Bird Flu (Avian Influenza)
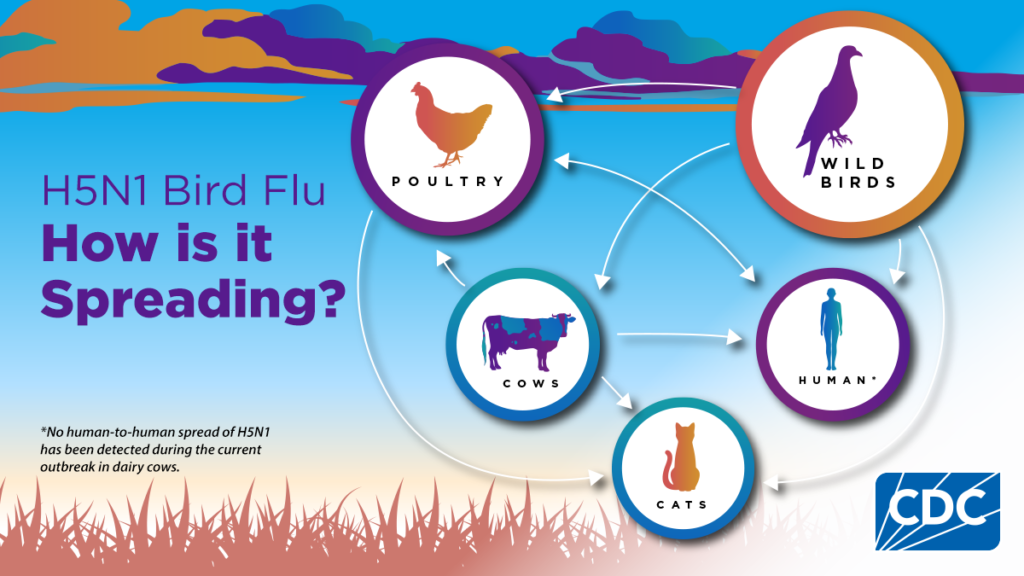
Context: Periodic outbreaks of Bird Flu, especially H5N1 strain, raise zoonotic and pandemic concerns.
What is Bird Flu?
- Bird Flu (Avian Influenza) is a viral infectious disease affecting birds.
- Primarily infects poultry and wild birds.
- Circulates naturally among 100+ bird species with limited harm.
Cause of Concern
- Virus occasionally jumps from wild birds → poultry farms.
- Crowded poultry settings enable rapid replication.
- Virus may mutate into highly pathogenic strains.
- Leads to large-scale bird mortality and culling.
H5N1 Bird Flu
- H5N1 = subtype of Influenza A virus.
- Causes severe respiratory disease in birds.
- Classified under Avian Influenza viruses.
Influenza A Classification
- Based on surface proteins:
- Hemagglutinin (H): 18 subtypes (H1–H18).
- Neuraminidase (N): 11 subtypes (N1–N11).
- Example: H1N1, H3N2, H5N1.
- Human Infection
- Rare but possible zoonotic transmission.
- Occurs via:
- Contact with infected birds.
- Handling dead poultry.
- Contaminated farm environments.
- Transmission Features
- Human-to-human spread: Very rare.
- Infection severity: High.
- Mortality rate: ~60%.
Origin & Global Spread
- Origin: Guangdong, China (1996) goose farm outbreak.
- Re-emergence: Europe (2020).
- Spread sequence:
- Africa & Asia
- North America (2021)
- South America (2022)
- Antarctica (2024)
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)

Context: The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) determines India’s policy interest rate to control inflation.
Monetary Policy
- Monetary policy uses central bank instruments to regulate money supply.
- It controls interest rates, liquidity, and credit availability.
- Objective: Achieve macroeconomic stability and policy goals.
- Legal Basis
- Conducted by Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Mandated under RBI Act, 1934.
- Amended in May 2016 to institutionalise inflation targeting.
- Primary Objective
- Maintain price stability.
- Support economic growth simultaneously.
- Price stability ensures sustainable long-term development.
- Inflation Targeting Framework
- Introduced through RBI Act amendment, 2016.
- Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) adopted.
- Inflation target set every five years.
- Decided by Government in consultation with RBI.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
- Constituted under Section 45ZB, RBI Act, 1934.
- Statutory body for policy rate decisions.
- Replaced Technical Advisory Committee system.
- Function
- Fixes benchmark policy rate (Repo Rate).
- Ensures inflation remains within target band.
- Policy decisions binding on RBI.
- Composition (6 Members)
- RBI Representatives (3)
- RBI Governor – Chairperson.
- Deputy Governor (Monetary Policy).
- One RBI Board nominee.
- Government Nominees (3)
- Appointed by Central Government.
- External experts in economics/finance.
- RBI Representatives (3)
- Tenure
- External members: 4-year fixed term.
- Not eligible for reappointment.
- Meeting & Quorum
- Meets at least four times annually.
- Quorum: Minimum four members.
- Governor or Deputy Governor mandatory.
- Decision-Making
- Decisions by majority vote.
- Governor holds casting vote in tie.
- Outcomes binding on RBI.
Sodium-ion Battery Technology

Context: India is reassessing battery strategy due to lithium supply risks and import dependence.
What is Sodium-ion Battery Technology?
- Sodium-ion batteries (SiBs) are rechargeable electrochemical energy storage devices.
- They use sodium ions (Na⁺) as charge carriers.
- Belong to rocking-chair battery family like lithium-ion cells.
- Use abundant raw materials instead of scarce lithium minerals.
Working Mechanism
- Charging Process
- Sodium ions move from cathode to anode.
- Ions travel through electrolyte medium.
- Electrons flow via external circuit.
- Discharging Process
- Sodium ions migrate back to cathode.
- Stored chemical energy converts to electrical energy.
- Power supplied to connected devices.
- Material & Design Features
- Aluminium used as current collector on both electrodes.
- Lithium-ion requires copper on anode side.
- Reduces cost and material criticality.
- Compatible with existing lithium-ion manufacturing lines.
Key Advantages
- Resource Availability
- Sodium abundantly available from salt and soda ash.
- Reduces dependence on lithium, cobalt, nickel.
- Energy Security
- Supports domestic battery manufacturing ecosystem.
- Reduces import vulnerability.
- Safety Profile
- Lower thermal runaway risk than lithium-ion.
- Safer storage and transportation at zero charge.
- Cost Potential
- Raw material abundance lowers long-term costs.
- Simplifies supply chain logistics.
- Strategic Relevance for India
- Suitable for grid storage and renewables integration.
- Aligns with clean energy transition goals.
Limitations / Challenges
- Energy Density Constraints
- Lower specific and volumetric energy density.
- Limits long-range electric vehicle deployment.
- Technology Maturity
- Early commercialisation stage globally.
- Performance optimisation ongoing.
- Manufacturing Sensitivity
- Moisture-sensitive materials require controlled environments.
- Increases drying and vacuum processing needs.
- Application Limits
- Better suited for stationary storage systems.
- Suitable for two-/three-wheelers and short-range mobility.
International Space Station (ISS)

Context: The International Space Station (ISS) is planned to be de-orbited in 2030 through controlled re-entry.
What is the International Space Station (ISS)?
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a permanently crewed modular space laboratory.
- It operates in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Used for microgravity research, technology testing, and long-duration human spaceflight.
- Continuous human presence onboard since November 2000.
- ISS operates through a five-agency international partnership:
- NASA:National Aeronautics and Space Administration (USA)
- Roscosmos: Russian State Space Corporation
- ESA: European Space Agency
- JAXA: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
- CSA: Canadian Space Agency
Launch & Assembly Timeline
- Assembly began with launch of Zarya module on 20 November 1998.
- First long-duration crew: Expedition 1 (November 2000).
- Continuous habitation maintained since then.
Aims & Objectives
- Enable advanced scientific research in microgravity conditions.
- Study human health impacts of long-duration space missions.
- Test space technologies for Moon and Mars missions.
- Promote international cooperation in space exploration.
- Support development of Low Earth Orbit space economy.
Key Features
- Modular Architecture
- Built using multiple modules contributed by partner nations.
- Assembled incrementally in orbit.
- Permanent Crewed Laboratory
- Supports astronauts for long-duration missions.
- Continuous experiments across scientific disciplines.
- Shared Governance Model
- Each agency manages its contributed modules/hardware.
- Integrated operational coordination ensures station functioning.
- Orbital Characteristics
- Located in Low Earth Orbit (~400 km altitude).
- Travels at ~28,000 km/h.
- Orbits Earth roughly every 90 minutes.
- End-of-Life Plan
- Dedicated U.S. Deorbit Vehicle planned.
- Controlled atmospheric re-entry over remote ocean by 2030.
Significance
- Advanced space medicine and microgravity biology research.
- Enabled materials science and fluid physics experiments.
- Supported Earth observation and climate monitoring.
- Built operational experience for deep-space missions.
- Symbol of sustained peaceful international space cooperation.
Armenia
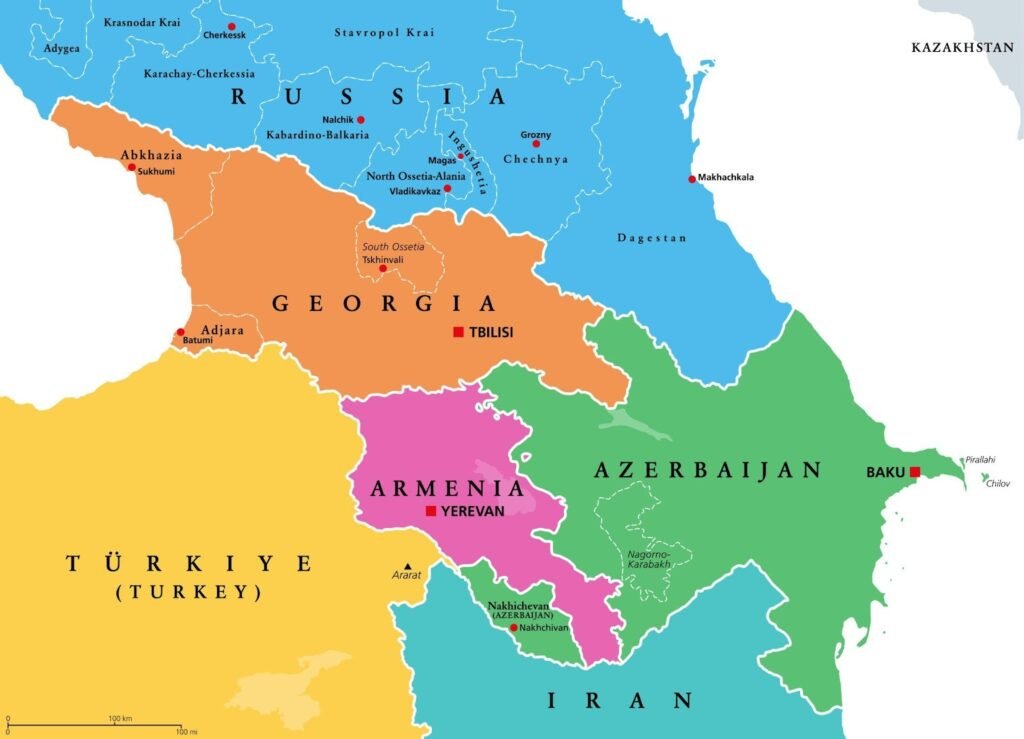
Context: India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan visited Armenia to deepen bilateral defence cooperation.
Location & Political Geography
- Armenia is a landlocked country in the South Caucasus (Transcaucasia) region.
- Lies at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia.
- Considered among the world’s oldest centres of civilisation.
- Capital: Yerevan
- Armenia shares borders with:
- Georgia – North
- Azerbaijan – East
- Iran – South
- Turkey – West
- Special Border: Borders Nakhchivan (Azerbaijan’s exclave) in the southwest.
Physiography & Geological Features
- Located on the Armenian Highland.
- Average elevation: ~1,800 metres.
- Among the most mountainous countries in the region.
Major Water Body
- Lake Sevan:
- One of the largest high-altitude freshwater lakes in Eurasia.
- Supports irrigation, hydropower, fisheries, and climate regulation.
Chabahar Port
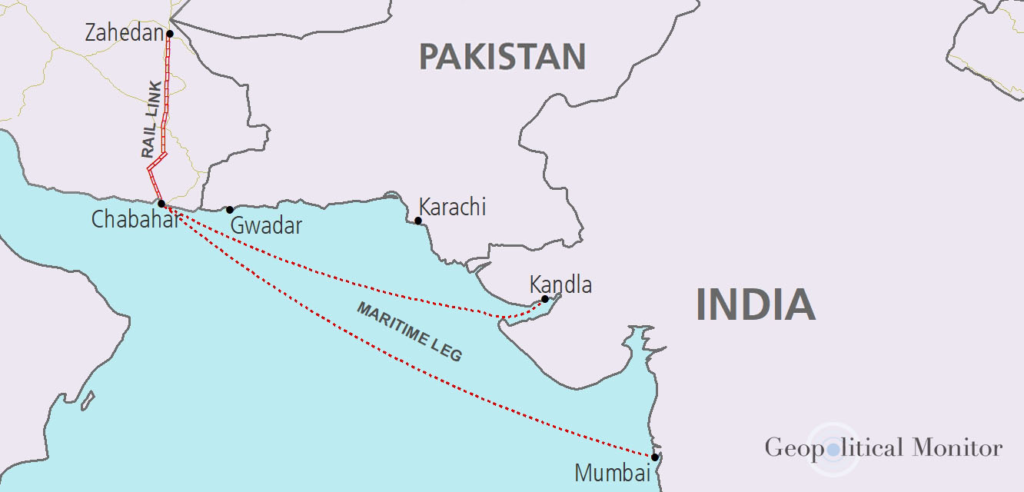
Context: India paid $120 million Chabahar port commitment before US sanctions waiver expires in April 2026.
More in news:
- Government ended annual Budget allocation for Chabahar port indicating inability to manage under US sanctions.
- 10-year MoU signed with Iran in May 2024; India fulfilled procurement commitment completely.
- US issued conditional sanctions waiver extended until April 26, 2026 after India-US discussions.
- Iranian Ambassador Mohammad Fathali said India hasn’t conveyed future plans for port management yet.
- Chabahar port crucial for Afghanistan re-engagement and keeping Central Asia access open for India.
Chabahar Port
- Deep-water seaport in southeastern Iran.
- Location / Mapping
- Sistan–Baluchistan province, Iran.
- On Gulf of Oman.
- Near Strait of Hormuz.
- Direct access to Indian Ocean.
- Port Structure
- Shahid Beheshti Terminal.
- Shahid Kalantari Terminal.
- Connectivity Significance
- Close to Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- Links India to Central Asia.
INSTC Linkage
- Multimodal transport network.
- Connects Indian Ocean to Caspian Sea.
- Extends to Europe via Russia.
- Distance Facts
- Kandla → Chabahar: ~550 nautical miles.
- Mumbai → Chabahar: ~786 nautical miles.
Chabahar Project
- Agreement
- Signed in May 2016.
- India-Iran-Afghanistan trilateral pact.
- India’s Role
- Developing Shahid Beheshti Terminal.
- India’s first foreign port project.
- Infrastructure Components
- Port development works.
- Chabahar–Zahedan rail link.
- Strategic Objectives
- Bypass Pakistan for Afghanistan access.
- Trade route to Central Asia.
- Alternative to Silk Route.

