
PRELIMS
Japan: AI Video on Mount Fuji Eruption
Why in News: On 26 August, Japan released an AI-generated video simulating an eruption of Mount Fuji to mark Volcano Disaster Prevention Day and the anniversary of its first volcano observatory (1911).
Aim: Raise awareness about potential eruption impacts and preparedness.
Mount Fuji’s Volcanic Status:
- Active volcano, last erupted in 1707.
- Still capable of erupting in the future.
Classification:
- Active – magma supply exists.
- Dormant – inactive for centuries but may erupt.
- Extinct – no magma connection.
Purpose of the AI Video:
- Shows ash clouds covering Tokyo, disrupting transport, communication & power.
- Advises residents to stock food, wear protective gear.
- Debate: Some call it alarmist (tourism concerns); others see it as precautionary, esp. after 2011 Tohoku earthquake & tsunami.
Volcanic Eruption Mechanics:
- Volcanoes form from openings in Earth’s crust linked to magma chambers.
- Magma rises → erupts as lava.
- Hazards: lava flows, ash clouds (do not melt, hard to clear), steam-blast eruptions (sudden).
Prediction of Eruptions:
- Indicators: seismic activity, ground deformation, heat anomalies, groundwater chemistry changes.
- Challenge: Some eruptions occur without warning; unrest may last years.
Challenges in Monitoring:
- Many volcanoes erupt rarely, limiting data.
- Each eruption is unique → past patterns not always reliable.
- Continuous monitoring + public education = essential for preparedness.
Ice Age-era Dragonfly
Why in News: Dragonfly species Crocothemis erythraea rediscovered in high-altitude regions of southern Western Ghats.

Key Facts:
Genus Crocothemis in India:
- C. servilia → widespread in lowlands.
- C. erythraea → high-elevation habitats (Europe, Asia, Himalayas, now Western Ghats).
First photographic record: 2018 Munnar high ranges survey.
Cited in 2021 monograph but later removed due to skepticism.
Multiple field expeditions (2019–2023) confirmed its presence.
Significance:
- Colonised southern India during the Pleistocene Ice Age, when cooler climate enabled temperate species to expand southwards.
- Discovery expands biodiversity records of Western Ghats (UNESCO World Heritage biodiversity hotspot).
Mahatma Ayyankali
Why in News: Prime Minister paid tribute to Mahatma Ayyankali on his Jayanti (28 August).

About:
- Born: 28 August 1863, Venganoor, Travancore (present-day Kerala).
- Community: Pulayar community (oppressed caste in Kerala).
- Faced extreme caste discrimination – denied education, roads, temples, schools.
Major Contributions:
Struggle for Education
- 1904: Launched “Vilaykal Samaram” → struggle to secure Dalit children’s admission in govt. schools.
- Faced violent opposition; eventually state conceded.
- Advocated education as path to liberation, echoing Ambedkar’s philosophy.
Agricultural Labour Movement
- 1907: Organized first agricultural labour strike in India, demanding better wages & dignity for Dalit workers.
- Forced landlords to improve conditions.
Formation of Organizations
- 1907: Founded Sadhu Jana Paripalana Sangham (SJPS) → uplift Dalits, spread education, fight oppression.
Fight for Public Rights
- Fought for Dalits’ right to walk on public roads & access public spaces.
- Inspired later movements like Vaikom Satyagraha (1924–25).
Political Representation
- 1912: Nominated to Sree Moolam Praja Sabha (Travancore’s legislative council).
- Used platform for land reforms, education, and equal rights.
Legacy & Recognition:
- Called “Mahatma Ayyankali” for fight against caste oppression.
- Known as Ambedkar of Kerala.
- Inspired later social reform movements.
- Recognized by Govt. of Kerala & India as a symbol of social justice, equality, and empowerment.
Free Medical Treatment for Officer Cadets Disabled During Training
Why in News: The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has sanctioned free medical treatment for officer cadets medically discharged with disabilities during training, under the Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS).
Key Facts:
- Earlier, such cadets were not eligible for ECHS benefits, since they were discharged before commissioning as officers.
- Now, they can access free treatment in:
- Military hospitals
- ECHS polyclinics
- Empanelled hospitals.

Scale of the Issue:
- Around 500 officer cadets discharged from top military academies (like NDA & IMA) in the past five years due to disabilities.
- Families were facing huge medical costs (₹50,000+ per month in some cases).
Other Benefits:
- Cadets now also eligible for ex-gratia disability award (20%–100% depending on extent).
- Ex-gratia payment: up to ₹40,000/month.
- Free one-time subscription fee of ₹1.2 lakh (for joining ECHS) waived.
Background:
- Supreme Court (Aug 18, 2025) flagged the issue in a suo motu case, based on reports of hardships faced by such cadets.
- Order seen as a step towards fairness, dignity, and social justice for disabled cadets.
Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS):
- Launched: 2003 by the Ministry of Defence.
- Objective: Provide cashless and quality medical care to ex-servicemen pensioners & their dependents.
- Coverage: Military hospitals, ECHS polyclinics, and empanelled civil hospitals.
- Governance: Managed by Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare (DESW) under MoD.
Eligibility (before recent decision):
- Retired Armed Forces personnel drawing pension + eligible dependents.
- Did not include cadets medically boarded out before commissioning.
New Change (Aug 2025):
- Officer cadets disabled during training (NDA, IMA, OTA, etc.) now included.
- Free treatment available under ECHS facilities.
Institutions Covered:
- National Defence Academy (NDA), Indian Military Academy (IMA), Officers Training Academy (OTA), etc.
Legal Context:
- MoD order extends ECHS benefits as a “special dispensation”, not setting a precedent for other categories.
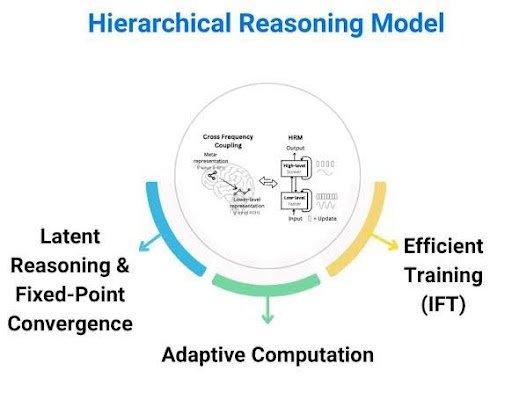
Hierarchical Reasoning Model (HRM) Challenges LLMs
Why in News: Researchers at Sapient, Singapore developed a new brain-inspired AI system called the Hierarchical Reasoning Model (HRM).
Context
- HRM has shown superior performance compared to conventional Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI and Anthropic on advanced AGI benchmarks.
Key Features of HRM:
- Brain-inspired design with two interconnected modules:
- High-level module → slow, abstract planning.
- Low-level module → fast, detailed computations.
- Uses iterative refinement (progressive short bursts of thinking).
- Unlike LLMs, does not depend on chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning (linear task breakdown).
Limitations of Traditional CoT Reasoning:
- Needs extensive training data.
- Brittle task decomposition → less flexible.
- Stepwise reasoning → increases latency.
Performance on ARC-AGI Benchmarks:
- ARC-AGI-1 test: HRM 40.3% (vs OpenAI o3-mini-high 34.5%, Claude 3.7 at 21.2%, DeepSeek R1 at 15.8%).
- ARC-AGI-2 test: HRM 5% (vs OpenAI 3%, DeepSeek 1.3%, Claude 0.9%).
Applications & Achievements:
- Solved difficult Sudoku puzzles.
- Found optimal paths in maze navigation.
- Shows advanced reasoning & planning beyond LLMs.
Insights:
- HRM’s performance not only due to hierarchical architecture but also refinement techniques during training.
- Demonstrates importance of training methods + architectural innovation.

