper transport → low copper levels in:
- Blood plasma
- Liver
- Brain
- Reduced activity of copper-dependent enzymes.
- Copper may accumulate abnormally in kidneys and other tissues.
- Leads to severe neurological damage and developmental delay.
Key Clinical Features
- Coarse, brittle, kinky (crinkly) hair – hallmark feature.
- Failure to thrive and poor growth.
- Neurological symptoms:
- Seizures
- Hypotonia (floppy muscles)
- Developmental delay
- Progressive damage to brain and nervous system.
Epidemiology
- Occurs in about 1 in 35,000 live male births.
- Extremely rare in females.
Treatment
- No permanent cure available.
- Early copper replacement therapy improves outcomes.
- Treatment includes:
- Copper histidine injections (parenteral copper supplementation).
- Early initiation can reduce symptom severity and prolong life.
Prognosis
- Without treatment, most children do not survive beyond 3 years of age.
- Early diagnosis is critical for survival benefit.


