
PRELIMS
Silver-Backed Chevrotain
Why in News :The silver-backed chevrotain, a tiny deer-like mammal, was rediscovered in Vietnam after nearly 30 years through camera traps, marking a major breakthrough in wildlife conservation.
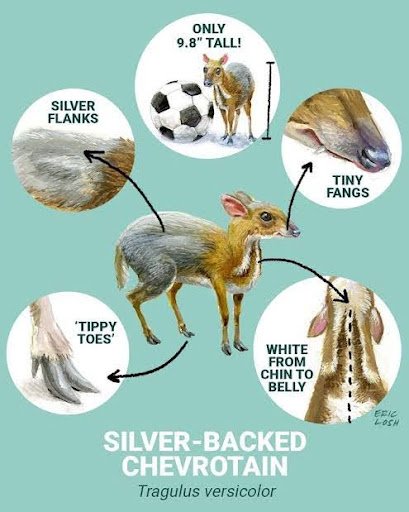
Species Name: Silver-backed chevrotain (also known as Two-tone mouse deer)
Rediscovery: After nearly 30 years; captured on camera traps in Vietnam’s Greater Annamites ecoregion
Status Before Rediscovery: Presumed extinct or lost to science
Location of Rediscovery: Southern Vietnamese lowland forests
Appearance:
- Size of a rabbit
- Russet head and front legs
- Silver-grey body and hind legs
- White grizzled rear
Habitat:
- Dense forests of the Greater Annamites, spanning Vietnam and Laos
- Biodiversity hotspot
Major Threats:
- Snaring by humans (most significant)
- Natural predators: leopards, wild dogs
Conservation Methodology:
- Used local ecological knowledge from villagers and forest rangers
- Camera traps set over months captured multiple independent sightings
Significance of Rediscovery:
- Shows that species presumed extinct may survive in remote habitats
- Highlights importance of technology + community engagement
- Stresses urgent anti-poaching and habitat protection efforts
Broader Implications:
- Rediscovery helps conserve entire ecosystems
- Boosts efforts to protect other ‘lost’ or endangered species
Old Trees, Ageing Farmers Worsen Outlook for Palm Oil Exporters
Why in News : Declining palm oil output from Malaysia and Indonesia due to ageing trees and ageing farmers.
Key Producers:
- Indonesia and Malaysia account for 85% of global crude palm oil supply.
- Smallholders control 40% of plantations in both countries.
Major Concerns:
- Ageing palm trees (20+ years) have declining yields.
- Elderly farmers hesitate to replant due to income loss during replanting period (3–5 years).
- Government subsidies for replanting have reduced.
- Biodiesel blending mandates in Indonesia are diverting palm oil from exports to domestic use.
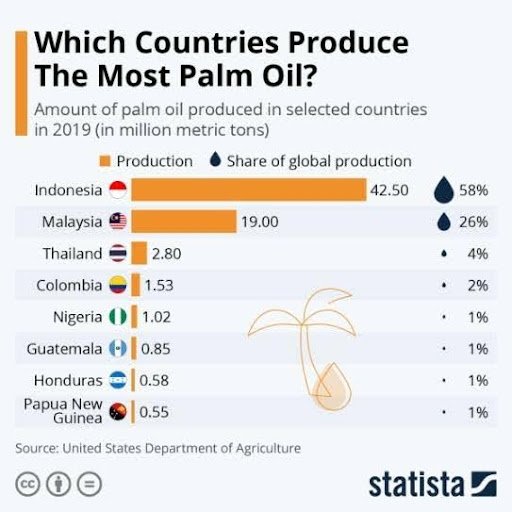
What is Palm Oil?
- Derived from African oil palm tree (Elaeis guineensis).
Two types:
- Crude Palm Oil (CPO) – from fruit pulp, used for cooking.
- Palm Kernel Oil (PKO) – from seed, used in cosmetics, pharma, cleaning products.
Both oils are colourless, odourless, and tasteless.
India’s Status
- India is the world’s largest importer of palm oil.
- Major oil palm producing states: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of national production).
Mission Launched:
- National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP), 2021
- Goal: Promote domestic cultivation, reduce import dependence on edible oils.
PM’s Pariksha Pe Charcha Sets Guinness World Record
Why in News: The 2025 edition of Pariksha Pe Charcha (PPC) has entered the Guinness World Records.
Record Title:
- Most people registered on a citizen engagement platform in one month.

Event Details:
- Pariksha Pe Charcha is an annual interactive programme where PM Narendra Modi engages with students, parents, and teachers.
- Focuses on exam stress management, motivation, and mental wellness.
Organisers:
- Conducted by the Ministry of Education in collaboration with MyGov.
- Started in 2018.
Exam Warriors – A Student-Centric Initiative
- Exam Warriors is a larger movement led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Aims to create a stress-free atmosphere for youngsters during examinations.
- Promotes a holistic and joyful approach to education.
- Seeks to involve students, parents, teachers, and society in fostering an environment where each child’s individuality is celebrated and encouraged.
Pariksha Pe Charcha (PPC) – A Component of Exam Warriors
- Pariksha Pe Charcha is an annual interactive programme under the Exam Warriors initiative.
WiFEX (Winter Fog Experiment)
Why in News: WiFEX (Winter Fog Experiment) has recently completed 10 successful years of operation and has now entered its next phase, WiFEX-II.
What is WiFEX?
- Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) is a long-term open-field research project focused on studying dense winter fog in North India and its impact on daily life and aviation safety.
Launch & Location:
- Started in winter 2015 at Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA), New Delhi.
Leading & Supporting Bodies:
- Led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), supported by India Meteorological Department (IMD) and National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF).
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).

Key Features:
- Uses advanced instruments like micrometeorology towers, ceilometers, and high-frequency sensors.
- Collects data on temperature layers, humidity, wind, turbulence, soil heat, and aerosols.
- Has developed a high-resolution (3 km) probabilistic fog prediction model.
- Predicts fog onset, density, duration, and clearing with over 85% accuracy for very dense fog (visibility < 200 meters).
WiFEX-II would be featuring:
- Localized, runway-specific fog predictions extended to more airports in North India.
- Installation of additional sensors for enhanced real-time monitoring.
- Helping airport operators manage operations safely and efficiently even during dense fog.
Significance:
- Enhances aviation safety during the winter fog season.
- Reduces costly flight diversions and delays.
- Provides critical data for better travel and operational planning during fog event
Supreme Court Empowers Pollution Control Boards to Impose Restitutionary Damages
Why in News: The Supreme Court has ruled that Pollution Control Boards (PCBs) have the power to impose and collect restitutionary and compensatory damages for restoring polluted air and water bodies.

Judgment:
Delivered by Justice P.S. Narasimha and Justice Manoj Misra.
Statutory Provisions Involved:
- Section 33A of the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- Section 31A of the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
Court Directions:
- PCBs can impose fixed monetary penalties or demand bank guarantees ex-ante (in advance) to prevent potential environmental damage.
- Power to be exercised after subordinate legislation (rules/regulations) is issued under both Acts.
- Rules must follow natural justice principles.
Doctrine Cited:
- Polluter Pays Principle – Polluting industries are responsible for bearing the cost of environmental restoration.
Purpose:
- To restore polluted ecosystems as close as possible to their original, pristine condition.
- Expanded Powers of PCBs under Water and Air Acts:
- Prevent, control, and abate pollution.
- Direct closure, prohibition, or regulation of industries or processes.
- Stop or regulate electricity, water, or service supply to polluting units.
- Exercise flexibility in issuing directions under environmental laws.
Significance:
- This landmark judgment enhances the regulatory authority of PCBs and strengthens environmental governance in India.

