
PRELIMS
Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-1)
Why in News: On August 24, 2024, ISRO successfully conducted its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-1), a key milestone for India’s maiden human spaceflight programme, Gajanan.
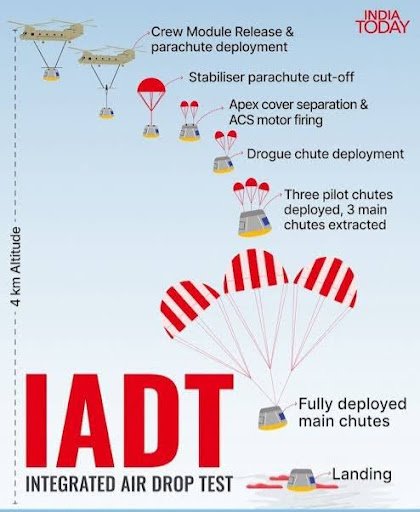
What is IADT?
- Test of the parachute-based deceleration system that slows the crew module during re-entry and landing.
- Ensures safe splashdown at ~8 m/s.
- Simulates the final stage of re-entry.
How was IADT-1 Conducted?
- 4.8-tonne dummy crew module lifted by Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter to ~3 km altitude.
- Released and parachutes deployed in sequence:
- Drogue parachutes → 3 main parachutes.
- Touchdown conditions matched expectations.
Agencies Involved
- ISRO – Led by Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (90% of activities).
- Indian Air Force – Helicopter lift & release.
- DRDO – Materials & safety systems.
- Indian Navy & Coast Guard – Post-splashdown recovery support.
Significance for Gaganyaan
- Gaganyaan: Human spaceflight to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) using human-rated LVM3 rocket.
Tests required:
- Crew Escape System (TV-D1 in Oct 2023; TV-D2 upcoming).
- Multiple IADTs, subsystem trials.
- Uncrewed mission (G1) with humanoid Vyommitra before human mission (H1).
- Thousands of tests planned before crewed flight.
- Critical systems under testing: ECLSS (life support), IVHMS (fault detection), strengthened LVM3 rocket.
Long-Term Goals of India’s Human Spaceflight Programme
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035.
- Indian crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- In-orbit docking technology demonstrated (SpaDeX mission, May 2025).
- H1 mission (first human flight) tentatively by 2027.
Suspension of Import Duty on Cotton
Why in News: On August 18, 2024, the Centre suspended the 11% import duty on cotton till September 30, 2024, to address raw material shortages in the textile industry.

Background
- Duty imposed in 2021 Budget to protect farmers when India produced 350 lakh bales (requirement: 335 lakh bales).
- Cotton imports still rose steeply — up 107.4% from $579.2 mn (FY 2023-24) to $1.2 bn (FY 2024-25).
- Past exemptions: April–Sept 2022 (later extended to Oct 2022).
Current Situation (2024–25 Cotton Season)
- Production: Down to 294 lakh bales (lowest in 15 years) vs requirement of 318 lakh bales.
- Imports: Likely ~40 lakh bales.
- Key suppliers: Australia ($258.2 mn), U.S. ($234.1 mn), Brazil ($180.8 mn), Egypt ($116.3 mn).
- CCI procurement: 100 lakh bales at MSP (₹37,500 cr); sold 73 lakh bales.
- MSP hiked by 8% for 2025–26 season starting October 1.
Implications of Withdrawal
- Only ~2 lakh bales (already in transit) will benefit from duty-free import.
- For exporters: Raw material costs fall → level playing field in global garment trade.
- For farmers: Viewed negatively; may discourage cotton cultivation.
Long-Term Solutions Suggested
1. Stable policy: Suspend duty annually in non-peak season (April–Sept) when farmers have sold most produce.
2. Financial support: 5% interest subvention for mills’ working capital → enables procurement during peak season, reducing dependence on MSP operations.
NSS 80th Round (Education) – Household Expenditure on School Education (April–June 2025)
Why in News: National Sample Survey (80th round, Comprehensive Modular Survey – Education) data (Apr–Jun 2025) highlights enrolment patterns and household expenditure on school education in India.

Key Findings
Enrolments
- Govt. schools: 55.9% of total enrolments.
- Rural: 66% students in govt. schools vs 30.1% in urban areas.
- Private unaided schools: 31.9% of enrolments.
Expenditure per student (2025-26 academic year)
- Govt. schools: ₹2,863.
- Non-govt. schools: ₹25,002 (≈ 9 times higher).
Private coaching
- Nearly 27% students take private coaching.
- Urban: 30.7% | Rural: 25.5%.
Education Expenses (All-India Average)
- Course fees: ₹7,111 (highest share).
- Textbooks & stationery: ₹2,002.
Urban–Rural gap:
- Urban course fees: ₹15,143.
- Rural course fees: ₹3,979.
Other Insights
Data collected from 52,085 households & 57,742 students through CAPI (Computer Assisted Personal Interviews).
Constitutional Provisions on Education
- Article 21A – Right to Education (RTE): Free & compulsory education for children 6–14 years.
- Article 45 (DPSP) – Early childhood care & education up to age 6.
- Article 46 (DPSP) – Promotion of educational & economic interests of SCs/STs and other weaker sections.
RTE Act, 2009
- Provides free and compulsory education for children 6–14 yrs.
- 25% reservation in private unaided schools for EWS.
- Prohibits capitation fees & screening procedures.
Key National Policies & Reports
- National Education Policy (NEP), 2020: Schooling restructured into 5+3+3+4 model. Focus on foundational literacy & numeracy, vocational integration.
- Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): Integrated scheme covering pre-school to Class XII.
- National Achievement Survey (NAS) & ASER Report (Pratham NGO): Measure learning outcomes.
Government Schemes Related to School Education
- PM SHRI Schools (2022) – Upgrading 14,500 schools as model schools aligned with NEP 2020.
- PM POSHAN (Mid-Day Meal) – Nutritional support to school children.
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) – For ST students.
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao (BBBP) – Focus on girl child education.
- Schemes for Disabled Students under Inclusive Education for Disabled at Secondary Stage (IEDSS).
CISF Launches First All-Women Commando Unit (2025)
Why in News: In 2025, the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) launched its first all-women commando unit, a milestone in gender inclusion in India’s security forces.

Training Details
- Location: Regional Training Centre, Barwaha (Madhya Pradesh).
- Duration: 8-week advanced course.
- Modules:
- Physical fitness, weapons handling, live-fire drills.
- Rappelling, survival techniques, forest training.
- 48-hour confidence-building exercise for decision-making under hostile conditions.
Role & Deployment
- To serve in Quick Reaction Teams (QRTs) and Special Task Forces (STFs).
Deployment areas:
- High-security installations: civil airports, metro systems, govt. & private sector sites.
- Tasks: Counter-terrorism, rapid response, specialised security operations.
Women’s Representation in CISF
- Current strength: 8% (12,491 women).
- Target: 10% female representation by 2026 with recruitment of 2,400 women.
Significance
- CISF becomes the first CAPF (Central Armed Police Force) to raise an all-women commando unit.
- Marks a policy shift from symbolic inclusion to operational parity.
- Enhances gender diversity and sets precedent for women’s integration in core combat roles.
- Regular all-women commando courses to be institutionalised.
Adi Karmayogi Initiative
Why in News: The Tribal Affairs Ministry has launched the Adi Karmayogi initiative to create a cadre of 20 lakh “change leaders” for tribal villages under the Dharti Aba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyaan for last-mile scheme delivery.
Key Features
- Objective: Build motivation and participatory problem-solving capacity among tribal officials, volunteers, and community leaders.
Approach:
- Activities include role-play, group tasks, “knot-tying”, “fishbowl”, and “lighting candle” exercises.
- Messages emphasised: “solution comes from within”, “initiate action”, “create opportunity from challenges”.

Training Structure
Cadre building:
- 240 State-level master trainers.
- 2,750 district-level trainers.
- 15,000+ block-level trainers.
- Training to reach 20 lakh village-level officials/volunteers.
Village sessions: Each with ~15 volunteers; participatory exercises to encourage local solutions.
Village Vision 2030
- Each of the 1 lakh target villages (550+ districts) to prepare “Village Vision” documents for 2030.
- To be displayed as public murals, acting as aspirational blueprints for State machinery.
Adi Seva Kendras
- Plan to set up 1 lakh Kendras as single-point interfaces for villagers to access all welfare schemes.
- Aim: 100% saturation of government schemes in tribal villages.

