Census in India

Core Concept
- Census is a systematic enumeration of population.
- Provides data on demography, socio-economic and cultural characteristics.
- Conducted at local, regional and national levels.
History
- First census conducted in 1872 (non-synchronous).
- First synchronous census held in 1881.
- Conducted under W.C. Plowden, Census Commissioner of India.
- Census is carried out every 10 years.
Institutional Responsibility
- Conducted by the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India (RGI).
- RGI functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Legal and Constitutional Basis
- Census is listed in the Union List (Entry 69) of the Seventh Schedule.
- Conducted under the Census Act, 1948.
Upcoming Census: Key Features
- Will be the 16th Census of India.
- It will be the 8th census after Independence.
- Census data will be collected digitally using a mobile application.
- Self-enumeration facility will be provided for the first time.
Pre-Census Preparations
- States must report changes in districts, towns and villages to RGI.
- Administrative boundaries are frozen before census operations.
- Boundary freeze occurs not earlier than one year before census reference date.
- Census work is preceded by house-listing enumeration.
Impeachment of Judges in India

Concept
- Impeachment refers to removal of Supreme Court or High Court judges.
- Grounds are proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
- The term “impeachment” is not explicitly used in the Constitution.
Constitutional and Legal Basis
- Article 124(4) governs removal of Supreme Court judges.
- Article 218 applies the same procedure to High Court judges.
- Procedure is detailed under the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
Initiation of Motion
- Motion can be introduced in Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha.
- Requires support of 100 MPs in Lok Sabha or 50 MPs in Rajya Sabha.
- Motion proceeds only after acceptance by the Speaker or Chairman.
Inquiry Committee
- A three-member inquiry committee is constituted.
- Members include a Supreme Court judge, a High Court Chief Justice, and an eminent jurist.
- Committee conducts a quasi-judicial inquiry.
Parliamentary Approval
- Motion must be passed in both Houses of Parliament.
- Requires special majority:
- Majority of total membership, and
- Two-thirds of members present and voting.
- Final removal order issued by the President of India.
Key Facts
- Proceedings usually end if the judge resigns mid-process.
- No judge has been successfully impeached in India till date.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
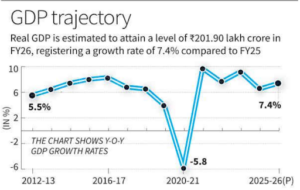
Context: The Union government estimated real GDP growth at 7.4% for FY 2025-26, up from 6.5% recorded the previous year.
More in News
- Government released First Advance Estimates for FY26; nominal growth projected at 8% for the current financial year.
- Reserve Bank of India had estimated GDP growth at 7.3% for FY26, with Q3 at 7% and Q4 at 6.5%.
- Private consumption spending expected to grow at 7% in FY26, marginally slower than 7.2% recorded last year.
- Service sector (tertiary) expected to grow faster at 9.1% in FY26 from 7.2% in FY25 while capital formation to grow by 7.8%.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Core Concept
-
-
- GDP measures the total market value of final goods and services produced domestically.
- GDP is used to assess the size and performance of an economy.
- GDP growth may occur due to higher production, price rise, or both.
-
- Nominal and Real GDP
-
- Nominal GDP is measured at current market prices.
- Real GDP is measured at constant prices.
- Real GDP excludes inflation effects using a price deflator.
- Real GDP growth ≈ Nominal growth − Inflation.
- GDP Deflator
-
-
- GDP deflator reflects price movement from base year to current year.
- GDP Deflator = Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP.
-
- Methods of GDP Calculation
- Income Method
-
-
-
- GDP calculated as sum of factor incomes.
- Includes wages, rent and profits.
-
-
- Production Method
-
-
-
- GDP measured through aggregate value of final output.
- Expressed as Gross Value Added (GVA).
-
-
- Expenditure Method
-
-
- GDP derived from total expenditure in the economy.
- Formula includes consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.
- In India, GDP is estimated using income and expenditure methods.
-
- GDP data is released by the National Statistical Office.
- NSO functions under Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)

Institutional Profile
-
- BIS is India’s National Standards Body responsible for standardisation, certification and hallmarking.
- Establishment and Legal Basis
-
- BIS was established in 1987.
- Came into force on 1 April 1987.
- Governed under the BIS Act, 2016.
- Headquarters located in New Delhi.
Historical Evolution
- Indian Standards Institution (ISI) was set up in 1947.
- ISI Certification Marks Scheme launched during 1952–56.
- ISI was transformed into BIS in 1987.
- BIS Act, 2016 expanded statutory powers.
Core Functions
- Formulates Indian Standards across sectors.
- Operates product certification schemes.
- Implements Compulsory Registration Scheme.
- Runs Foreign Manufacturers Certification Scheme.
- Conducts hallmarking of precious metals.
- Provides laboratory testing and recognition services.
Recent Initiatives
- BIS Standardisation Portal launched for digital standards lifecycle.
- SHINE programme focuses on women-centric capacity building.
- BIS-SAKSHAM recognises institutional excellence.
Goldilocks Phase
Core Concept
- Goldilocks phase denotes an economy that is neither overheating nor slowing.
- Characterised by a balance between growth and inflation.
Key Features
- Economic growth remains steady and sustainable.
- Inflation stays low and stable.
- Interest rates remain moderate and manageable.
- Enables policy continuity without aggressive interventions.
Monetary Policy Context
- Inflation remains within or below RBI’s target range.
- Growth is strong but non-inflationary.
- Monetary conditions support investment, consumption and credit expansion.
Policy Significance
- Provides RBI policy space.
- Allows neutral or accommodative stance.
- Reduces need for frequent rate changes.
- Indicates effectiveness of inflation targeting framework.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)

About the Platform
-
- ONDC is an open, interoperable digital commerce network.
- Enables platform-agnostic buying and selling using open protocols.
- Designed to prevent platform monopolies.
- Launch and Ministry
-
-
- Launched in April 2022.
- Implemented by DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
-
- Core Aim
-
- Democratises e-commerce by breaking platform silos.
- Creates a level playing field for sellers, buyers and service providers.
- Focuses on MSMEs, competition and inclusivity.
Operating Model
- ONDC is a decentralised network, not a marketplace.
- Does not own listings or process orders.
- Uses open protocols and standard APIs for interoperability.
Key Participants
- Buyer apps handle search and ordering.
- Seller apps manage catalogues and pricing.
- Logistics providers handle delivery and tracking.
- Technology enablers provide digital infrastructure.
Domains Covered
- Includes Food & Beverage, Grocery and Electronics.
- Covers Mobility, including autos, cabs and metro.
- Extends to Financial Services and Agriculture.
- Includes ONEST for Education and Training.
Mpemba Effect

Context: Indian scientists simulated the Mpemba effect using a supercomputer model.
Core Concept
-
- Mpemba effect describes hot water freezing faster than cold water under certain conditions.
- It is a counterintuitive physical phenomenon.
- Discovery and Naming
-
- Named after Erasto Mpemba.
- Scientifically reported in 1969.
- Phenomenon noted earlier by Aristotle, Francis Bacon and René Descartes.
- Scientific Nature
-
- Occurs only under specific experimental conditions.
- No single universal mechanism explains the effect.
- Classified as a non-equilibrium thermodynamic phenomenon.
- Scientific Relevance
-
- Relevant to phase transitions in physics.
- Studied using computational and experimental methods


