Syllabus: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Context and Strategic Trigger
- Recent rift between Europe and the U.S. has shaken NATO’s internal cohesion.
- Dispute linked to U.S. position over Greenland, a Danish territory.
- Europe’s trust in the U.S. as security guarantor has weakened.
- Occurs alongside expiry of key nuclear arms control frameworks.
NATO’s Traditional Nuclear Role
- NATO formed in 1949 as a defensive nuclear alliance.
- Designed to counter the Soviet Union’s strategic threat.
- The U.S. functioned as the principal nuclear security provider.
- Alliance credibility historically depended on mutual trust.
Implications of Alliance Rupture
- U.S. unilateralism has hollowed NATO’s nuclear credibility.
- Europe now reassessing its independent security architecture.
- Future deterrence models may shift significantly.
- Could redefine global nuclear security debates.
Evolution of Nuclear Deterrence Thinking
- Nuclear deterrence shaped by Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) framework.
- NPT institutionalised divide between nuclear and non-nuclear states.
- Security threats have diversified beyond nuclear rivalry.
- Includes terrorism, climate change, inequality and regional conflicts.
Certainty vs Uncertainty in Deterrence
- Early nuclear debates focused on deterrence psychology.
- Uncertainty doctrine relied on ambiguity of nuclear response.
- India–Pakistan deterrence (1980s–1998) reflected this model.
- Israel’s opaque nuclear posture also reflects uncertainty deterrence.
- Major powers emphasised certainty deterrence through stockpiles and testing.
- Arsenal size signalled intent and retaliatory capability.
Nuclear Taboo and Arms Control
- No nuclear weapon used since 1945.
- Normative taboo on nuclear use strengthened globally.
- Arms control treaties reduced U.S.–Russia stockpiles.
- Yet doctrinal thinking on deterrence remained unchanged.
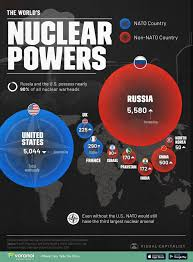
Renewed Nuclear Modernisation
- U.S., Russia and China modernising nuclear arsenals.
- China reportedly adding 100 warheads annually since 2023.
- U.K. reversed stockpile reduction; now around 225 warheads.
- New START Treaty expiry may trigger renewed arms race.
Lessons from Ukraine War
- Russia issued nuclear threats during Ukraine conflict.
- Deterrence worked through conventional response certainty.
- Ukraine, though non-nuclear, resisted nuclear adversary.
- Highlights limits of nuclear weapons in modern warfare.
Europe’s Emerging Security Choices
- Europe exploring post-U.S. defence frameworks.
- France and U.K. nuclear umbrella proposals discussed.
- “Coalition of the Willing” formed to support Ukraine.
- Future architecture may blend nuclear and conventional deterrence.
Strategic Significance
- Europe’s choices may reshape global nuclear doctrine.
- Could redefine role of nuclear weapons in security.
- Signals potential transition from Cold War deterrence logic.
