
PRELIMS
Machine Readable Electoral Rolls
Why in News: Allegations of “vote theft” and demands that the Election Commission (EC) provide machine-readable voter rolls to political parties are in picture.Current voter rolls are shared only as image PDFs, making analysis difficult.
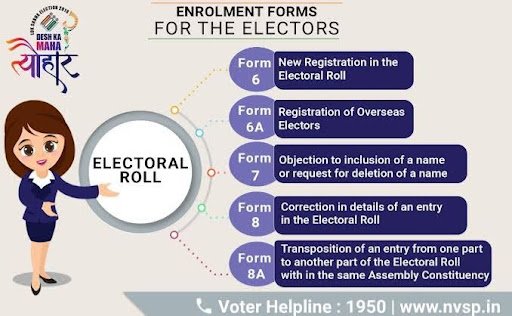
Electoral Rolls:
- Authoritative list of eligible voters, updated regularly through ERONET (EC’s digital application).
- India has 99+ crore voter entries (as of Jan 2025)
Current Format:
- Available as image PDFs (or printouts).
- Photos excluded; difficult to search/identify duplicates.
Machine Readable Rolls (Text PDFs):
- Can be searched, indexed, and analysed by computers.
- Help detect duplicate or irregular entries faster.
- Used earlier by activists (e.g., P.G. Bhat before 2018).
Why EC Stopped Sharing (2018):
- Order by then CEC O.P. Rawat: to prevent foreign access to sensitive voter data (names, addresses).
- Supreme Court (Kamal Nath vs EC, 2018): Refused to compel EC; said petitioners can convert PDFs themselves using OCR.
Challenges in Analysis:
- Over 6 crore pages of voter rolls; split into many parts.
- OCR conversion resource-heavy — costs around $40,000 per revision list (as per Google AI pricing).
Transparency Debate:
- Advocates argue that searchable rolls enhance accountability and prevent fraud.
- EC fears privacy and data misuse if full searchable rolls are made public.
ERONET (Electoral Roll Management System):
- A centralised, IT-based system used by the EC for additions, deletions, and corrections in the voter list.
Format of Rolls:
- Rolls include name, age, gender, part number, and photograph of the voter.
- Machine-readable “text mode” is mentioned in EC’s manual, but currently EC provides only image PDF format.
Charge-Coupled Devices (CCDs)
Why in News: George Smith, co-inventor of the Charge-Coupled Device (CCD), passed away on May 28, 2025. CCDs revolutionised digital imaging, earning Smith and Willard Boyle the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics.
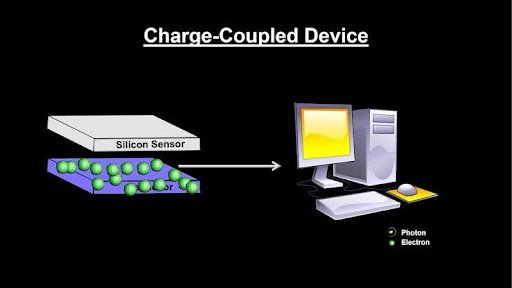
What is a CCD?
- Invented in 1969 at Bell Labs (U.S.).
- Converts light (photons) into electrical signals using an array of capacitors.
- Each pixel acts as a tiny light sensor, storing charge proportional to light intensity.
- Charges are transferred sequentially (like a bucket brigade) → readout → digitised into an image.
How CCDs Work (Principle)
- Based on the photoelectric effect.
- Photons strike semiconductor → generate electron-hole pairs → electrons stored as charge in pixels.
- Sequential charge transfer → converted into voltage → amplified → digital image.
Applications
- Digital Cameras & Media: Enabled film-free photography and instant image storage.
- Medical Diagnostics: X-rays, CT scans, endoscopy (high sensitivity and resolution).
- Astronomy: Gold standard in telescopes; detects faint galaxies, exoplanets, cosmic phenomena.
- Scientific Instruments: Microscopes, spectrometers, particle detectors.
- Security Systems: CCTV cameras, surveillance technology.
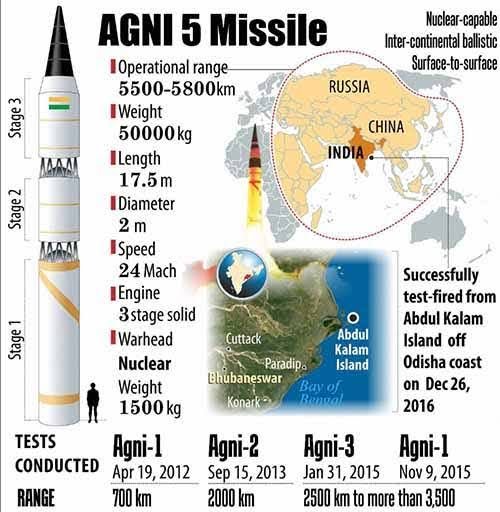
Agni-5 Missile Test
Why in News: On August 20, 2025, India successfully test-fired the Agni-5 missile from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha.
About Agni-5
Type: Indigenously developed Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
Range: ~ 5,000 km (covers nearly all of Asia and parts of Africa & Europe).
Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
Guidance System: Advanced navigation and control systems.
Propulsion: 3-stage solid-fuelled missile.
Role: Strategic deterrence, long-term national security needs.
Key Features
- Tested earlier with MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology → allows striking multiple targets with a single launch.
- Enhances second-strike capability under India’s nuclear doctrine.
Stages of Ballistic Missile Flight
1. Boost Phase
- Missile uses all its propellant during this short phase.
- For an ICBM, lasts only a few minutes.
- After this, trajectory is fixed.
2. Midcourse Phase
- Missile stops accelerating → continues on momentum.
- Warhead coasts through outer space.
- For an ICBM, this phase can last up to 20 minutes.
3. Terminal Phase
- Begins when warhead(s) re-enter Earth’s atmosphere.
- Ends upon impact or detonation.
- Shortest but most critical phase for interception.
Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, 2025
Why in News: Lok Sabha passed the Bill by voice vote on August 20, 2025.Seeks to ban real money gaming (fantasy sports, online card games, etc.) where users risk money.

Key Provisions
- Prohibits: Offering, operating, facilitating, advertising, promoting, and participating in online money games.
- Authority Creation: New body to promote e-sports, recognised as creative & recreational industry.
- Games Covered:
- “Real money gaming” → platforms like Dream11, PokerBaazi.
- Bill makes distinction between skill & chance irrelevant, bans all online money gaming.
Punishments:
- Imprisonment up to 3 years and/or fine up to ₹1 crore for violating provisions.
- Ban on advertisements and facilitation of such games.
- Financial institutions barred from processing transactions related to banned platforms.
Concerns & Challenges
- Industry may challenge constitutionality (grounds: trade restrictions, Centre’s legislative competence).
- Potential clash with Right to Trade/Occupation (Article 19(1)(g)).
- Fear of driving activities underground.
Rationale Behind the Bill
- Lifetime savings of people evaporating due to addiction.
- Algorithms may enable fraud and cheating.
- Growing social, financial, psychological, and public health harms.
Anna Chakra – PDS Supply Chain Optimisation Tool
Why in News: Implemented in 30 out of 31 States/UTs (except Manipur) to optimise the Public Distribution System (PDS) supply chain.
Developed by: World Food Programme (WFP) + Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT), IIT Delhi + Department of Food and Public Distribution.
Serves ~ 81 crore beneficiaries under the PDS.
Working Mechanism
- Uses advanced algorithms for efficient routing of food grains.
- Integrates with:
- Freight Operations Information System (FOIS) of Indian Railways via Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
- PM Gati Shakti platform (geo-location of FPS & warehouses).

Scale & Coverage
- Covers ~ 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPS).
- ~ 6,700 warehouses included in optimisation.
Benefits
- Cost savings: ~ ₹250 crore annually (reduced transport costs).
- Environmental gains: Lower fuel use → reduced CO₂ emissions → supports climate commitments.
- Efficiency: Faster, transparent, real-time food grain delivery.
Future Prospects
- Sets precedent for tech-driven supply chain optimisation in public welfare.
- Potential for expansion to other sectors.
Ideonella sakaiensis (Plastic-Degrading Microbe)
Why in News:Scientists are exploring microbial degradation as a sustainable solution to plastic pollution.
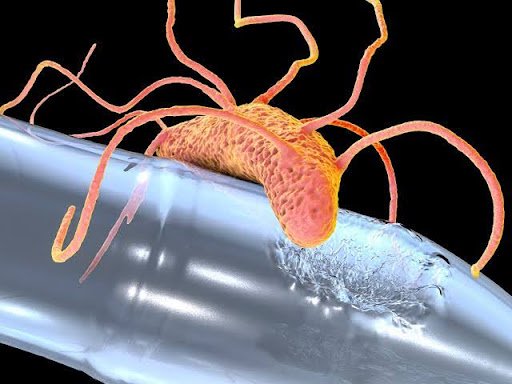
Ideonella sakaiensis is a bacterium that can break down Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), a widely used plastic.
Key Facts
Discovered by: Japanese researchers Kohei Oda and Kenji Miyamoto (Kyoto Institute of Technology & Keio University).
Habitat: PET-contaminated soil; thrives in oxygen-rich moist soil and sewage sludge.
Classification:
Genus – Ideonella
Family – Comamonadaceae / Sphaerotilaceae
Type – Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile, non-sporing bacterium.
Mechanism
- Produces enzymes that break PET into environmentally benign building blocks.
- Degraded compounds are consumed as food by I. sakaiensis and other microbes.
Advantages
- Can completely degrade PET (commonly used in bottles & packaging).
- Supports eco-friendly recycling of plastics.
Other Plastic-Degrading Organisms
- Bacteria: Gordonia (polypropylene), Arthrobacter (polystyrene).
- Insects: Waxworms (Galleria mellonella) – eat plastic bags due to similarity with honeycomb (polyethylene).
Other polymers degraded by microbes:
- Cellulose (plant fibres)
- Chitin (fungi, insects)
- Cutin (leaf surfaces)
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
- Strong, stiff polyester family polymer.
- Common in bottles & food packaging.
- Produced by polymerisation of ethylene glycol + terephthalic acid.
- Fibres blended with wool/cotton to enhance properties.

