In short :
Concerns have resurfaced over China’s planned dams on the Yarlung Tsangpo (upper stream of the Brahmaputra), especially the proposed Medog Hydropower Project, which could impact downstream flows into India.
China’s Interventions & Concerns
Medog Hydropower Project (Planned):
- 60,000 MW capacity – would be world’s largest.
- Located near the “Great Bend” before entering Arunachal.
- Minimal known details; unlikely to have a large storage component.
South-North Water Diversion (SNWD) Project:
- No official data, but suspected to include diversion from Yarlung Tsangpo.
- If executed, it could reduce flows to India.
Impact on India:
- Most Chinese dams are run-of-the-river types with minimal water storage.
- Assam CM: 65–70% of flow generated within India – Chinese restrictions may reduce floods.
- Monsoon & tributaries (e.g. Subansiri, Manas, Lohit) contribute significantly to Indian flows.
Potential Impacts & Mitigation
Limited overall impact expected on Indian flow due to high monsoonal yield in NE India.
Concerns remain over:
- Sudden water releases/floods due to reservoir mismanagement or dam failure.
- Morphological and ecological impacts on Indian river systems.
- Hydropower production patterns and irrigation timing in India.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Strategic storage projects (e.g. Upper Siang Project).
- Scientific modeling and basin-wise hydrological monitoring.
- Strengthen real-time data-sharing protocols with China.
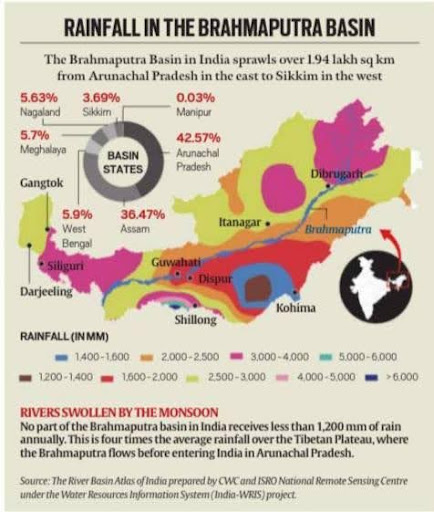
India’s Water Usage & Projects
- 30% of India’s total water resource potential lies in the Brahmaputra system.
- 41% of total hydropower potential (as per CWC-ISRO estimates).
- Hydropower remains underutilized due to land acquisition, forest clearance issues.
Proposed River Linking Projects:
- Manas–Sankosh–Teesta–Ganga Link
- Jogighopa–Teesta–Farakka Link
- Aim: Transfer surplus water to Ganga basin.
- Not expected to be affected by Chinese upstream interventions.
BRAHMAPUTRA RIVER
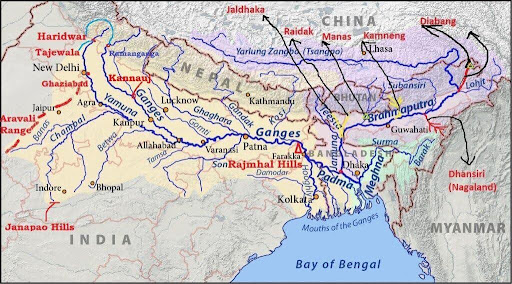
- Origin: Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet.
- Names in India: Siang (Arunachal Pradesh), Brahmaputra (Assam).
- Terminates as: Jamuna in Bangladesh.
- Course in India: Enters near Gelling (Arunachal), flows through Assam, exits into Bangladesh.
- Catchment Area in India: Only 34.2% of basin area, but contributes over 80% of the river’s water yield due to heavy monsoon rainfall.
UPSC Relevance
GS2 – International Relations:
Transboundary river governance with China, Lack of water-sharing treaty on Brahmaputra, Diplomatic need for data-sharing protocols and flood warning systems
GS3 – Disaster Management & Environment:
Flood risks due to upstream dam releases or failures, Strategic use of Brahmaputra’s hydropower and water potential, Concerns over ecological impact and sediment flow disruption
Possible Mains Question
“China’s upstream interventions on the Brahmaputra raise concerns for India’s water security and ecological stability.” Discuss with reference to India’s strategic and environmental preparedness. (250 words)

