
Prelims
World Bank: Country Income Classification
Why in News: The World Bank revised its country income classifications based on 2024 GNI per capita, reflecting global economic changes and affecting development policies and aid eligibility.
World Bank Country Income Classification: Key Points
What is it?
The World Bank classifies countries into four income groups based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita:
- Low income
- Lower-middle income
- Upper-middle income
- High income
Update Frequency:
- Updated annually on July 1, based on the previous year’s GNI data.
Measurement:
- GNI per capita is converted to USD using the Atlas method to smooth exchange rate fluctuations
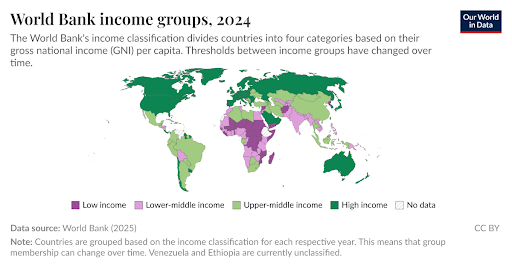
Income Thresholds (latest):
- Low income: $1,135 or less
- Lower-middle income: $1,136 – $4,495
- Upper-middle income: $4,496 – $13,935
- High income: Above $13,935
Current Status of India:
- India is classified as a lower-middle-income country.
Threshold Adjustment:
- Annual inflation adjustments are made using the Special Drawing Rights (SDR) deflator.
Purpose:
- Provides a standardized way to compare countries’ economic development and guides international lending and aid.
Trends:
- Low-income countries decreased from 30% (1987) to 12% (2023).
- High-income countries increased from 25% (1987) to 40% (2023).
- South Asia saw the biggest drop in low-income classification (from 100% to 13%).
Movement Between Groups:
- Countries can move up or down income groups due to economic changes, inflation, exchange rates, or population shifts.
Significance:
- Helps policymakers and researchers track economic progress and development globally.
Alpine Musk Deer Conservation
Why in News: Central Zoo Authority (CZA) report (Dec 2024) flagged species misidentification in Indian zoos, confusing Alpine musk deer with Himalayan musk deer (Moschus leucogaster).
Species: Alpine musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster)
Key Challenges:
- Sympatric distribution causes misidentification
- No clear captive population of Alpine musk deer
- Breeding centres (Uttarakhand & Darjeeling) lacked targeted programmes
CZA Role:
- Established: 1992 (under Wild Life Protection Act, 1972)
- 2022 amendment: Included conservation breeding centres as zoos
Musk Deer –
Habitat:
- A solitary, shy animal inhabiting mountainous regions from Siberia to the Himalayas.
Species Found in India:
1. Himalayan Musk Deer (Moschus leucogaster)
2. Alpine Musk Deer (Moschus chrysogaster)
Alpine Musk Deer –

Scientific Name: Moschus chrysogaster
Common Name: Alpine Musk Deer
Family: Moschidae (Not a true deer; more closely related to Bovidae – antelopes, goats, sheep, bovines)
Distribution:
- Found in India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China
Habitat:
- Mountainous regions at 3,000–5,000 m elevation
- Prefers coniferous and deciduous forests
Diet:
- Ruminant herbivore and browser
- Eats forbs, grasses, mosses, lichens, shoots, leaves, and twigs
Unique Traits:
- Musk sac visible between testes in males
- Fangs grow during mating season (used in male-male sparring)
- Solitary and crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk)
Conservation Status:
IUCN: Endangered
CITES: Appendix I
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Threats: Poaching for musk (used in perfumes, cosmetics, traditional medicine)
Himalayan Musk Deer
Common Names: White-bellied Musk Deer, Kasturi Mriga (Nepali), Lah (Tibetan)
Range in India: Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand (northern UP), Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh
Earlier Classification: Once a subspecies of Alpine Musk Deer, now distinct (different skull structure)
IUCN Status: Endangered
Key Characteristics:
- Musk Gland:
- Present only in males
- Located in a sac between genitals and umbilicus
- Musk used in perfumes, medicines, and cosmetics (driving illegal poaching)
- Teeth: Long, curved upper canines in males
- Diet: Herbivorous-Feeds on grasses, lichens, twigs, mosses, and plant shoots
Behaviour:
- Nocturnal and secretive
- Hides during the day; forages at night
Lifespan: 10–14 years
Election to the Vice-President of India, 2025
Why in News: The Election Commission of India (ECI) has announced the election schedule for the 17th Vice-Presidential Election (2025).
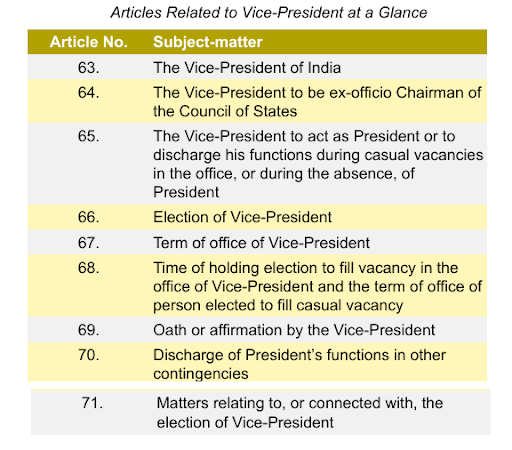
Constitutional Provisions:
Article 66(1): Election by Proportional Representation with Single Transferable Vote and secret ballot.
Article 67: Term of office – 5 years.
Article 68(2): Election to fill vacancy must be held before expiry or within 6 months of vacancy.
Article 324: ECI empowered to supervise elections.
Electoral College:
- Consists of both elected and nominated members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- Total Strength: 782 MPs.
- State legislative assemblies not involved (unlike Presidential election).
Eligibility:
- Must be a citizen of India.
- Minimum age: 35 years.
- Eligible for Rajya Sabha membership.
Election Procedure:
- Nomination: Needs 20 proposers + 20 seconders, ₹15,000 security deposit.
- Voting: In Parliament House, using special ECI-supplied pens.
- First preference vote is compulsory.
- Returning Officer: Secretary General, Rajya Sabha.
- No party whip allowed.
Safeguards & Rules:
- Use of unauthorized pen or violation of secrecy invalidates vote.
- Bribery or undue influence can lead to disqualification (under Presidential & VP Elections Act, 1952).
AI-Designed Proteins to Boost Immunity
Why in News: Harvard scientists have used AI-designed proteins to activate Notch signalling and generate large numbers of T cells, enhancing immune response against cancer and viral infections. Published in Cell journal.
Notch Signalling Pathway:
- Vital for T cell development and cellular differentiation.
- Crucial in maintaining tissue homeostasis.
- No effective molecular activators existed for therapeutic use until now.
Innovation:
- Scientists developed soluble Notch agonists using AI protein design.
- Overcame limitations of previous lab methods (e.g., immobilised Notch ligands).
- Successfully activated Notch signalling in vivo (inside living organisms).
Technology Used:
- AI-driven protein design, developed by Nobel laureate David Baker, with Demis Hassabis and John Jumper (2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry).

Applications:
- Enables large-scale T cell generation in bioreactors.
- Boosts CAR-T cell therapies (cancer immunotherapy).
- Enhances vaccine response by increasing memory T cells.

