
PRELIMS
Eco-Friendly Virus Controls Teak Defoliator Pest
Why in News: Kerala Forest Research Institute (KFRI) has developed an eco-friendly biological method using the Hyblaea puera Nucleopolyhedrosis Virus (HpNPV) to control the teak defoliator pest.

Developed by: Kerala Forest Research Institute (KFRI).
Pest: Teak defoliator moth (Hyblaea puera), which severely damages teak plantations by repeated leaf defoliation.
Economic impact: Causes loss of about 3 cubic metres of wood per hectare annually; ₹562.5 crore loss in Kerala and ₹12,525 crore across India.
Previous control method: Chemical pesticides via aerial spraying—environmentally harmful, caused public protests, and harmed non-target species.
New solution: Use of Hyblaea puera Nucleopolyhedrosis Virus (HpNPV), a natural virus that specifically infects and kills teak defoliator larvae.
How it works:
- Virus infects larvae, multiplies inside, causing death.
- Dead larvae release more virus, spreading infection further.
- Sub-lethal infections weaken pests and transfer virus to next generation.
Advantages:
- Eco-friendly and sustainable.
- Target-specific, safe for other forest organisms and ecosystems.
Significance: Prevents large-scale teak defoliation early in pest outbreaks, protecting valuable teak resources.
Understanding Prophylaxis: Gold Standard Treatment in Haemophilia Care
Why in News: Recent advances in prophylactic treatment offer a “gold standard” approach to prevent bleeds, improve quality of life, and reduce healthcare burdens.
Haemophilia: A rare inherited bleeding disorder causing deficiency of clotting factors (mostly Factor VIII in Haemophilia A), leading to excessive bleeding and spontaneous internal bleeds, especially in joints and muscles.
Challenges in India:
- Estimated haemophilia cases: 1 to 1.5 lakh
- Diagnosed cases: ~29,000 (only 20% of estimated)
Reasons: Lack of awareness, limited diagnostics, socioeconomic barriers
Untreated bleeds reduce life expectancy and cause disabilities.
Prophylaxis Treatment:
- Preventive regular replacement therapy of deficient clotting factors to avoid bleeds before they happen.
- Can be administered via intravenous injections or newer subcutaneous injections.
- Contrasts with on-demand therapy, which treats bleeds only after they occur.
Advantages of Prophylaxis:
- Prevents joint damage and disability by maintaining clotting factor levels continuously.
- Improves quality of life: fewer bleeds, less pain, more independence, normal school and work life.
- Reduces healthcare burden: fewer hospitalizations and lower overall treatment costs.
Global Scenario:
- ~90% of haemophilia patients in developed countries use prophylaxis, leading to near-normal life expectancy.
- India still primarily uses on-demand therapy; some states have started prophylaxis in children under 10.
Way Forward:
- Increase awareness, improve access through policy and education.
- Early diagnosis and regular prophylaxis essential to prevent disabilities and improve patient outcomes.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA)
Why in News: Recent studies show GLP-1 RAs can treat both Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes.
What are GLP-1 RAs:
Synthetic drugs that mimic GLP-1 hormone actions.
Extended Lifetime:
Fatty acid acylation attaches a fatty acid to GLP-1, protecting it from breakdown, extending drug action up to 160 hours.
Role of Albumin:
Fatty acid attachment allows GLP-1 RA to bind albumin, a transport protein, preventing rapid degradation and kidney clearance.
Druggability:
GLP-1 RA solves the druggability problem by enhancing stability and therapeutic effect through albumin binding.
Forms Available:
Injectable and increasingly oral formulations.
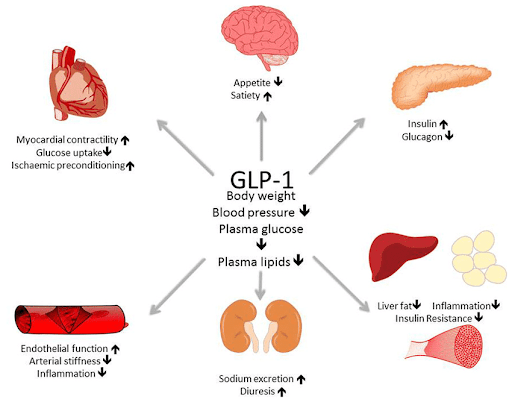
Uses:
- Stimulates insulin secretion to lower blood sugar.
- Controls appetite and weight.
- Slows gastric emptying, promoting fullness and reducing calorie intake.
- May have neuroprotective effects beneficial in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Reduces systemic inflammation.
Treatment Applications:
- Mainly for Type 2 diabetes and obesity; potential for neurodegenerative diseases.
World Meteorological Organization Certifies Mega Flash Lightning Record
Why in News: The World Meteorological Organization officially certified the longest single lightning flash ever recorded—829 km in the USA (2017), highlighting advances in weather monitoring and increasing lightning incidents globally, including a 57% rise in India.
Record:
- Longest single lightning flash recorded at 829 km (USA, 2017), from eastern Texas to near Kansas City.
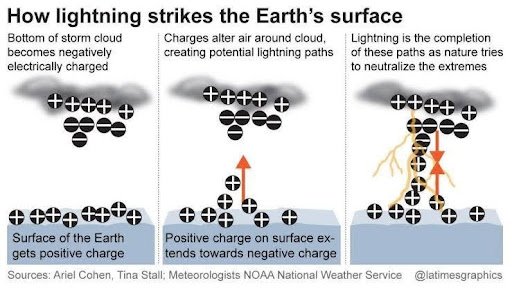
Lightning Basics:
- Caused by large buildup of opposite electrical charges between clouds or cloud and ground, breaking air insulation and creating a giant spark.
Impact:
- Lightning rapidly heats air causing expansion and thunder (loud sound). Lightning + thunder = thunderstorm.
Causes of Increased Lightning:
- Temperature rise (1°C increase can raise lightning by 7%-18% in India).
- Pollution (aerosol levels).
- Urbanisation.
Trends in India:
- 57% rise in lightning incidents from 2019-2024 (IMD & CROPC).
Hazards:
- Electric fires, explosions, tree damage, loss of life.
India’s NDMA Approach:
- Scientific solutions + community implementation.
- Action Plan on Prevention and Management against Lightning (2019).
- Protocols for early warning dissemination.
- Mobile app: SACHET.
IMD Lightning Forecasts:
- Lightning outlook (5 days to 24 hours).
- Nowcast.
- Damini mobile app.
Detection Infrastructure:
- Three lightning detection networks.
- Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs).

