President’s Rule (Article 356)
Context: President’s Rule ended in Manipur; Yumnam Khemchand Singh sworn in as Chief Minister.
What is President’s Rule?
- President’s Rule = Suspension of State Government + Legislative Assembly.
- State comes under direct control of Union Government.
- Also called State Emergency / Constitutional Emergency.
- Imposed under Article 356.
- Constitutional Basis
- Article 355: Union ensures States function as per Constitution.
- Article 356: Proclamation of President’s Rule.
- Article 365: Non-compliance with Union directions → Ground for Rule.
- Grounds for Imposition
- Breakdown of constitutional machinery in State.
- Governor’s report or other credible information.
- Failure to follow Union Government directions.
- Parliamentary Approval
- Must be approved within 2 months by Parliament.
- If Lok Sabha dissolved → Valid till 30 days after reconstitution.
- Requires Simple Majority (present and voting).
- Duration
- Initial period → 6 months.
- Extendable every 6 months → Maximum 3 years.
- Beyond 1 year → Requires:
- National Emergency in force, OR
- Election Commission certification.
- Beyond 3 years → Constitutional Amendment required.
- Revocation
- President may revoke anytime.
- No Parliamentary approval required.
Effects of President’s Rule
- Executive
- President assumes State executive powers.
- Governor acts on behalf of President.
- Legislative
- Assembly suspended/dissolved.
- Parliament legislates for State (Art 357).
- Financial
- President authorises expenditure from Consolidated Fund of State.
- Later Parliamentary approval required.
- Fundamental Rights
- No suspension of Fundamental Rights.
- Differs from National Emergency.
Key Judicial Pronouncements
- S. R. Bommai Case (1994): Judicial review allowed and the floor test made mandatory.
- Sarbananda Sonowal Case (2005): Reinforced Union duty under Article 355.
- Rameshwar Prasad Case (2006): Assembly dissolution without floor test invalid.
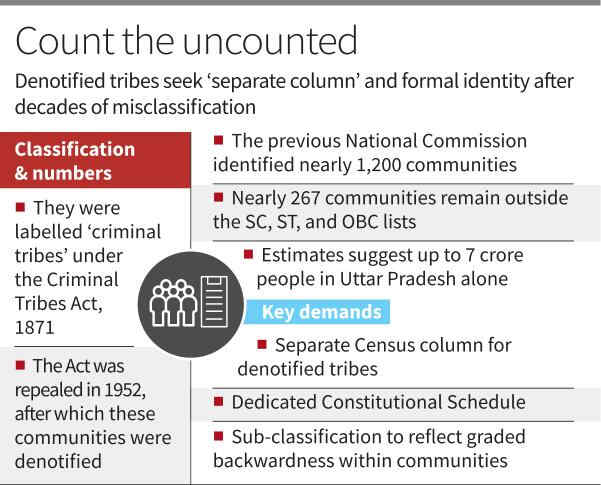
Denotified Tribes (DNTs)

Context: Denotified, nomadic tribes demand separate Census column in 2027.
Who are Denotified Tribes (DNTs)?
- Communities earlier notified as “criminal tribes” under colonial law.
- Label removed after repeal of Criminal Tribes Act, 1952.
- Hence called Denotified Tribes (DNTs).
- Historical Background
- 1871: Criminal Tribes Act enacted by British government.
- 1924: Act amended, expanded surveillance powers.
- 1952: Act repealed; communities “denotified”.
- Many later merged into SC / ST / OBC categories.
Current Demand
- Separate constitutional Schedule for DNTs.
- Separate Census column/code in Census 2027.
- Claim political misclassification within SC/ST/OBC lists.
- Demand sub-classification to show graded backwardness.
- Legal & Policy Developments
- Supreme Court (Aug 2024) allowed SC/ST sub-classification.
- Used as basis for graded backwardness demand.
- Social Justice Ministry recommended Census inclusion.
- Registrar General of India (RGI) agreed to include DNTs.
National Commission on DNTs
- Chaired by Bhiku Ramji Idate.
- Identified ~1,200 DNT communities nationwide.
- 2017 Report: Listed 267 unclassified DNT communities.
- Key Issues Faced
- Lack of distinct Census identity.
- Absence of DNT community certificates by States.
- Inability to compete within larger SC/ST/OBC groups.
SEED Scheme (For DNTs)
- Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs.
- Planned outlay: ₹200 crore.
- Actual spending (till Dec 2025): ₹69.3 crore.
- Low utilisation due to non-issuance of DNT certificates.
Project Vault

Context: USA launched Project Vault to stockpile critical minerals.
What is Project Vault?
- US critical minerals stockpiling programme.
- Public–private strategic reserve initiative.
- Similar to Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) model.
- Launched by: United States Government and funded via private capital + US Export–Import Bank.
Aim
- Ensure uninterrupted critical mineral supply.
- Reduce dependence on China’s mineral processing.
- Strengthen defence, manufacturing, clean energy chains.
Minerals Covered
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs).
- Cobalt, Gallium, other strategic metals.
Key Features
- Stockpiling Mechanism
- Government purchases and stores minerals.
- Managed through private commodity traders.
- Advance Purchase Contracts
- Firms commit to future mineral purchases.
- Fixed inventory pricing mechanism.
- Access Model
- Withdrawal allowed with replacement obligation.
- Full access during major supply disruptions.
- Price Stabilisation
- Mandatory repurchase at same price.
- Reduces global price volatility.
- Private Sector Role
- Sourcing and storage by traders.
- Examples: Mercuria, Traxys.
Significance
- Enhances strategic autonomy.
- Secures defence supply chains.
- Supports EV, aerospace, semiconductor sectors.
- Protects against export controls.
- Stabilises rare earth markets.
Chief Election Commissioner (CEC)

Context: Opposition parties discussed initiating removal proceedings against CEC Gyanesh Kumar.
Who is the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC)?
- Head of Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Supervises elections to Parliament, State Legislatures, President, Vice-President.
- Constitutional Basis
- Article 324 → Establishes Election Commission of India.
- Provides powers, composition, independence.
- Appointment of CEC: Appointed by President of India.
- As per 2023 Act: Selection Committee
- Prime Minister.
- Leader of Opposition (Lok Sabha).
- Union Cabinet Minister (nominated by PM).
- Tenure
- 6 years or till 65 years age, whichever earlier.
Removal of CEC
- Constitutional Provision
- Article 324(5) governs removal.
- Same manner as Supreme Court Judge removal.
- Linked to Article 124(4).
- Grounds for Removal
- Proved misbehaviour.
- Incapacity (physical or mental).
- Removal Procedure
- Notice of Motion: Introduced in either House of Parliament.
- Minimum MP Support: Requires prescribed number of MPs.
- Inquiry Committee: Investigates charges and evidence.
- Special Majority: Majority of total membership + Two-thirds present and voting (both Houses).
- Presidential Order: President issues removal order.
Turtle Trails

Context: Union Budget 2026–27 proposed development of Turtle Trails along Olive Ridley nesting coasts.
What are Turtle Trails?
- Regulated eco-tourism pathways near turtle nesting beaches.
- Promote conservation awareness and nature-based tourism.
States Covered
- Odisha → Rushikulya, Gahirmatha coast.
- Karnataka → Coastal nesting beaches.
- Kerala → Arabian Sea nesting stretches.
Target Species
- Focus on Olive Ridley Sea Turtle nesting sites.
Key Features
- Guided access during breeding / nesting season.
- Regulated visitor movement in nesting zones.
- Conservation education for tourists.
- Community participation (fishers, NGOs, volunteers).
- Low-impact infrastructure (temporary walkways, viewing zones).
- Linked with eco-tourism policy frameworks.
Significance
- Protects endangered marine turtles.
- Promotes scientifically managed tourism.
- Generates livelihoods for coastal communities.
- Reduces unregulated human interference.
Project Himank

Context: Snow leopard sighting recorded by Project Himank in High Himalayas.
What is it?
- BRO road infrastructure project in Ladakh.
- Launched in 1985.
Objective: Develop strategic road communication in Ladakh.
Location: Operates across Ladakh high-altitude region.
Key Features
- Maintains ~2,216 km road network.
- Works in extreme high-altitude terrain.
- Limited annual working season.
- Builds and maintains airfields.
Strategic Role
- Ensures connectivity near Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Supports military logistics and mobility.
PM VIKAS Scheme

Context: Union Minority Affairs Minister informed Rajya Sabha about PM VIKAS scheme.
What is it?
- Central Sector Scheme.
- Launched in 2025.
- Focuses minority socio-economic empowerment.
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Minority Affairs.
Target Groups
- Six notified minority communities.
- Artisans and craft workers.
- Minority women and youth.
- School dropouts.
Objectives
- Skill Development
- Provides need-based skill training.
- Enhances employability.
- Cultural Preservation
- Promotes traditional arts and crafts.
- Documents manuscripts and literature.
- Showcases Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH).
- Educational Support
- Open schooling certification.
- Covers 8th, 10th, 12th levels.
- Leadership & Entrepreneurship
- Empowers minority women.
- Provides enterprise support.
Key Features
- Financing via National Minorities Development & Finance Corporation (NMDFC).
- Education support for school dropouts.
- Market linkages via Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH).
- Hub and Spoke model for Vishwakarma Villages.
Tender Years Doctrine

Context: Delhi High Court held child welfare overrides Tender Years Doctrine.
What is Tender Years Doctrine?
- Common law child custody principle.
- Applies in family law jurisprudence.
Core Presumption
- Custody of young children with mother.
- Applies to children below ~5 years.
Doctrinal Basis
- Biological bond with mother.
- Presumed maternal caregiving ability.
- Early childhood developmental needs.
- Emotional security considerations.
Historical Origin
- Emerged in late 19th century.
- Rooted in common law systems.
Application Area
- Raised in divorce custody disputes.
Changing Relevance
- Declining due to gender equality.
- Recognises shared parenting roles.
Recent Judicial Position
- Child welfare paramount principle applied.
- Overrides Tender Years Doctrine.
- Case-specific custody evaluation required.
- Rejects stereotypical parental assumptions.

