Why in News: India and the U.K. signed a trade pact with a key digital trade chapter, offering duty-free access for most Indian exports while raising debates over digital sovereignty and regulatory oversight.
Introduction
- The recently concluded India–U.K. Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) represents a paradigm shift in India’s trade diplomacy.
- Chapter 12 of the agreement focuses on digital trade and reflects a compromise between digital sovereignty and global market integration.
- While hailed as a landmark in India’s engagement with the global digital economy, the agreement has also raised debates about its implications for regulatory oversight and national interests.
Digital Wins
- Recognition of e-signatures and contracts – mutual recognition reduces paperwork for SaaS firms and MSMEs.
- Paperless trade and e-invoicing – improves efficiency in cross-border payments and documentation.
- Zero customs duty on electronic transmissions – protects India’s $30 billion software exports.
- Regulatory sandboxes – allow fintech and data-driven firms to test innovations under supervision, boosting credibility.
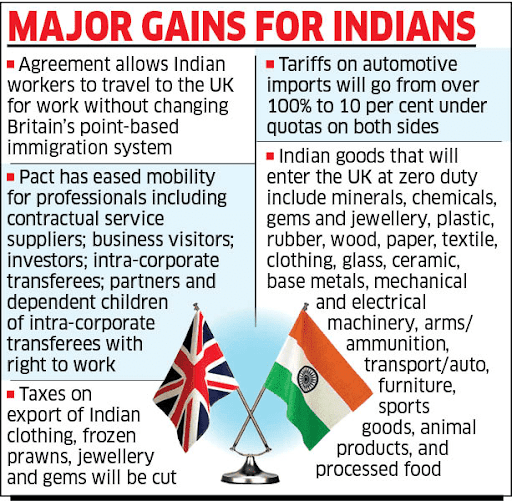
- Market access beyond digital – duty-free entry for 99% of merchandise exports, removal of textile tariffs (12% to zero), new openings in U.K. public procurement, and social security waivers lowering payroll costs.
Digital Costs and Concerns
- Ban on blanket source-code inspections – regulators can access only during investigations or court orders; seen as dilution of oversight.
- Government procurement excluded – no restriction on accessing code for state purchases, but private regulation limited.
- General security exceptions – retained for critical infrastructure (power grids, payment systems), but critics fear gaps in routine regulation.
- Government data openness voluntary – no binding obligation; India retains discretion.
- Review mechanism limited – no automatic Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause for data flows; only consultations and a formal review within 5 years.
Strategic Significance
- Departure from past trade scepticism – aligns India with modern trade norms and reflects strategic engagement in the digital economy.
- Strengthens India’s global credibility – signals willingness to integrate into digital trade frameworks.
- Balances sovereignty with access – retains critical security safeguards while enabling trade facilitation.
- Boosts export competitiveness – especially in textiles, IT, and SaaS, benefiting hubs like Tiruppur and Ludhiana.
- Positions India as a digital rule-shaper – aligns trade policy with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
Challenges Ahead
- Need for institutional safeguards – trusted labs for sensitive code review under strict protocols.
- Audit trails for data flows – essential to ensure accountability of cross-border intermediaries.
- Rapid technological change – AI and emerging tech demand frequent treaty reviews (every 3 years instead of 5).
- Domestic readiness – rules under the Data Protection Act need notification for coherence with external commitments.
- Stakeholder consultations – absence of pre-negotiation consultations may raise governance and trust issues.
Way Forward
- Integrate openness with oversight – combine trade facilitation with robust regulatory tools.
- Accredit independent labs – for secure source-code inspections under tight safeguards.
- Mandate audit trails – to track accountability of data intermediaries across borders.
- Institutionalise consultations – involve industry, civil society, and regulators before finalising treaties.
- Regular treaty reviews – schedule reviews every 3 years to align rules with emerging digital risks and technologies.
Conclusion
Going forward, India must balance commerce with code, ensuring that digital sovereignty and global integration work in harmony to power its economic ambitions in the 21st century.
UPSC Relevance
General Studies Paper II: International Relations
- India–U.K. Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA).
General Studies Paper III: Indian Economy
- Effects of trade agreements on exports, MSMEs, and digital services.
Mains Practice Questions
Q. The digital trade chapter in the India–U.K. pact has been hailed as a milestone, but also criticised as a retreat from digital sovereignty. Critically examine. (15 marks, 250 words)
