
PRELIMS
ISRO’s Gaganyaan Mission: Air Drop Test (IADT-01)
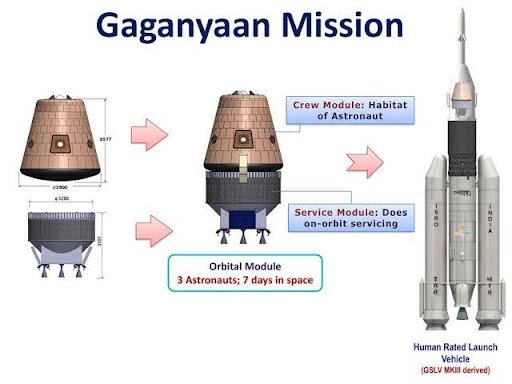
Why in News: ISRO has successfully carried out its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-01) for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission, validating the parachute-based deceleration system using a dummy crew capsule dropped from a Chinook helicopter.
Event: ISRO successfully conducted its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-01) on Sunday.
Purpose: End-to-end demonstration of parachute-based deceleration system for safe recovery of crew module.
How Conducted:
- Dummy crew capsule (~5 tonnes) lifted by Chinook helicopter.
- Dropped from altitude; parachutes deployed in sequence to slow descent to splashdown speed.
Significance:
- Critical milestone for Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission.
- Tests safety of astronauts during descent and splashdown phase.
Agencies Involved: ISRO, Indian Air Force, DRDO, Indian Navy, Indian Coast Guard.
Gaganyaan Mission:
- India’s first human spaceflight programme by ISRO.
- Aim: Send astronauts (Vyomnauts) into low Earth orbit (~400 km) for up to 7 days.
- Expected launch: 2025 (planned).
- Cost: ~₹9,000 crore.
Key Features:
- Orbital Module (OM) = Crew Module (CM) + Service Module (SM).
- Crew Module: Human-rated, re-entry capsule with life support & thermal protection.
- Crew Escape System (CES): For emergency abort.
- Launch Vehicle: Human-rated GSLV Mk III (LVM-3).
- Astronaut Training: Conducted in India with support from Russia’s Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Centre.
Comparable Global Missions:
- NASA’s Apollo Programme (1960s–70s).
- Russia’s Soyuz Programme.
- China’s Shenzhou Programme.
AIBD Executive Board, 2025
Why in News: India has been elected Chairman of the Executive Board of the Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development (AIBD) at the 23rd General Conference in Phuket, Thailand, marking its return to the top leadership role after nearly a decade and strengthening its influence in global broadcasting.

Event: In August 2025, India was elected Chairman of the Executive Board of the Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development (AIBD).
Where: During the 23rd AIBD General Conference in Phuket, Thailand (19–21 August 2025).
India’s Role:
- Already President of the AIBD General Conference until Aug 2025.
- Now also Chairman of the Executive Board → dual leadership positions.
- Represented by Prasar Bharati, India’s public service broadcaster.
- Gaurav Dwivedi (CEO, Prasar Bharati) chaired the Conference.
Theme of Conference: “Media for People, Peace & Prosperity”.
AIBD Background:
- Established in 1977 under UNESCO.
- Inter-governmental organisation for cooperation in broadcasting/media.
- 92 members from 45 countries (26 government members, 48 national broadcasters, 44 affiliates).
Significance:
- India returns to top leadership role after nearly a decade.
- Strengthens India’s voice in global broadcasting governance.
- Enhances regional media cooperation, content sharing, and sustainable development initiatives.
Cloudburst
- Definition (IMD): Rainfall >100 mm in 1 hour over an area of ~20–30 sq. km.
- Definition (WMO): Rainfall rate of ≥100 mm per hour; also refers to “skyfall” (Swedish term) →
- 1 mm/min (60 mm/hr) for short bursts.
- 50 mm/hr when sustained longer.
Physical Process:
- Occurs in thunderstorms when strong updrafts hold large water amounts aloft → sudden collapse releases intense rain.
- Orographic lifting (moist air forced up mountains) also contributes.
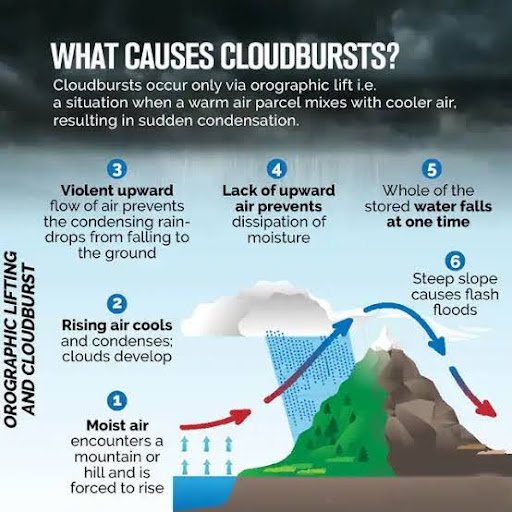
Nature:
- Localised, short-lived, very intense rainfall.
- Capable of causing flash floods and landslides, esp. in Himalayan regions.
Impact Area: Though localised, water flow may affect larger downstream regions.
North Block to host ‘Time and Timelessness’ heritage gallery
Why in News: North Block in New Delhi will house a new 1,500 sq m gallery “Time and Timelessness” under the Yuge Yugeen Bharat Museum, showcasing 100 landmark artefacts on India’s civilisational relationship with time
North Block Heritage Gallery
Location: North Block, Central Secretariat, New Delhi
Theme: Showcasing 100 landmark artefacts exploring Bharat’s civilisational relationship with time – cultural, philosophical, and scientific evolution.

Highlights on Display:
- Indus Valley terracotta hourglass (2500–1750 BC)
- Konark Sun Wheel (13th century)
- Chola-period Ghatika Yantra (10th century)
- Yantraraja manuscript (14th century)
- Calendar Panchanga Manuscript (18th century)
- Chola-period Nataraja bronze (10th–11th century)
Museum Complex: Part of Yuge Yugeen Bharat Museum (North & South Blocks).
Sections:
- Kaal-Avadharana – Time as a philosophical concept.
- Kaal-Ganana – Measured science of time (sundials, water clocks, astronomical manuscripts).
Key Artefacts in Time and Timelessness Gallery
Indus Valley Terracotta Hourglass
- Period: 2500–1750 BC
- Origin: Indus Valley Civilisation
- Significance: Early concept of measuring time using terracotta objects.
Konark Sun Wheel
- Period: 13th century
- Origin: Sun Temple, Konark (Odisha)
- Significance: Stone-carved wheel, functions as a sundial; symbol of time and cosmic order.
Chola-period Ghatika Yantra
- Period: 10th century
- Origin: Chola dynasty
- Significance: Ancient astronomical instrument to calculate time.
Yantraraja Manuscript
- Period: 14th century
- Type: Text on astronomy and instruments
- Significance: Guide to using yantras (instruments) for astronomical measurements.
Calendar Panchanga Manuscript
- Period: 18th century
- Origin: Traditional Indian calendar system
- Significance: Shows timekeeping in relation to celestial bodies; used for rituals & daily life.
Chola-period Nataraja Bronze
- Period: 10th–11th century
- Origin: Tamil Nadu (Chola dynasty)
- Significance: Depicts Lord Shiva as cosmic dancer, symbolising cyclical time (creation–destruction–regeneration).
Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS)
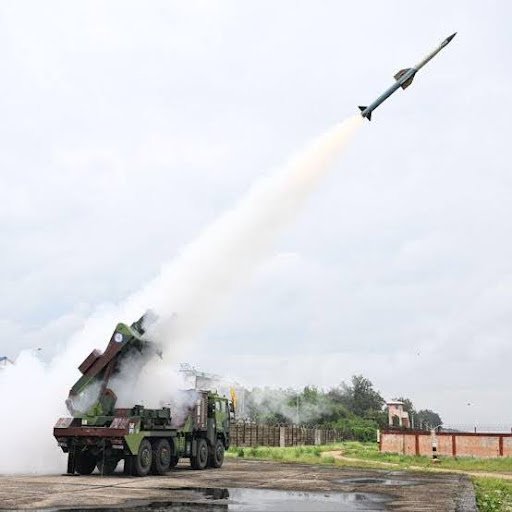

Why in News: DRDO successfully conducted maiden flight tests of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) off the coast of Odisha.
Key Features:
- Multi-layered Air Defence System developed indigenously.
Components:
- Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missiles (QRSAM)
- Advanced Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)
- High-power laser-based Directed Energy Weapon (DEW)

