
Latest News
-
Record Low Snow Persistence: The HKH region recorded its lowest snow cover in 23 years during the 2024–2025 winter, raising alarms about climate-driven water scarcity and ecological disruption. This decline threatens water security for millions dependent on Himalayan rivers.
About the Hindu Kush Himalaya
-
Geography:
-
Span: ~3,500 km across 8 countries – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar, Pakistan.
-
Area: ~4.2 million sq. km.
-
Highest Peak: Tirich Mir (7,708 m) in Chitral, Pakistan.
-
Key Divisions:
-
Eastern Hindu Kush
-
Central Hindu Kush
-
Western Hindu Kush (Bābā Mountains).
-
-
Unique Features: Inner valleys with desert-like aridity and sparse vegetation.
-
Ecological & Climatic Significance
-
Third Pole:
-
Holds the largest ice reserves outside the polar regions, critical for regulating global climate.
-
4 Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Hosts endangered species like snow leopards, red pandas, and Himalayan tahr.
-
-
River Systems:
-
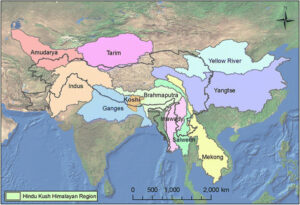
10 Major Asian Rivers Originate Here:
-
South Asia: Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra.
-
Southeast Asia: Irrawaddy, Salween, Mekong.
-
East Asia: Yangtse, Yellow River, Tarim.
-
Central Asia: Amu Darya.
-
-
Water Source: Supports 1.9 billion people (25% of the global population).
-
-
Ecosystem Diversity: Glaciers, alpine meadows, forests, wetlands, and grasslands.
Climate Vulnerability
-
Snow & Ice Melt: Recent low snow persistence exacerbates risks of:
-
Water Shortages: Reduced river flows impact agriculture, hydropower, and drinking water.
-
Extreme Weather: Increased floods, landslides, and glacial lake outbursts (GLOFs).
-
Biodiversity Loss: Threatens endemic species and fragile ecosystems.
-
Key Takeaways
-
-
Climate Crisis: Declining snow cover underscores urgent need for regional climate action and adaptation strategies.
-
Geopolitical Importance: Transboundary water management is vital for stability among HKH nations.
-
Biodiversity Hub: Conservation efforts are critical to protect unique ecosystems and species.
-
Human Impact: Over 1.9 billion people rely on HKH rivers; sustainable practices are essential to avert crises.
-
FAQs
-
Which rivers originate in the HKH?
-
Ans: Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra, Amu Darya, Irrawaddy, Mekong, Salween, Yangtse, Yellow River, and Tarim.
-
-
What is the highest peak in the Hindu Kush?
-
Ans: Tirich Mir (7,708 m) in Pakistan.
-
-
Why is HKH called the “Third Pole”?
-
Ans: It holds the largest ice cover outside the Arctic and Antarctica, crucial for global climate stability.
-
