Context and Fiscal Background
- After the Union Budget, policy focus shifts toward the fiscal health of States.States play a crucial role in sustaining India’s overall growth momentum.
- During April–January FY2025, States’ revenue receipts increased by 18%.
- Actual revenues exceeded budget estimates, reflecting stronger fiscal performance.
- However, fiscal performance varied significantly across individual States.
Revenue Trends and Structural Drivers
- GST collections grew by 23%, surpassing the budgeted 22% growth.
- Improved compliance and expanding economic activity strengthened GST buoyancy.
- Lower GST rates and income tax rationalisation reduced potential revenue mobilisation.
- Strong revenue mobilisation offset lower devolution of excess Integrated GST funds.
- Stamp duty and registration revenues grew modestly at 11–13% annually.
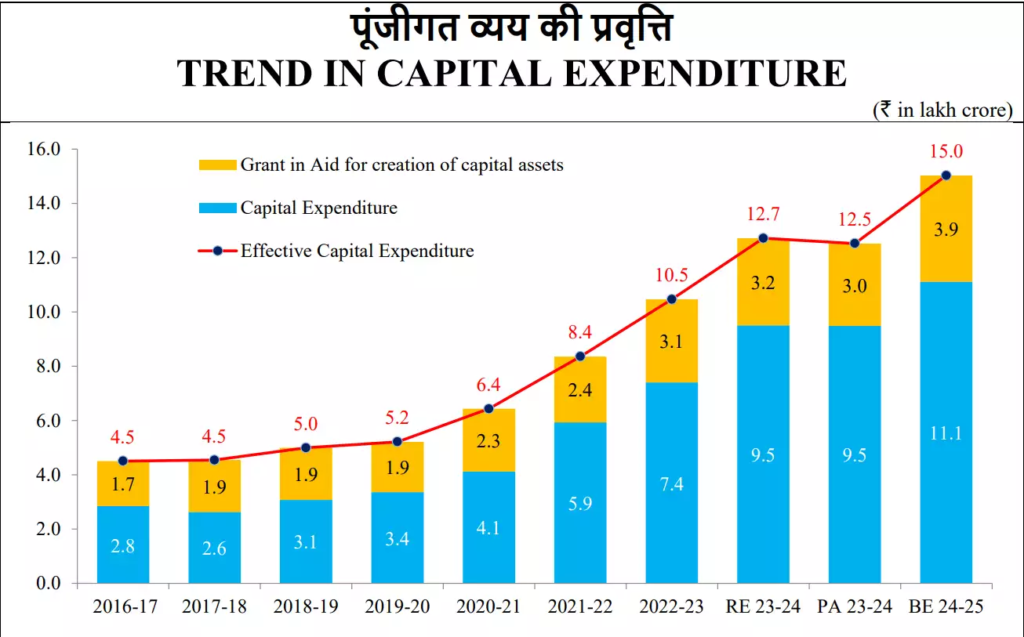
Capital Expenditure Performance
- States’ capital expenditure increased by 7.7% during April–January FY2025. This growth remains significantly below the budgeted 22% expansion target.
- However, capital spending surged by 25.7% in the third quarter. Thus the moderating revenue growth nudged States to slow revenue expenditure expansion.
- Sustained public capital investment remains essential for long-term economic growth.
Centre–State Fiscal Transfers
- Central grants to States were budgeted at ₹13.9 trillion this fiscal year. This amount was lower than previous actual transfers of ₹14.2 trillion.
- During April–November, Central grants declined by 18% year-on-year. States projected nearly 60% grant growth in the remaining months.
- Fiscal transfers significantly influence States’ developmental and infrastructure spending capacity.
Outlook and Growth Implications
- Moderating revenue growth may encourage States to restrain overall expenditure.
- However, sustained capital expenditure can crowd-in private investment effectively.
- The Centre’s 50-year interest-free capex loans support infrastructure development.
- Of the ₹1.5 trillion allocation, ₹1 trillion was disbursed by January 2025.
- Continued capital expenditure expansion can strengthen India’s macroeconomic stability.
About Capital Expenditure
- Meaning and Concept
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx) refers to spending on long-term productive assets. These assets provide economic benefits over several financial years.
- Such assets are not meant for sale but enhance productive capacity.
- Capital expenditure supports long-term development and increases earning potential.
- It is recorded as an asset and reduced gradually through depreciation.
- Key Features and Examples
- Capital expenditure creates assets that are not consumed within one year.
- It generally increases the capacity, efficiency, or life of assets.
- Examples include constructing buildings, highways, and public infrastructure.
- Purchasing machinery, land, vehicles, or upgrading technology are common instances.
- Such spending strengthens institutional and economic growth foundations.
- Significance of Capital Expenditure
- Capital expenditure promotes long-term economic growth and development.
- It enhances productivity by improving infrastructure and technological capability.
- Infrastructure investment generates employment and stimulates private investment.
- Improved public services enhance citizens’ overall quality of life.
- Higher public CapEx can create a positive multiplier effect in the economy.
