Rafah Crossing
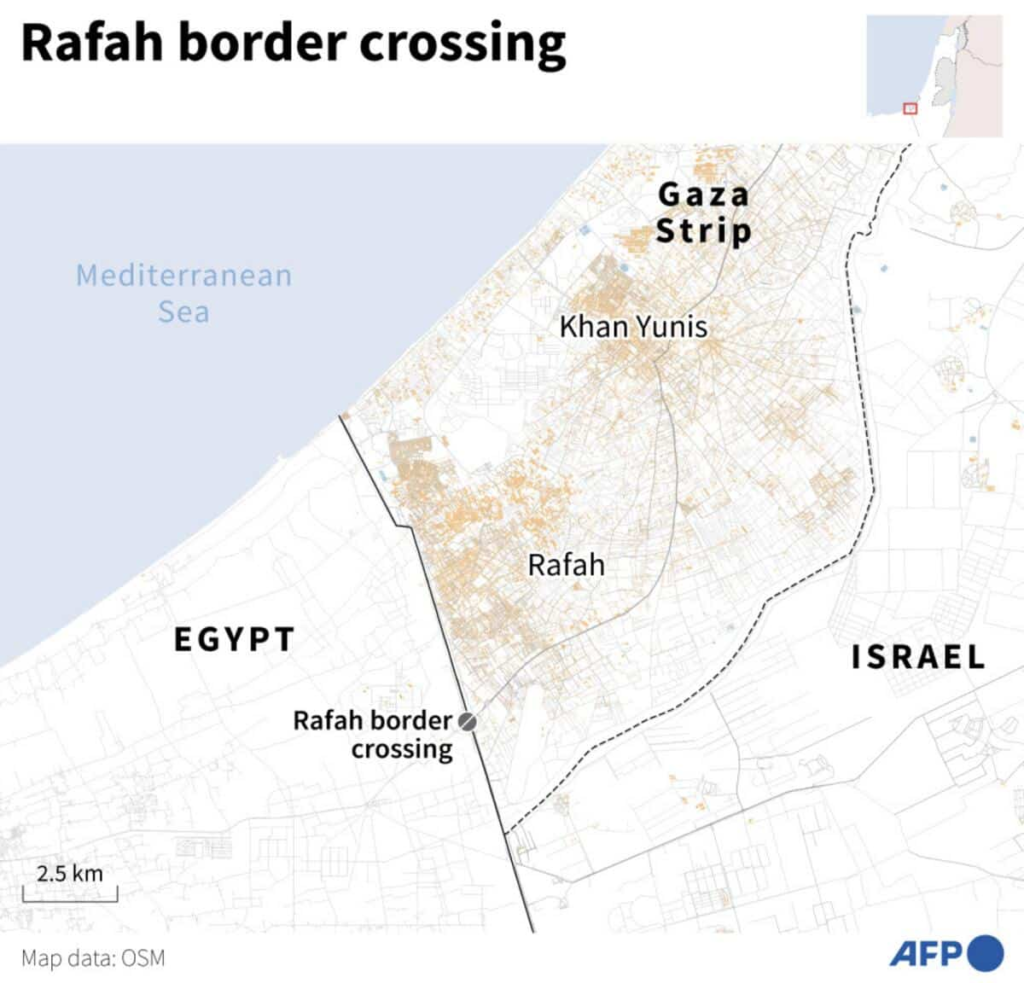
Context: The Rafah Crossing remains the only operational exit for Gaza after Israel closed Erez and Kerem Shalom.
- Southernmost border crossing of the Gaza Strip
- Connects Gaza with Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula
- Controlled by Egypt
- Unique Feature: Only Gaza exit not leading into Israeli territory
Other Gaza Crossings
- Erez Crossing: Located in north, used for movement into Israel
- Kerem Shalom Crossing: Located in south, used for commercial goods only
- Both crossings controlled by Israel
Current Status
- Erez and Kerem Shalom remain closed
- Rafah functions as sole humanitarian access point
Strategic Importance
- Only route for humanitarian aid entry into Gaza
- Primary passage for civilian movement out of Gaza
Bharat-VISTAAR

Context: The Union Finance Minister proposed the Bharat-VISTAAR tool for the agriculture sector during recent budget announcements.
What is Bharat-VISTAAR?
- Multilingual artificial intelligence tool for agricultural advisory and integration
- Stands for Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources
- Integrates AgriStack portals with ICAR agricultural practice packages
Core Objectives
- Enhances farm productivity through data-driven advisory support
- Improves farmer decision-making using customised recommendations
- Reduces agricultural risks through real-time digital guidance
Key Features
- Provides AI-based, location-specific farming advisories
- Enables integration of research-based agricultural best practices
- Supports multilingual farmer interaction and access
What is AgriStack?
- Digital foundation platform for India’s agriculture ecosystem integration
- Brings together farmers, governments, and service providers digitally
- Functions of AgriStack
- Facilitates access to cheaper agricultural credit
- Enables availability of quality farm inputs
- Provides localised, data-driven farming advice
- Improves market access and price discovery for farmers
- Supports government scheme planning and beneficiary targeting
Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)

Context: The Union Budget clarified that capital gains tax exemption does not apply to secondary market SGB purchases held to maturity.
What are Sovereign Gold Bonds?
- Government securities denominated in grams of gold
- Act as substitutes for physical gold holding
Launch and Issuance
- Scheme launched on October 30, 2015
- Issued by Reserve Bank of India on behalf of Government of India
Eligible Investors

- Open to resident Indian individuals
- Includes Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs)
- Available for Trusts, Universities, and Charitable Institutions
Denomination and Limits
- Issued in one gram denominations and multiples
- Minimum investment one gram of gold
- Maximum four kilograms for individuals and HUFs
- Maximum twenty kilograms for trusts
Joint Holding Rule
- Four kilogram limit applies to first applicant only
Tenure and Exit
- Eight-year bond tenure
- Exit allowed in fifth, sixth, and seventh years
- Exit exercised on interest payment dates
Sales Channels
- Sold through nationalised and scheduled banks
- Available at designated post offices
- Distributed via SHCIL and authorised stock exchanges
Kalbelia Community

Context: The National Human Rights Commission issued a notice to Rajasthan over Kalbelia burial ground protests in Barmer.
Who are Kalbelias?
- Snake-charmer folk community from Rajasthan, India
- Traditionally engaged in catching snakes and trading snake venom
- Recognised for vibrant dances and black embroidered attire
Cultural Recognition
- Songs and dances inscribed on UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage list
- Recognised in 2010 as key marker of community cultural identity
Religious Tradition
- Follow the Nath tradition
- Practice burial of dead kin, not cremation
Kalbelia Dance (Sapera Dance)
- Folk dance central to Kalbelia cultural identity
- Performed mainly by women dancers
- Reflects close association with snakes through movements and costumes
- Features fast-paced, flexible, and swirling dance patterns
Musical Accompaniment
- Performed by men musicians
- Instruments include pakhawaj, dholak, jhanjhar, harmonium, sarangi
- Signature instrument is pungi (been)
Kavach 4.0

Context: Indian Railways commissioned 472.3 route kilometres of Kavach Version 4.0 for enhanced train safety.
- National Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system for collision prevention
- Originally called Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS)
- Adopted as national standard in 2020
Version Timeline
- Kavach 4.0 approved in July 2024
- Major rollout completed by January 30, 2026
Core Objective
- Creates digital safety shield for real-time train protection
- Prevents signal passing and train-to-train collisions
Technology Components
- GPS and Radio Communication
- Uses GPS for precise train location tracking
- Employs UHF radio towers for continuous train-station communication
- Onboard Microprocessors
- Processes real-time operational and signal data
- Enables automatic braking during risk situations
- RFID Tags
- Installed every one kilometre along railway tracks
- Resets train position and direction accuracy
- Optical Fibre Network
- Enables high-speed data transfer between stations
- Ensures connectivity in remote and difficult terrains
World Nuclear Outlook Report

Context: The World Nuclear Outlook Report stated that China, France, India, Russia, and the United States may jointly account for nearly 980 GWe nuclear capacity by 2050.
About the Report
- Reviews national nuclear capacity targets against global tripling goal by 2050
- Assesses current and future nuclear contribution to global energy supply
- Summarises available nuclear reactor technologies
Findings
- Global Capacity Projections
- Global nuclear capacity may reach 1,446 GWe by 2050
- Exceeds tripling target of 1,200 GWe
- Growth driven by under-construction, planned, and government-backed projects
- Major Capacity Contributors
- Dominated by China, France, India, Russia, and United States
- Newcomer countries targeting 157 GWe combined capacity
- Regional Trends
- South Asia emerging as major nuclear growth region
- Growth led by India’s rising electricity demand and urbanisation
Key Recommendations
- Integrate nuclear energy into national climate action plans
- Extend existing reactor operational lifetimes
- Reform electricity markets for nuclear inclusion
- Promote neutral and accessible nuclear financing
- Scale supply chains and advanced reactor deployment
India’s Nuclear Status
- Current nuclear capacity around 8.8 GW
- Long-term target of 100 GW by 2047
- Allows private and foreign participation with state majority control
- Supports low-carbon energy transition and grid stability

