
PRELIMS
Diabetes
Why in News: Indian Institute of Science (IISc) researchers have discovered how glucose transporters (GLUTs) behave in pancreatic beta cells and how their dysfunction may contribute to Type-2 diabetes.
Type-2 Diabetes:
- Characterized by insulin resistance and defective insulin secretion.
- Unlike Type-1, where insulin production is absent due to autoimmune destruction.
Pancreatic Beta Cells:
- Located in Islets of Langerhans.
- Produce insulin, the hormone that lowers blood glucose.
Key Findings
- Pancreatic beta cells manage blood glucose by taking it up and releasing insulin.
Glucose Transporters (GLUTs):
- Humans → GLUT1 is the main “gateway”.
- Mice → GLUT2 plays the same role.
In healthy cells:
- Rising glucose → GLUTs rapidly deployed to cell membrane.
- GLUTs cycle in/out via clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
In Type-2 diabetes:
- This process falters, disrupting glucose entry into beta cells.
- IISc team used advanced live-cell imaging to track GLUT transporters.
Focus: Step before insulin release → actual entry of glucose.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Why in News: Kerala’s Kozhikode Health Department issued an alert after 3 cases (1 death) of Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) were reported recently.
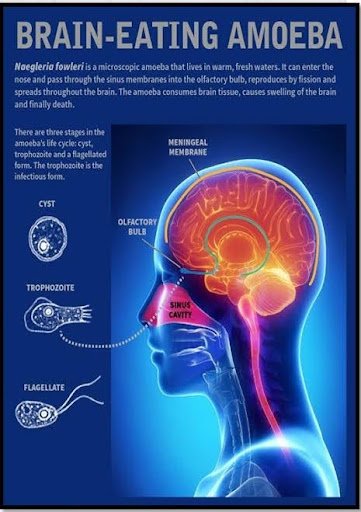
Naegleria fowleri:
- Known as the “brain-eating amoeba.”
- Found in warm freshwater (lakes, ponds, rivers, hot springs).
- Cannot survive in salt water or properly chlorinated pools.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM):
- Acute, fulminant brain infection.
- Extremely rare but >95% fatality reported globally.
- Incubation: 2–15 days, death usually within 5–7 days after symptom onset.
Global Facts:
- First discovered in 1965 in Australia.
- Cases reported in USA, India, Pakistan, Latin America, Africa.
- WHO considers PAM a neglected infection due to rarity but high lethality.
Cause: PAM is caused by Naegleria fowleri (free-living amoeba).
Transmission:
- Enters body through nose (from stagnant water during swimming/bathing).
- Reaches the brain via cribriform plate (more porous in children).
- Can also infect through damaged eardrum.
- Not transmitted person-to-person.
Symptoms (appear in 5–10 days):
- Severe headache, fever, nausea, vomiting.
- Stiff neck, light sensitivity.
- In children → refusal to eat, inactivity, preferring to lie down.
- Severe cases → fading memory, epilepsy, fainting.
Prevention:
- Avoid swimming/bathing in stagnant or unhygienic water sources.
- Use nose clips while swimming.
- People with nasal/ear surgeries should not enter ponds or stagnant waters.
Unemployment Rate
Why in News: According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), Unemployment Rate (UR): Declined to 5.2% in July 2025 (from 5.6% in June).

Key Current Affairs Pointers
Unemployment Rate (UR):
- Overall: 5.2% (June: 5.6%).
- Rural: 4.4% | Urban: 7.2%.
Women:
- Rural → 3.9%.
- Urban → 8.7%.
Men:
- Rural → 4.6%.
- Urban → 6.6%.
Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR):
- Overall: 41.4%.
- Women: 25.5% (June: 24.5%).
- Men: 57.4%.
Worker Population Ratio (WPR):
- National: 52% (up from 51.2% in June).
- Rural: 54.4%.
- Urban: 47%.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)
Background
- Initiated by National Statistical Office (NSO) in 2017 to generate frequent labour force data.
- First annual report: Released in 2019, based on data from July 2017 – June 2018.
Objectives
- Provide quarterly estimates of labour force indicators for urban areas.
- Provide annual estimates for both rural and urban areas.
- Capture indicators under Usual Status (365 days) and Current Weekly Status (CWS).
Key Indicators
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): % of persons in the labour force (working/seeking work) in the population.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): % of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): % of unemployed among persons in the labour force.
Activity Status Approaches
Usual Status (365 days):
- Based on the activity for most of the past year.
- Shows lower unemployment rates (as people usually find some work in a year).
Current Weekly Status (CWS):
- Based on the preceding 7 days.
- People considered unemployed if they did not work ≥1 hour in the week but actively sought work.
- Produces higher unemployment rates compared to usual status.
China’s Ejiao Boom
Why in News: A UK-based NGO, The Donkey Sanctuary, reported (June 2025) that nearly 6 million donkeys are killed annually for the production of Ejiao, a traditional Chinese medicine made from donkey-hide gelatin.

Ejiao:
Definition:
- Ejiao (pronounced uh-gee-ow) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) made by boiling donkey hides to extract gelatin, which is then dried into cakes, powders, or pills.
Uses in Traditional Medicine:
- Believed to nourish blood, boost immunity, improve skin, and treat anaemia, infertility, and menstrual disorders.
- Also promoted as an anti-ageing product.
- No strong scientific evidence to support these claims.
Historical Background:
- Used in China for over 2,500 years, traditionally consumed by the wealthy elite.
- It became a luxury product in the Ming and Qing dynasties.
Production Process:
- Requires donkey hides boiled to produce gelatin.
- Usually mixed with herbs or alcohol for consumption.
Economic Aspects:
- Ejiao is a multi-billion-dollar industry in China.
Global Impact:
- China’s donkey population fell sharply → led to massive imports from Africa, South America, and Asia.
- Caused illegal trade, animal cruelty, and livelihood disruption in exporting countries.
Conservation:
- Several African countries imposed bans on donkey exports (e.g., African Union ban in 2024).
Soaps and Detergents
Why in News: With rising environmental concerns, industries are focusing on biodegradable surfactants and eco-friendly alternatives in soaps and detergents.
Origin & History
- Ancient India: Soap nuts, tree bark, flowers used for cleaning.
- First soaps: Traced back to 2800 BC, Mesopotamia.
- Industrial Revolution: Mass production of soaps began.
- 19th century Europe: Soaps considered a luxury item, taxed heavily.
- WWI: Shortage of natural oils/fats → spurred chemically synthesized detergents.
What is Soap?
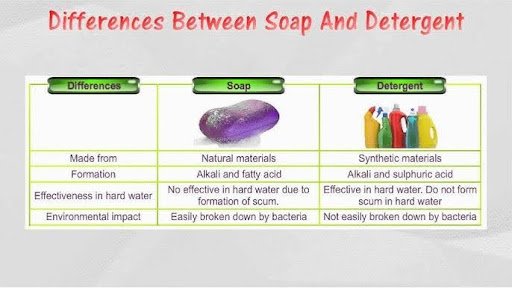
- Sodium (Na) or Potassium (K) salt of fatty acid.
- Formula: RCOONa (solid soap) or RCOOK (liquid soap).
- Example: Lauric acid (C12H24O2) from coconut oil → C11H22COONa.
Soap-Making Process
1. Vegetable oil triglycerides treated with hot water → fatty acids + glycerin.
2. Fatty acids + NaOH → soap + water.
3. Soap mass → vacuum dried → extruded into soap noodles.
4. Noodles blended with:
- Perfumes (sandalwood, synthetic scents),
- Colours (plant pigments/oxides),
- Fillers (talc, sodium silicate, sulphates),
- Surfactants (sodium lauryl sulphate),
- Additives (antifungal, antibacterial like triclosan, neem oil).
5. Extruded → cut → stamped → packed.
Total Fatty Matter (TFM): Higher TFM = better cleaning quality.
Why Soaps Clean?
- Soap molecule: Hydrophilic head + Hydrophobic tail.
- Hydrophobic tail embeds in grease; hydrophilic head binds to water.
- Scrubbing + rinsing → dirt removed with water.
Detergents
- Essentially liquid soaps but with high surfactant content.
- Additives: bleach, dyes, fragrances.
- Advantage: Effective in hard water.
- Concern: Many surfactants (phosphates, sulphonates) are non-biodegradable → cause nutrient pollution & long-term persistence.
Current efforts: Developing biodegradable surfactants & enzymes as phosphate substitutes.
Other Important points
TFM (Total Fatty Matter): BIS standard for soaps in India.
- Toilet soap: ≥ 60–75% TFM.
- Laundry soap: ~ 50% TFM.
Surfactants: Reduce surface tension of water.
Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS): Common surfactant.
Phosphates in detergents: Cause eutrophication (nutrient pollution in water bodies).
Bering Strait Shipping Cooperation
Why in News: A recent study shows strong adherence by mariners to the 2018 shipping guidelines in the Bering Strait, despite rising U.S.-Russia tensions post-Ukraine war.
Geographical Significance
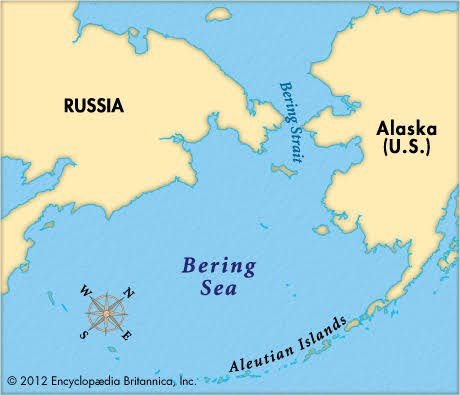
- The northernmost part of Pacific Ocean : connects the Bering Sea (Pacific) with the Chukchi Sea (Arctic Ocean).
- Separates Asia (Russia) and North America (USA).
- Narrowest width: 85 km (Cape Prince of Wales – Alaska & Cape Dezhnev – Russia).
- Depth: ~50 m (shallow).
- Islands: Diomede Islands (Big Diomede–Russia, Little Diomede–USA, divided by International Date Line); St. Lawrence Island (6th largest in USA).
2018 IMO Shipping Guidelines
- Voluntary rules under International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Recommend designated shipping lanes & avoidance of ecologically sensitive areas.
- Protects marine mammals & migratory birds.
- Compliance (2015–2022 data): High adherence by cargo vessels, tankers, tugs.
Rising Maritime Traffic
- Transits: 242 (2010) → 665 (2024) (tripled).
- Concerns: Risk of oil spills, beach changes near Little Diomede, threats to indigenous livelihoods & biodiversity.
Political Context
- U.S.–Russia ties worsened post-2022; Russia excluded from the Arctic Council.
- Yet, maritime safety cooperation persists (Cold War precedent).
- Experts suggest buffer zones around Diomede Islands.
Way Forward
- Expand designated avoidance zones.
- Continued monitoring & compliance with IMO guidelines.
- Maintain U.S.-Russia dialogue on maritime safety & ecology.

