
PRELIMS
Healthocide:
Why in News: Researchers from the American University of Beirut coined the term “healthocide” in BMJ Global Health (Aug 2025)

Origin: Coined by researchers from American University of Beirut (Lebanon) in BMJ Global Health (Aug 5, 2025).
Meaning: Refers to deliberate, large-scale destruction of entire health ecosystems in conflict zones.
Includes: killing clinicians, bombing hospitals, blocking ambulances, dismantling supply chains.
Comparison: Framed as akin to genocide → destruction of a collective good essential to life and dignity.
Purpose: To galvanise the medical community; demands stronger legal protections for healthcare in conflict zones.
Extreme Weather Events in Jammu & Kashmir
Why in News: A flash flood in Kishtwar district, J&K (Chasoti village near Machail Mata temple) killed at least 65 people and left over 50 missing.
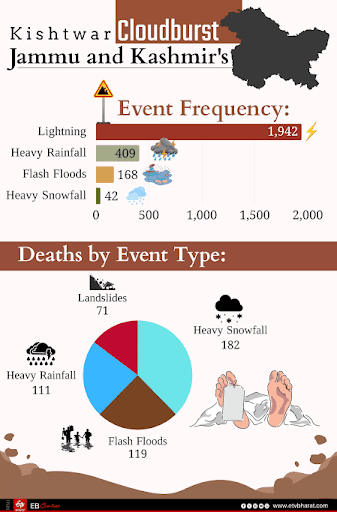
Trend: Sharp rise in extreme weather events in J&K; linked to global warming & climate change.
Major Causes:
- Rising Temperatures – Western Himalayas are warming 2x faster than the Indian subcontinent.
- Shrinking Glaciers – unstable glacial lakes → risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- Changing Western Disturbances – now beyond winter; Arabian Sea heating → more moisture, heavier rainfall.
- Topography – mountain terrain + orographic rainfall → prone to floods & landslides.
Human Impact:
- Districts worst-hit: Kishtwar, Anantnag, Ganderbal, Doda.
- Flash floods: highest fatalities.
- Heavy rain & snow: deadliest weather events overall.
India’s Sovereign Credit Rating Upgrade
Why in News: S&P Global Ratings has upgraded India’s sovereign credit rating from BBB- to BBB after 14 years, citing steady economic growth, fiscal consolidation, and resilience, making borrowing cheaper and boosting investor confidence.
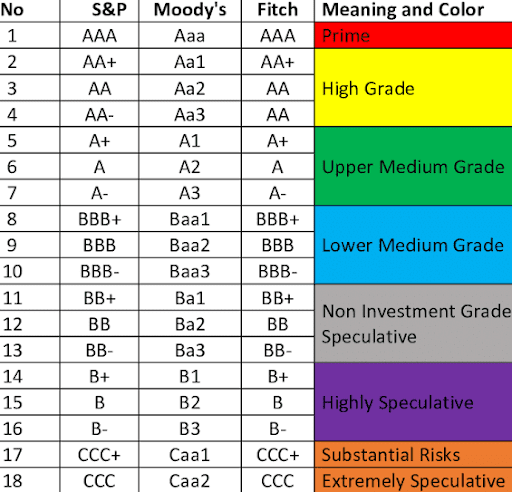
India’s S&P Rating Upgrade
Agency: S&P Global Ratings
Upgrade: From BBB- to BBB (first upgrade in 14 years, since 2011).
Significance: Moves India from the lowest investment grade closer to mid-level; lowers cost of borrowing, improves investor confidence.
Reasons for Upgrade
- Steady economic improvement despite Covid shock.
- Fiscal discipline: Fiscal deficit consistently reducing; below 3% in 2007-08, pandemic pushed it to ~9.2% (2020-21), now declining.
- Debt-to-GDP ratio: Projected to fall from 81% (2020-21) to ~75% by 2030-31.
- Nominal GDP growth: Among world’s fastest growing economies (~11.5% average nominal growth over last decade).
- Resilient growth: India remains one of the strongest-performing economies, despite global slowdown.
Rating Scale Context
- Current position: India at BBB, stable outlook.
- Next step: BBB+, then A category.
- Peers: India with BBB rating joins countries like Italy, Indonesia, Philippines.
- A-rated group: Includes Cyprus, Poland, Malaysia; richest = Australia, Canada, Denmark, Germany.
- Best rating countries: U.S., downgraded to AA+ in 2011 (first downgrade in history).
Implications
Positive:
- Opens the door for global funds inflow.
- Lowers cost of sovereign and corporate borrowing.
- Encourages private investment & growth.
Challenges:
- Maintaining fiscal discipline.
- Managing high debt & interest costs.
- Need for structural reforms to sustain growth.
Credit Rating – Static Information
Definition:
A credit rating is an independent assessment of a borrower’s (sovereign, corporate, or financial institution) ability to repay debt, expressed through letter grades.
Purpose:
- Helps investors assess credit risk.
- Determines cost of borrowing (higher rating → lower interest rates).
- Influences capital inflows and investor confidence.
Animal Blood Bank Network
Why in News: The Centre has released draft Guidelines/SOPs for Blood Transfusion & Blood Bank for Animals in India to establish a National Veterinary Blood Bank Network (N-VBBN) for standardising animal blood banking and transfusion.

Draft Guidelines for Animal Blood Bank
Prepared by:
- Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
Need:
- India: 536.76 million livestock (20th Livestock Census 2019).
- Companion animals: ~125 million.
- Livestock sector: ~30% of Agri GVA & 5.5% of Indian economy.
- Lack of national standards → dependence on hospital-based donors.
Donor Criteria:
- Clinically healthy, disease-free.
- Dogs: 1–8 yrs, ≥25 kg; Cats: 1–5 yrs, ≥4 kg.
- Fully vaccinated, esp. rabies.
- Female donors not pregnant/lactating.
National Veterinary Blood Bank Network (N-VBBN):
- Digitally integrated donor registry.
- Real-time inventory management.
- Helpline + online portal linking clinics, hospitals, donors.
- Standardised practices & adverse reaction logs.
Hosting Centres:
- Veterinary colleges & universities.
- Referral hospitals & polyclinics.
- Large diagnostic centres.
- Govt multi-speciality animal hospitals.
Related-Party Transactions (RPT)
Why in News: Value of RPTs in India has fallen below pre-pandemic levels.
Definition:
- Deal/arrangement between two entities with a pre-existing business relationship or common interest.
- Legal but can be misused to benefit promoters at the cost of minority shareholders.
Usage:
- Buying/selling of goods, raw materials, services among group companies.
- Reported in Balance Sheet (assets, liabilities, equity) & Profit-and-Loss Statement (net sales).
Regulation:
- Regulated by: SEBI.
- Law: Companies Act, 2013.
- Rule: SEBI mandates shareholder approval for RPTs crossing a defined threshold.
Recent Regulation Change:
- SEBI consultation paper proposes easing minimum threshold for shareholder approval.
- Aim: Reduce compliance burden for large-turnover companies.
Sector-wise Impact:
- High RPT usage: Steel, Real Estate, Pharmaceuticals.
- Real Estate: RPTs = ~17% of assets.
- Multiple sectors: RPTs = ≥20% of net sales.

