PRELIMS
India’s Deep Ocean Mission and Samudrayan
Why in News: India achieved its first deep ocean dives beyond 4,000 m in the Atlantic, a step towards the Samudrayan Mission with the indigenous MATSYA-6000.
Event: In August 2025, two Indian aquanauts descended to depths of 4,025 m and 5,002 m in the Atlantic Ocean.
Global Standing: India joins <6 nations to explore such extreme depths.
Collaboration: Part of Indo-French mission with IFREMER; dives carried out using French submersible Nautile from ship L’Atalante.
Significance:
- India’s first dives beyond 4,000 m.
- Boosts deep-sea research capacity, technology skills, and global scientific standing.
- Supports India’s Deep Ocean Mission and blue economy goals.
MATSYA-6000 Submersible:
- India’s indigenous human submersible under Samudrayan Mission.
- Depth capacity: 6,000 m; endurance 12 hrs.
- Features: Titanium hull, lithium-polymer batteries, acoustic communication, emergency escape system.
- Trials: Wet trials (2025) completed; shallow trials (2026) planned; deep-sea missions (2027–28).
Strategic Importance:
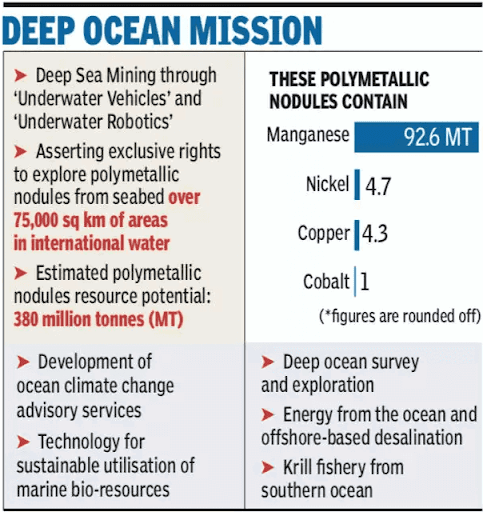
- India’s EEZ rich in marine resources.
- Contracts with International Seabed Authority for mining polymetallic nodules (4,000–5,500 m depth).
- Mission also covers ocean climate services & sustainable resource use.
National Vision: Complements space missions; ocean + space seen as twin pillars of India’s future economic growth.
PelV-1: Giant Marine Virus Discovered
Why in News: Scientists have discovered a giant marine virus named PelV-1 in the North Pacific, notable for its exceptionally long 2.3 micrometre tail — the longest ever seen in a virus — and its role in infecting plankton critical to ocean ecosystems.
What: Newly identified giant virus PelV-1 infecting plankton Pelagodinium.
Where: Discovered in North Pacific Subtropical Gyre at Station ALOHA (north of Hawaii).
Unique Feature:
- Capsid size: 200 nanometres.
- Tail length: 2.3 micrometres → longest viral appendage known (≈19× coronavirus length).
- Tail aids in host cell attachment; disappears after entry.
Genome:
- Contains unusual genes for energy production, light-harvesting proteins, rhodopsins → may harness sunlight.
Ecological Role:
- Infects phytoplankton key to marine food webs.
- Influences energy flow, nutrient cycling, and algal bloom dynamics.
Other Findings:
- Discovered alongside co-PelV virus (no tail, but with metabolic genes).
Significance:
- Expands understanding of giant viruses (much larger, gene-rich than typical viruses).
- Challenges conventional definitions of viruses in biology.
PM Modi’s Independence Day address:
Theme: Strong push for Atmanirbharta (self-reliance) linked with aatma samman (self-respect).
Defence: Highlighted use of Indian-made arms and weapon systems during Operation Sindoor.
GST Reforms: Announced Task Force for 2nd Generation GST Reforms; promised price relief in essential goods.
Next-Gen Reforms: Creation of a High-Powered Task Force for next-generation economic reforms.
Employment Scheme: Launch of Pradhan Mantri Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana – ₹1 lakh crore corpus; ₹15,000 one-time grant for first-time employees; incentives for private sector hiring.
MSMEs: Commitment to reduce compliance burden and protection from arbitrary legal actions.
Semiconductors: India to launch Made-in-India semiconductor chips by end of 2025; six units operational, four more approved.
Innovation Push: Focus on AI, cybersecurity, deep-tech, and OS for global competitiveness.
Internal Security: Claimed terror corridors in Chhattisgarh have become green corridors; mention of anti-Naxal success.
Demographic Mission: Warned of conspiracy to change demographic character, especially in border areas; announced High Powered Demographic Mission.
Farmers: Asserted protection of farmers’ interests; need to reduce fertilizer import dependency.
Global Context: Indirect reference to challenges from U.S. tariff hikes (50%); stressed India’s growth must come from own strength.
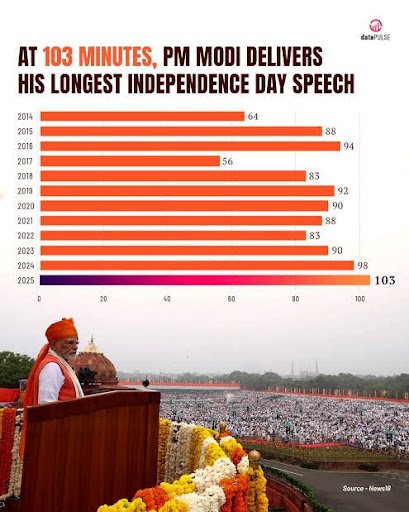
Historic Note: Longest Independence Day speech ever – 103 minutes, breaking his previous 98-minute record.
Seva Bhoj Yojana:
Why in News: Ministry of Culture published state-wise & institution-wise data on financial assistance disbursed under the scheme.

Scheme Type: Central Sector Scheme (launched in 2018 by Ministry of Culture).
Aim: Reimburse CGST & Central share of IGST on purchase of specific raw food items by eligible institutions.
Raw Food Items Covered: Ghee, edible oil, sugar, burra, jaggery, rice, atta, maida, rava, pulses.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Legally registered under Income Tax Act, 1961 / Companies Act / Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Institution must have existed for at least 3 years before applying.
- Distributing free food/prasad/langar/bhandara without discrimination.
- Serving at least 5000 people/month free of cost.
- Should not be receiving any govt. financial aid for free food.
- Not blacklisted under FCRA.
Beneficiaries: Charitable/religious institutions like Gurudwara, Temple, Dharmik Ashram, Mosque, Dargah, Church, Mutt, Monasteries.
Quantum of Assistance: Reimbursement of GST already paid on specified raw food items.
Major GST Shake-up
Why in News: Centre has proposed next-generation GST reforms, including major rationalisation of tax slabs.
Key Proposal:
- 12% & 28% slabs to be scrapped.
- 5% & 18% slabs retained.
- New concessional rate (<1%) for precious metals (gold, silver – 3%; semi-precious stones – 0.25%).
- New “sin rate” of 40% for 5–7 items (e.g., tobacco, gutka).
Shifting of Goods:
- 99% of items in 12% slab → moved to 5%.
- 90% of items in 28% slab → moved to 18%.
- Aspirational/white goods (like ACs, toothpaste, soap, shampoo) → rate cuts proposed.
- No additional cess beyond GST rates.
Revenue Impact:
- 28% slab → 11% of GST revenue.
- 12% slab → 5% revenue.
- 5% slab → 7% revenue.
- 18% slab → ~67% revenue (major contributor).
RBI had earlier pegged avg. GST rate at 11.6% – now expected to fall further.

Ease of Living & Other Reforms:
- Tech-driven reforms: faster GST registration, pre-filled returns, quicker refunds.
- Correction of inverted duty structure to resolve working capital issues.
- Similar items to be taxed at the same rate (e.g., all namkeens at one rate).
Implementation:
- Proposal sent to Group of Ministers (GoM) of GST Council.
- Deliberations likely in Sept–Oct, aim to implement within FY 2025–26.
- Centre to engage States for consensus.
Perpetual Tolling
Why in News: Public Accounts Committee (PAC) criticized the perpetual tolling system in India.
Origins:
- Introduced via 2008 amendment → allowed toll collection even after project costs were recovered.
- Formalised in 2023.

Current System:
- Toll rates fixed in 2008 policy, with annual 3% increase.
- After end of a Build-Operate-Toll (BOT) project concession → toll plazas operated by NHAI.
- Revenue collected goes into Consolidated Fund of India (CFI).
PAC Concerns:
- Continuation of tolling beyond cost recovery seen as burden on commuters.
- Lack of transparency in operation & maintenance (O&M) cost justifications.
Proposed Solutions:
- Tech-driven system for automatic toll refunds during highway maintenance/poor conditions.
- Creation of an independent oversight authority to justify tolling beyond cost recovery.
- Transparent assessment of actual O&M costs to ensure fairness.

