
PRELIMS
Maleconazo Anniversary: Places in News
Why in News: On August 5, 2025, Cuban activists and journalists reported arbitrary detentions, house arrests, and internet shutdowns by state authorities on the anniversary of the 1994 “Maleconazo” protest.
Maleconazo (1994):
- A major anti-government protest in Havana, Cuba on August 5, 1994, during Fidel Castro’s rule.
- Triggered the “rafter crisis”, where thousands of Cubans attempted to flee to the U.S. by sea.
- Sparked by economic hardship and political repression.
Microplastic Contamination
Why in News: A recent MoES survey (2022-25) identified abandoned fishing gear and riverine inputs as key contributors to microplastic contamination along India’s east and west coasts, raising environmental and health concerns.
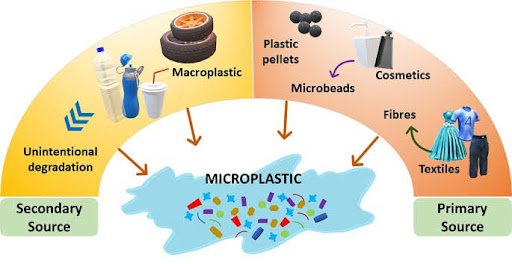
About Microplastics
Definition: Plastic particles smaller than 5 mm, persistent and hard to remove from the environment.
Major Sources of Microplastic Pollution:
- Riverine inputs
- Abandoned, Lost, and Discarded Fishing Gear (ALDFG)
Types:
Primary microplastics: Manufactured tiny particles used in products like cosmetics and microfibers from clothing and fishing nets. Enter environment through product use, spills, or washing.
Secondary microplastics: Result from breakdown of larger plastics (e.g., bottles) due to sun exposure and ocean waves.
Impacts of Microplastics
- Do not biodegrade; accumulate in the environment.
- Ingested by marine life, causing harm and bioaccumulation through the food chain.
- Can carry toxic chemicals and pollutants, increasing ecological and health risks.
Russia Ends Commitment to 1987 INF Treaty
Why in News: Russia has officially ended its commitment to the 1987 INF Treaty, citing recent US military moves such as deploying nuclear submarines near Russian shores and missile systems in the Philippines, raising global nuclear security concerns.
About INF Treaty:
- Signed in 1987 between the US and Soviet Union.
- Required destruction of all ground-launched ballistic and cruise missiles with ranges of 500–5,500 km.
- First major arms control agreement to reduce nuclear arsenals, remove an entire class of weapons, and allow on-site inspections.
- US withdrew from the treaty in 2019, weakening it significantly.

Reason for Russia Ending Commitment:
Cited recent US military actions:
- Repositioning two US nuclear submarines closer to Russian shores.
- Deployment of Typhon missile system in the Philippines.
Implications of INF Treaty Breakdown:
- Erosion of Arms Control Frameworks: Loss of trust; hinders future disarmament efforts.
- Negative Impact on Nuclear Disarmament: Accelerated nuclear modernization by major powers; non-nuclear states reconsider non-proliferation commitments.
- Return to Cold War Politics: Raises fears of European missile crises like during the Cold War.
- Increased Security Risks: Shorter missile flight times increase chances of accidental nuclear conflict.
Key Nuclear Arms Control Agreements:
- (Non-Proliferation Treaty, 1970): Prevents spread of nuclear weapons and technology.
- SORT (Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty, 2002): Limits US-Russia strategic nuclear warheads.
- New START (2010): Further limits strategic arms between US and Russia.
- TPNW (Treaty on Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, 2017): Prohibits participation in nuclear weapon activities (UN adopted).
Nilgiri Tahr
Why in News: A joint census by Kerala and Tamil Nadu reports 2,668 Nilgiri Tahrs.

Scientific Name: Nilgiritragus hylocrius
Type: Mountain ungulate (hoofed mammal)
Endemism: Endemic to Western Ghats (Tamil Nadu & Kerala)
State Animal: Tamil Nadu
Key Habitat: Eravikulam National Park has the largest population
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Conservation Efforts:
- Project Nilgiri Tahr (Tamil Nadu, 2023)
- Nilgiri Tahr Day: Celebrated on 7 October
Threats: Habitat loss due to plantations, infrastructure development, and land-use changes.
OpenAI’s New Open-Weight Models (2025)
Why in News: OpenAI released two open-weight language models — gpt-oss-120B and gpt-oss-20B, marking its first such release in six years (last was GPT-2 in 2019).
Open-Weight AI Models:
- Model weights are publicly available.
- Can be fine-tuned and run on personal devices.
- Training data not disclosed.
- Training procedures/code not shared.
- Model architecture usually shared.
- Not fully transparent.
- Lower legal risk for users.
Open-Source AI Models:
- Weights, code, training data, and procedures all disclosed.
- Fully modifiable and redistributable.
- Released under OSI-approved open-source licenses.
- High transparency.
- May involve legal risks if training data includes copyrighted content.
Key Difference:
- Open-weight = Only weights shared.
- Open-source = Full model ecosystem (weights, data, code) is open.

