Padma Awards

Overview
- Nature: National civilian honours of India
- Instituted: 1954
- Announcement: Annually on the eve of Republic Day (26 January)
- Purpose: Recognise distinguished public service and excellence across diverse fields
- Conferred by: President of India (Ceremony in March/April)
Categories (Order of Precedence)
- Padma Vibhushan: Exceptional and distinguished service
- Padma Bhushan: Distinguished service of high order
- Padma Shri: Distinguished service
Disciplines Covered
- Art and Culture
- Social Work
- Public Affairs
- Science and Engineering
- Trade and Industry
- Medicine
- Literature and Education
- Sports
- Civil Service
- Other fields involving public service
Eligibility
- Open to all persons
- No distinction of race, sex, occupation, or position
- Includes Indian citizens, NRIs, foreigners, and OCI holders
Selection Mechanism
- Padma Awards Committee reviews nominations
- Appointed annually by: Prime Minister
- Chairperson: Cabinet Secretary
- Members include:
- Home Secretary
- Secretary to the President
- 4–6 eminent persons
- Final approval: Prime Minister → President of India
Key Features
- Maximum awards per year: 120 (Excludes posthumous, NRI, foreigner, and OCI recipients)
- Form of award:
- Sanad (certificate)
- Medallion
- Replica for ceremonial use
- No monetary grant
Rules & Limitations
- Not a title: Cannot be used as prefix/suffix to the name
- Posthumous awards: Generally avoided
- Higher category: Minimum 5-year gap, unless waived by Committee
- Years not conferred: 1978–79 and 1993–97
Constitutional & Legal Status
- Article 18(1): Prohibits titles, except military and academic distinctions
- Supreme Court (Balaji Raghavan v. Union of India, 1996):
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are not titles
- Recognise merit and public service, hence constitutional
MuleHunter

Overview
- Nature: AI/ML-based fraud detection model
- Developed by: Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH) (Subsidiary of RBI)
- Purpose: Detect and track mule bank accounts used in financial fraud and money laundering
- Status: Pilot tested with two large Public Sector Banks
Key Functions
- Mule Account Detection: Analyses transaction behaviour to flag suspicious fund movement patterns
- Real-time Monitoring: Enables prompt alerts and intervention during fraudulent transactions
- Advanced Analytics: Uses machine learning to identify trends, anomalies, and risk indicators
- Inter-Agency Coordination: Facilitates data sharing among banks, PSPs, and law enforcement agencies
- Regulatory Support: Strengthens compliance with AML and CFT norms
Significance
- Enhances digital payments security
- Improves early fraud prevention capability
- Supports financial system integrity
- Strengthens RBI’s tech-driven supervisory framework
What is a Mule Bank Account?
- Definition: Bank account used by criminals to launder illegal funds
- Ownership Pattern: Often acquired from financially vulnerable or low-tech literacy individuals
- Money Mule: Person whose account is misused for illegal transfers, often unknowingly
- Law Enforcement Challenge: Account holder becomes traceable, while actual fraudsters remain hidden
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)

Overview
- Nature: Premier central investigating agency of India
- Role: Investigates corruption, economic offences, special crimes; coordinates with Interpol
- Motto: Industry, Impartiality and Integrity
Genesis
- Established: 1963
- Basis: Recommendation of Santhanam Committee (1962–64) on Prevention of Corruption
Legal Status
- Type: Non-constitutional, non-statutory body
- Governing Law: Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946
Administrative Control
- Ministry: Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Public Grievances
Organisation Structure
- Head: Director, CBI
- Assisted by: Special Director / Additional Director
- Hierarchy: Joint Directors → DIGs → SPs → Police ranks
Tenure
- CBI Director: Fixed tenure of 2 years
- 2021 Ordinance: Allows extension up to 5 years (annual review basis)
Types of Cases
- Anti-Corruption
- Economic Offences
- Special Crimes
- Suo Motu Cases
State Consent (Section 6, DSPE Act)
- General Consent: Allows CBI to investigate in a state without case-wise approval
- Specific Consent: Required for each case, if general consent withdrawn
- States withdrawing general consent: West Bengal, Punjab, Telangana, etc.
Appointment of CBI Director
- In Common Cause v. Union of India (2019), the Selection Committee for appointing the Director was created which includes:
- Prime Minister (Chairperson)
- Remember: Leader of Opposition / Largest Opposition Party Leader
- Chief Justice of India / SC Judge nominated by CJI
Key Judicial Pronouncements
- Vineet Narain v. Union of India (1997): Struck down “Single Directive”; strengthened CBI autonomy
- Subramanian Swamy v. CBI (2014): Section 6A of DSPE Act declared unconstitutional (prior sanction removed)
- CBI v. Sanjiv Chaturvedi (2024): CBI not fully exempt from RTI; corruption & human rights info disclosable
Functions
- Corruption in public services
- High-value financial and economic crimes
- Cyber and high-technology crimes
- International police cooperation (Interpol cases)
ExoMiner++: Planet Spotter

Overview
- Nature: Deep-learning Artificial Intelligence (AI) model for exoplanet detection
- Developed by: NASA researchers
- Successor to: ExoMiner (Kepler mission-based)
Purpose
- Identifies exoplanets by analysing stellar brightness data
- Detects transit signals—dip in star’s brightness when a planet passes in front
Data Sources
- Kepler Space Telescope
- TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite)
Working Mechanism
- Analyses light curves (brightness vs time graphs)
- Differentiates true planetary transits from false positives such as:
- Binary stars
- Background stellar objects
- Instrumental noise
Key Features
- Explainable AI:
- Assigns probability score for planetary signal
- Explains reasoning behind classification
- High-throughput:
- Can compare thousands of stars simultaneously
- Open-source:
- Released on GitHub for global scientific use
Achievements
- ExoMiner (earlier version):
- Validated 370 exoplanets from Kepler data
- ExoMiner++:
- Identified ~7,000 potential exoplanet candidates from TESS data
Scientific Significance
- Enhances speed and accuracy of exoplanet validation
- Reduces dependency on slow manual verification methods
- Supports future missions like:
- Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
National Voters’ Day (NVD)

Observed on: 25 January (since 2011)
Occasion: Foundation Day of the Election Commission of India (ECI) (est. 25 Jan 1950)
Purpose
- Promote universal adult suffrage
- Encourage youth participation and voter enrolment
- Strengthen democratic values and informed voting
Theme (2026)
- Theme: “My India, My Vote”
- Tagline: “Citizen at the Heart of Indian Democracy”
Key Features
- Celebrated at national, state, district, constituency, and polling booth levels
- Focus on first-time voters and newly eligible youth
- Public awareness drives on electoral rights and responsibilities
- Organised by: Election Commission of India (ECI)
Forever Chemicals (PFAS)

Overview
- Forever chemicals = PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances)
- Large family of thousands of synthetic, toxic, and highly persistent chemicals
- Called “forever” due to extreme resistance to environmental degradation
Chemical Basis
- Built on carbon–fluorine (C–F) bonds
- One of the strongest chemical bonds, causing long environmental and biological persistence
- Bioaccumulate in humans and wildlife over time
Uses
- Consumer Products
- Cosmetics and skin-care products
- Non-stick cookware (frying pans, baking equipment)
- Food packaging (microwave popcorn bags)
- Textiles and fabric treatments
- Outdoor clothing and footwear
- Car and floor polishes
- Dishwasher rinse aids
- Industrial Applications
- Firefighting foams
- Grease- and water-resistant coatings
- Manufacturing of durable, non-stick, and anti-grease materials
- Environmental Pathways
- Leak into soil, water, and air during use and disposal
- Spread through contaminated drinking water, food chains, and air
Human Exposure
- Consumption of PFAS-contaminated water or food
- Use of PFAS-containing consumer products
- Inhalation of PFAS-laden air or dust
- Health Impacts
- Immune system suppression
- Liver and thyroid disorders
- Increased cholesterol and hypertension
- Developmental delays in infants
- Elevated risk of kidney and testicular cancers
- Regulation & Global Framework: Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
Sonic Boom

Overview
- Sonic boom: Loud explosive sound produced when an object travels faster than the speed of sound (Mach 1).
- Commonly generated by supersonic aircraft, rockets, or re-entering space debris.
Formation Mechanism
- Moving object compresses air molecules, forming shock waves along its flight path.
- Pressure builds up and is released suddenly, reaching the ground as a boom-like sound.
Factors Affecting Intensity
- Altitude: Higher altitude → weaker boom at ground level.
- Size & mass: Larger, heavier objects displace more air → stronger shock waves.
- Shape & design: Aircraft geometry influences wave pattern.
- Maneuvers: Turns and acceleration alter shock wave strength.
- Atmospheric conditions: Temperature, pressure, and wind affect sound propagation.
Types
- Single boom: Typical for compact or shorter aircraft.
- Double boom: Long aircraft produce two shocks (nose and tail).
Visible Phenomenon
- Vapor cone/cloud: Temporary cloud of condensed water vapour due to rapid pressure and temperature drop around the aircraft.
- Not the sound itself, but a visual effect of shock waves.
Impacts
- Can rattle structures and shatter glass at low altitude.
- Generally low direct risk to humans on the ground.
Key Terms
- Mach number: Ratio of object speed to local speed of sound.
- Shock wave: Thin region of abrupt pressure, temperature, and density change.
Java Island
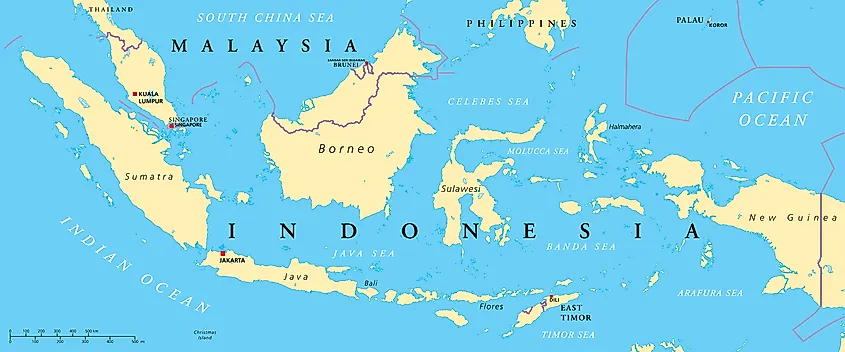
Context: Recent landslide event highlights high geological and disaster risk due to volcanic terrain and dense population.
Location & Setting
- Country: Indonesia
- Region: Part of the Greater Sunda Islands (with Sumatra, Borneo, Sulawesi).
- Boundaries:
- North: Java Sea (Borneo across it)
- South: Indian Ocean
- Northwest: Sunda Strait (separates Java from Sumatra)
Physical Geography
- Global rank: 13th largest island in the world; 5th largest in Indonesia.
- Geological origin: Volcanic island arc formed by Australian Plate subducting beneath the Sunda Plate.
- Terrain: Mountainous volcanic spine with fertile plains and river basins.
Human Geography
- Population: ~156.4 million (≈ 56% of Indonesia’s population) — most populated island globally.
- Capital: Jakarta (northwest coast).
Historical Significance
- Centre of Hindu–Buddhist kingdoms → later Islamic sultanates.
- Core of the Dutch East Indies administration.
- Major role in Indonesia’s independence movement (1930s–1940s).

