Paathara Practice
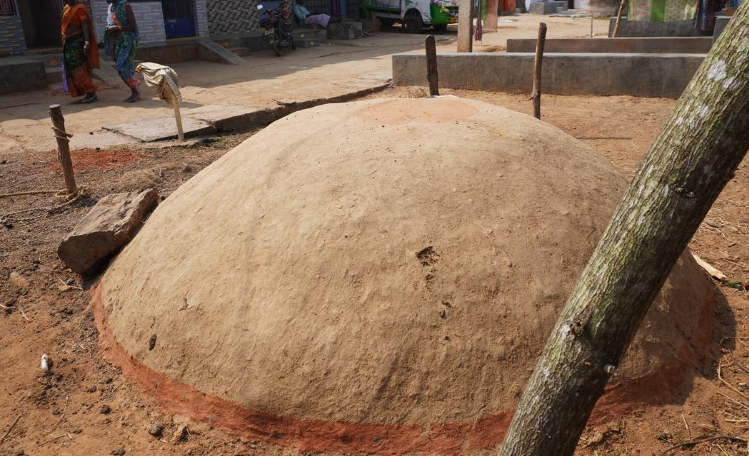

Context: The Paathara underground grain storage tradition is rapidly declining in Srikakulam district, Andhra Pradesh.
What is Paathara Practice?
- Ancestral underground grain storage system used by paddy-growing families
- Stores freshly harvested paddy grains in sealed earthen pits
Location
- Practised in Uddanam region of Srikakulam district
- Along Mahendratanaya River banks
- Near Andhra Pradesh–Odisha border
Geographical Setting
- Common in inland and hilly terrain areas
- Underground storage suited for moisture and pest protection
Structural Features
- Rectangular pit dug into the ground
- Plastered with straw and clay mixture
- Sealed using cow dung layer on top
Cultural Significance
- Built in front of thatched rural houses
- Symbolises joint family agricultural system
Storage Pattern
- Families store grain sufficient for annual household consumption
Advantages
- Protects against rodents, contamination, and theft
Reasons for Decline
- Lack of space in modern housing layouts
- Reduced awareness of traditional practices
- Changing rural architecture patterns
El Niño
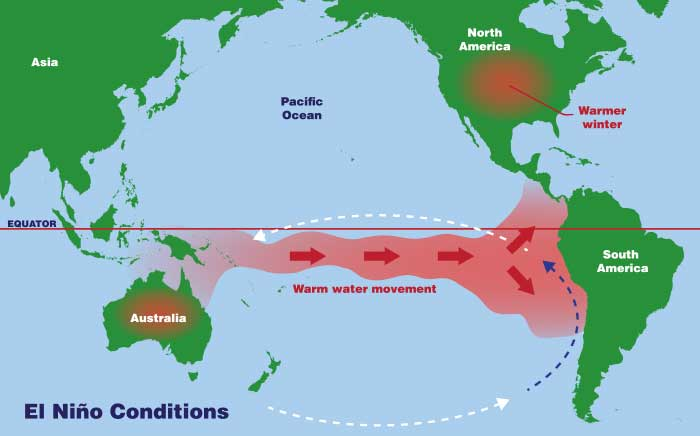
What is El Niño?
- Warm phase of ENSO marked by abnormal Pacific surface warming
- Occurs irregularly every two to seven years
- Leads to rise in global average temperatures
- Impacts eastern and central equatorial Pacific Ocean
Formation Mechanism
- Trade winds weaken, shifting warm waters eastward toward South America
- Thermocline deepens in eastern Pacific, suppressing cold-water upwelling
- Alters atmospheric pressure system called Southern Oscillation
- Disrupts Walker Circulation across the Pacific basin
Scientific Indicators
- Sea Surface Temperature anomalies in designated Niño regions
- Subsurface heat buildup at 100–250 metre ocean depth
- Oceanic Niño Index: SST anomaly ≥ +0.5°C for five overlapping seasons
- Weak or reversed trade winds along equatorial Pacific
Controlling Factors
- Strength and persistence of Pacific trade winds
- Subsurface heat content in equatorial Pacific Ocean
- Ocean-atmosphere feedback mechanisms
- Influence of long-term global warming
Global Implications
- Contributes to record-breaking global temperature years
- Triggers extreme weather patterns across continents
Regional Impacts
- India: Higher probability of weak monsoon and drought conditions
- South America: Heavy rainfall, floods, coastal erosion risks
- Australia and Southeast Asia: Droughts, heatwaves, wildfire events
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB)

Context
- The Central Ground Water Board functions as the national apex agency for scientific groundwater management under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
What is CGWB?
- Multidisciplinary scientific organisation under Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Provides scientific inputs for groundwater management and regulation
- Acts as the national apex body for groundwater resources
- Establishment and Evolution
- Established in 1970 by renaming Exploratory Tube Wells Organisation
- Merged with Ground Water Wing of Geological Survey of India in 1972
- Functions under Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation.
- Mandate
- Develops technologies for sustainable groundwater development and management
- Monitors and implements national groundwater policies
- Organisational Structure
- Headed by a Chairman with five members
- Comprises hydrogeologists, geophysicists, chemists, engineers, and hydrologists
- Headquarters
- Located at Bhujal Bhawan, Faridabad, Haryana
Major Activities
- Implements National Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme (NAQUIM)
- Conducts groundwater exploration and aquifer delineation studies
- Undertakes geophysical surveys for groundwater-bearing zones
- Performs periodic national groundwater resource assessments
- Monitors groundwater levels and quality through observation wells
- Disseminates groundwater data and scientific knowledge
New START Nuclear Treaty

Context: The New START treaty will expire on 5 February 2026 as the last US–Russia arms control agreement.
What is New START?
- Bilateral nuclear arms control treaty between United States and Russia
- Places legally binding limits on strategic nuclear weapons
- Covers weapons targeting core political, military, and industrial centres
Treaty Background
- Signed: April 2010
- Entered into force: February 2011
- Signed by: Barack Obama and Dmitry Medvedev
- Duration: Ten years with one five-year extension
- Extension exercised: 2021
Status Update
- Russia suspended participation in February 2023
- Halted inspections and data exchanges
- Continued observance of core numerical limits
Core Objectives
- Prevent strategic nuclear arms race
- Enhance transparency and predictability
- Reduce miscalculation and accidental escalation risks
- Promote global strategic stability
Key Numerical Limits
- Caps 1,550 deployed strategic nuclear warheads per side
- Limits 700 deployed delivery systems
- Includes Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs), Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) and heavy bombers
- Allows 800 total launchers deployed and non-deployed
Verification Mechanisms
- Conducts on-site inspections
- Mandates regular data exchanges
- Requires deployment and movement notifications
Strategic Importance
- Serves as last formal constraint on US–Russia nuclear forces
- Shapes nuclear force planning during political hostility
Expiry Implications
- Removes formal limits on strategic nuclear arsenals
- Increases risk of renewed nuclear arms race
- Allows additional warhead loading on existing missiles
Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP)

Context: The Government of India introduced OALP under HELP to accelerate hydrocarbon exploration and production nationwide.
What is OALP?
- Allows companies to select and propose exploration blocks independently
- Permits Expression of Interest submission throughout the year
- Areas accumulated and auctioned three times annually
Launch Framework
- Implemented under Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy, 2016
- Launched along with National Data Repository in June 2017
- Replaced New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP) framework
What is HELP?
- Stands for Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy
- Approved in March 2016
- Aims to simplify rules and boost domestic hydrocarbon production
Uniform Licensing System
- Provides single license for all hydrocarbon types
- Covers oil, natural gas, and coal bed methane
- Replaces multiple licenses under NELP system
Revenue Sharing Model
- Government receives share of gross revenue from production
- Eliminates cost recovery scrutiny by government agencies
- Replaces profit sharing model of NELP
Pricing and Marketing Freedom
- Allows free marketing of crude oil and natural gas
- Reduces contract complexity and profit manipulation risks
Royalty Structure
- Introduces graded royalty rates based on water depth
- Higher royalties for shallow water exploration areas
- Lower royalties for deep and ultra-deep water blocks
Advantages of HELP
- Promotes Ease of Doing Business in upstream sector
- Shifts from government control to government facilitation
- Encourages private and foreign investment in E&P activities
OALP Significance
- Provides company-driven block selection flexibility
- Improves access to geological data through National Data Repository
New Consumer Price Index (CPI) Series
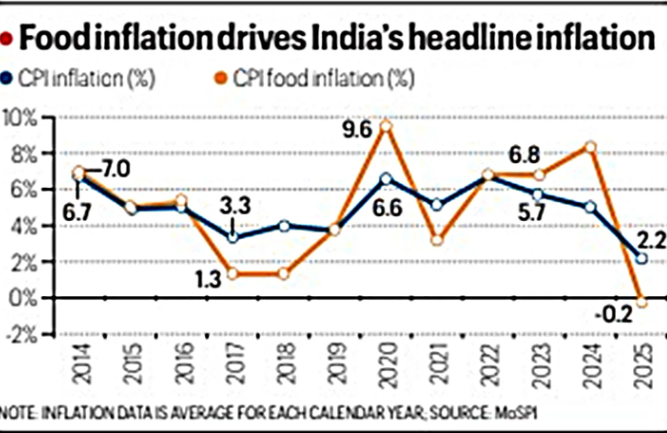
Context: The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released the new Consumer Price Index series with base year revised to 2023–24.
What is the New CPI Series?
- Updated framework for measuring retail inflation in India
- Base year revised from 2011–12 to 2023–24
- Weights derived from Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023–24
- Serves as headline inflation indicator for monetary policy targeting
Organisations Involved
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- Data Source: Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES)
Historical Background
- CPI Combined (Rural and Urban) introduced during 2011–12
- Earlier weights based on 2011–12 consumption patterns
- Revision reflects income growth, urbanisation, and services consumption shift
- Periodic base revision follows international statistical best practices
Methodology and Coverage
- Uses HCES 2023–24 rural and urban consumption shares
- Covers 1,465 rural and 1,395 urban markets across 434 towns
- Includes 12 online markets in major cities
- Item basket expanded from 299 to 358 items
- Improves House Rent Index methodology and rural rent coverage
- Excludes employer-provided accommodation from rent calculation
- Includes e-commerce prices for airfares, OTT, and telecom plans
Key Features
- Food and beverages weight reduced to approximately thirty-seven percent
- Reflects Engel’s Law on declining food expenditure share
- Housing weight increased to around seventeen percent
- Strengthens services sector representation in inflation basket
- Incorporates digital economy price components
- Reduces weather-driven food inflation volatility
Significance
- Improves credibility and accuracy of inflation measurement
- Supports Reserve Bank of India monetary policy decisions
- Reflects structural shift toward housing and services consumption
Stealth Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)
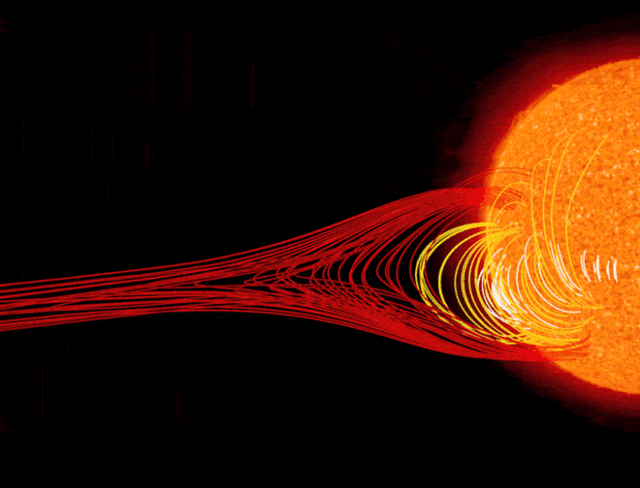
Context: Astronomers linked the March 2023 geomagnetic storm to a Stealth Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) lacking visible solar warning signals.
What are Stealth CMEs?
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) without clear low-coronal solar signatures
- Lack solar flares, X-ray bursts, or strong radio emissions
- Appear optically weak or invisible in standard solar imaging
- Still capable of triggering severe geomagnetic storms on Earth
Typical Origin Zones
- Active solar regions with weak or slowly evolving magnetic fields
- Areas near coronal holes with open solar magnetic field lines
Formation Process
- Magnetic flux rope forms silently in the solar corona
- Low-energy magnetic reconnection releases plasma gradually
- High-speed solar wind from coronal holes accelerates the CME
- CME expands and rotates during interplanetary space travel
Geoeffectiveness Factors
- Travels behind high-speed solar wind streams
- Magnetic cloud expansion increases Earth-impact potential
- Southward magnetic field orientation enhances magnetospheric reconnection
Implications
- Challenges space weather early-warning systems
- Disrupts satellites, Global Positioning System (GPS), and radio communications
- Threatens power grids and aviation navigation systems
Observation Platforms Used
- Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) – National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- Solar Orbiter – European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA mission
- Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory-A (STEREO-A) – NASA spacecraft
- WIND – NASA solar wind monitoring spacecraft
Cytoplasm
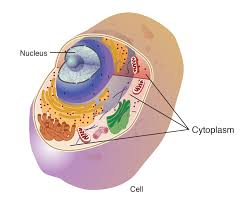
Context: Scientists highlighted cytoplasm reorganization as critical for early cell development in fertilized eggs.
What is Cytoplasm?
- Thick cellular fluid enclosed by the cell membrane
- Composed mainly of water, salts, and proteins
In Eukaryotic Cells
- Includes all cell material outside the nucleus
- Nucleus contains separate fluid called nucleoplasm
Organelles in Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria: Site of ATP energy production
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Site of protein and lipid synthesis
- Golgi apparatus: Modifies, packages, and sorts proteins
- Lysosomes and peroxisomes: Intracellular digestion of macromolecules
Cytosol
- Liquid portion surrounding all organelles
- Composed of about eighty percent water
- Contains salts, sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, and enzymes
Functions
- Site of most cellular metabolic activities
- Enables easy transport of materials within cell
Structural Support
- Supported by cytoskeleton protein framework
- Provides shape and internal organization to cells
In Prokaryotic Cells
- Present without membrane-bound organelles
- Contains ribosomes for protein synthesis
Hanle Dark Sky Reserve
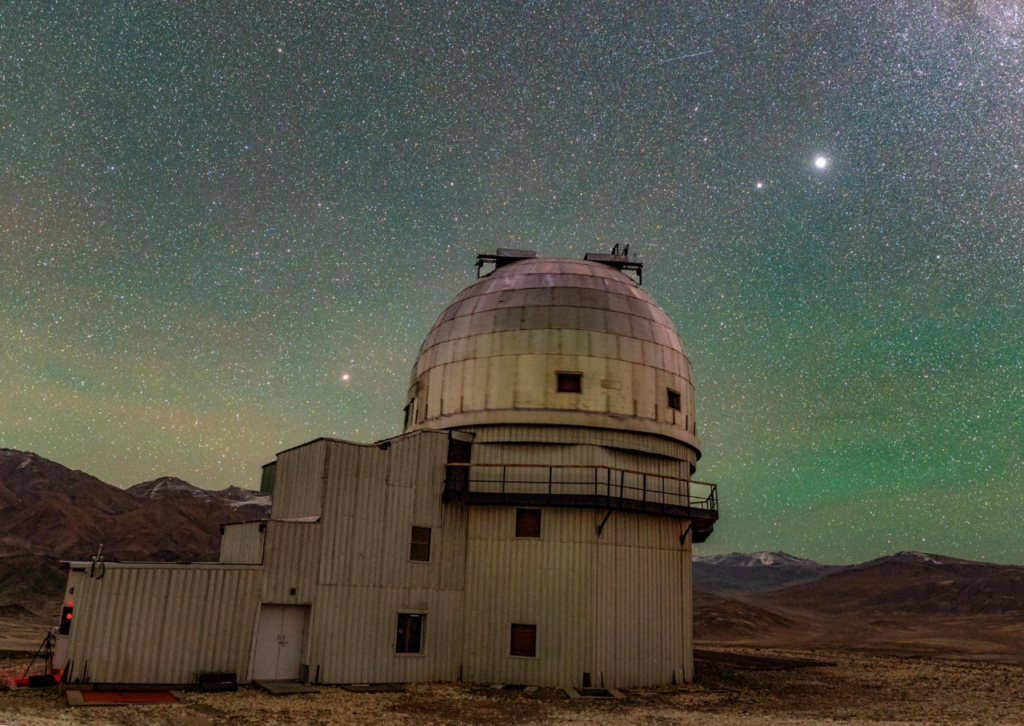

Context: A rare blood-red aurora was recorded by the Indian Astronomical Observatory all-sky camera at Hanle Dark Sky Reserve.
Location
- Situated at 4,500 metres altitude
- Located in Changthang region, Ladakh
- Part of Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary
Status and Recognition
- Notified in December 2022 by Government of Ladakh
- India’s first International Dark Sky Reserve
- Offers Bortle-1 dark sky classification
Core Institution
- Centred around Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO), Hanle
- Managed by Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA)
- Functions under Department of Science and Technology (DST)
Objectives
- Curtails light pollution across Changthang region
- Promotes astro-tourism for local livelihood generation
Administrative Support
- Supported by Union Territory Ladakh administration
- Funds astro-tourism initiatives and light management plans
Scientific Significance
- Enables observation of faint and distant celestial objects
- Provides high atmospheric transparency and minimal light interference

