
Budget Context and Strategic Vision
- Union Budget 2026 targets productivity enhancement and employment generation amid volatile global economic conditions.
- Finance Minister emphasised deep integration with global markets to attract stable, long-term investment.
- The Budget marked the ninth consecutive presentation by the same Finance Minister.
- No major direct tax rate relaxations were announced for individuals or corporations.
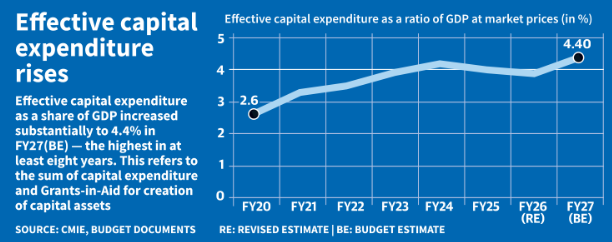
- The Centre’s capital expenditure target is set at ₹12.2 lakh crore for 2026–27.
- This exceeds ₹10.9 lakh crore Revised Estimates of 2025–26 and ₹11.2 lakh crore Budget Estimates.
- Capex is positioned as a growth multiplier for productivity, infrastructure, and employment creation.
Structural Reforms and Growth Framework
- The Budget aims to support Viksit Bharat 2047 through sustained growth and competitiveness.
- It focuses on building resilience to volatile global dynamics and boosting domestic capacity.
- Emphasis is placed on enhancing productivity across sectors through systemic reforms.
Three Kartavyas for Development
- First Kartavya
- Accelerate growth by strengthening manufacturing, infrastructure, and energy security.
- Targeted areas include seven strategic sectors, MSMEs, and city-economic regions.
- Second Kartavya
- Build capacity through education, skilling, and services sector development.
- Focus sectors include healthcare, medical tourism, AVGC, design, and animal husbandry.
- Third Kartavya
- Promote inclusion by empowering farmers, Divyang, and vulnerable populations.
Infrastructure and Regional Initiatives
- Support for rare earth corridors in Odisha, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Announcement of a new national waterway in Odisha connecting industrial and port regions.
- Launch of East Coast Industrial Corridor and a Dankuni–Surat freight corridor.
Trade and Energy Measures
- Customs duty reductions target marine, leather, and textile exports.
- Measures aim to accelerate India’s energy transition and export competitiveness.
Basics of Capital Expenditure in Government Budgeting
- Capital Expenditure (Capex) refers to government spending on creating long-term productive assets.
- It includes investments in machinery, buildings, health facilities, education infrastructure, and equipment.
- Capex focuses on capacity creation and future economic returns, not immediate consumption.
- Components of Capital Expenditure
- Acquisition of fixed and intangible assets such as infrastructure, technology, and institutional facilities.
- Upgradation of existing assets to improve efficiency, capacity, and service delivery.
- Repair and maintenance of assets to extend operational life and productivity.
- Repayment of government loans, which reduces public liabilities and fiscal burden.
- Multiplier Effect and Economic Impact
- Capex generates the highest multiplier effect among government expenditure categories.
- It stimulates ancillary industries, services expansion, and large-scale job creation.
- According to the National Institute of Public Finance and Policy, revenue spending yields ₹0.98 multiplier.
- Capex delivers a ₹2.25 multiplier in the same year and ₹4.80 over full expenditure cycle.
- Role in Productivity and Stability
- Capex improves labour productivity by strengthening physical and institutional infrastructure.
- It functions as a macroeconomic stabiliser during economic downturns.
- It supports countercyclical fiscal policy by boosting demand and investment during slowdowns.
- Revenue Generation and Fiscal Benefits
- Asset creation enables long-term revenue streams through improved operational efficiency.
- Repayment of loans under capex helps in reducing government liabilities.
- Government capex crowds in private investment, expanding production capacity.
- Contribution to Economic Growth
- Sustained capex accelerates economic growth and employment generation.
- It strengthens the foundation for long-term development and industrial expansion.
