
PRELIMS
Great Nicobar Project
Why in News: The Tribal Council of Little Nicobar and Great Nicobar has complained to the Union Tribal Affairs Minister that the forest rights of tribals under FRA, 2006 were never settled for the ₹72,000-crore Great Nicobar Project.
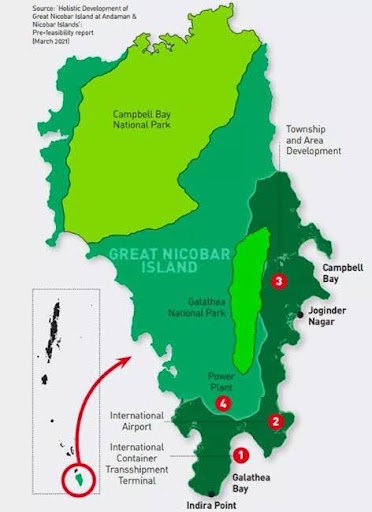
Project Components: Transshipment port, airport, power plant, township.
Issue Raised:
- The A & N administration claimed in 2022 certificate that FRA rights were “identified and settled”.
- Tribal council asserts the process not even initiated, hence consent invalid.
Legal Conflict:
- FRA, 2006 → Forest diversion only after settlement of rights + consent of Gram Sabha.
- PAT 1956 (Protection of Aboriginal Tribes Act) → Administrator has wide powers to divert forest land.
- Tribal Council’s Claim: Nicobarese were not part of the Gram Sabha meeting.
Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006
- Recognizes and vests forest rights over land and resources to forest-dwelling Scheduled Tribes (FDST) and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFD) who have been residing in forests for generations.
Covers:
- Title Rights (ownership upto 4 hectares for pre-2005 occupancy),
- Use Rights (minor forest produce, grazing, resource access),
- Community Rights and Habitat Rights especially for PVTGs,
- Forest Management Rights (to protect, regenerate, manage resources).
- Rights must be recognized through Gram Sabha, then vetted by Sub-Divisional and District Committees.
2. Protection of Aboriginal Tribes Regulation (PAT), 1956
- A special law for Andaman & Nicobar that grants the Administrator sweeping powers over tribal areas, including forest diversion, without FRA stipulations.
Kerala: India’s First Fully Digitally Literate State
Why in News: Kerala has become the first State in India to achieve full digital literacy under the Digi Kerala Project, after training 21.87 lakh citizens across all local bodies.

Project: Achieved under the Digi Kerala Project (Phase I completed).
Survey Coverage:
- Covered 1.5 crore people from 83.46 lakh families.
- 99.98% (21.87 lakh) trained and passed evaluation.
Inclusivity: Participants of all ages; training delivered through local bodies (decentralised governance).
Significance:
- Bridges digital divide, ensures access to schemes (Ayushman Bharat, PM-Kisan, Jan Dhan).
- Promotes financial inclusion, transparency, accountability.
- Empowers citizens to file grievances, RTIs, and engage in digital democracy.
Alignment: Supports Digital India Mission goals → inclusive digital access and socio-economic empowerment.
Impact: Strengthens livelihood opportunities, helps marginalised groups, enhances resilience during crises (pandemics, disasters).
NASA’s Surya AI
Why in News: NASA, in collaboration with IBM, has launched Surya, an AI model trained on Solar Dynamics Observatory data, to predict solar flares and eruptions up to two hours in advance, helping safeguard satellites, power grids, aviation, and GPS systems.

News: NASA launched Surya, an advanced AI model for space weather prediction, developed with IBM.
Data Source: Trained on 9 years of Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) data.
Function:
- Forecasts solar flares & coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- Provides up to 2 hours advance warning.
- Improves forecast accuracy by ~16% over existing models.
Significance:
- Protects satellites, GPS, aviation, power grids, and astronauts from space weather hazards.
- Successfully simulated the 2015 St. Patrick’s Day geomagnetic storm.
Technical Innovations:
- Combines spectral block layers + long-short transformer backbone.
- Integrates frequency-aware + time-series modelling.
Scientific Use Cases:
- Forecast of solar flare strength.
- Prediction of active region emergence.
- Estimation of solar wind speeds (up to 4 days ahead).
- Forecasting extreme ultraviolet spectra.
Collaboration: NASA + IBM + universities + research institutes; supported by NSF and NVIDIA.
Open Source: Framework released publicly for global collaboration in heliophysics research.
National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMC)
Why in News: PM recently lauded flagship programmes including the National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMC) for their role in achieving Viksit Bharat.

Definition: Critical minerals → Primary or processed minerals essential for economic production, but prone to supply risks due to scarcity or price volatility.
Announced in: Union Budget 2024–25.
Vision: Secure a long-term, sustainable supply of critical minerals for India’s economic growth.
Objectives:
1. Secure supply chains via domestic & foreign sourcing.
2. Strengthen value chains – exploration, mining, beneficiation, processing, recycling.
3. Promote innovation, skills, and global competitiveness.
Key Components:
- Domestic production: 1,200 exploration projects to expand mining.
- Acquisition abroad: Support mapping & exploration in resource-rich countries.
- Recycling: Incentive scheme for mineral recycling.
- Trade: Import duties on critical minerals to be eliminated as per strategic needs.
- R&D: Establish Centre of Excellence (CoE) on critical minerals (Hub & Spoke Model).
- Human resource: Specialised modules in mining, metallurgy, and recycling courses.
- Finance: Budgetary measures & fiscal incentives for critical mineral ecosystem.
OpenAI’s Entry and IndiaAI Mission
Why in News: OpenAI (maker of ChatGPT) has announced plans to open its first office in New Delhi, registering OpenAI India Private Limited.
Significance:
- Supports Government’s IndiaAI Mission.
- Aim: Build AI for India, with India, in collaboration with govt. & ecosystem.
- India = 2nd largest market after U.S. for ChatGPT users.
- User base in India grew 4x in one year; among top 5 markets globally by developers.
Hiring:
- Local team being set up; first postings in sales roles.

OpenAI:
- Founded: December 2015, by Sam Altman, Elon Musk, Greg Brockman, Ilya Sutskever & others.
- Headquarters: San Francisco, USA.
- Mission: Develop Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) that benefits all humanity.
IndiaAI Mission:
- Announced: Union Budget 2023–24.
- Aim: Establish a comprehensive program for AI research, innovation, startups, and digital infrastructure.
- Envisions AI computing infrastructure, datasets, and policy framework to make India a global AI hub.

