Prelims Pinpointer
Retail Inflation
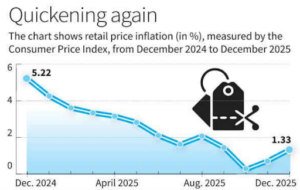
In News
- India’s retail inflation rose to 1.33%, a three-month high, but remained below RBI’s lower tolerance of 2%.
- The low inflation was driven by a broad-based decline in prices across sectors.
- Core inflation rose to a 28-month high of 4.8%, mainly due to precious metals (gold and silver).
- Retail inflation, also called CPI inflation, measures the change in prices of goods and services consumed by households.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
-
- CPI is calculated for a fixed basket of goods and services.
- The change in CPI over time is called retail inflation.
- What CPI Indicates
-
- Cost of living
- Purchasing power of consumers
- Relative prices of goods and services
- Value of the Indian rupee
- How CPI is Calculated
-
- CPI is measured as a percentage change from a base year.
- Base year for CPI = 2012.
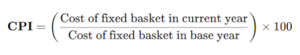
- Who Releases CPI Data?
-
- Compiled and released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Published monthly for Rural, Urban, and Combined sectors at All-India and State levels.
- How CPI is Used
-
- Primary measure of inflation in India.
- Used by RBI for inflation targeting and monetary policy.
- Helps assess price stability.
- Acts as a deflator in national income accounts.
- Measures real value of wages, salaries and pensions and currency purchasing power.
- RBI Inflation Targeting Framework
-
- Target inflation: 4%
- Tolerance band: 2% – 6%
- Retail inflation below 2% is considered below comfort level.
Nipah Virus (NiV)
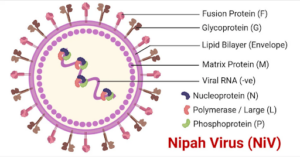
Context: Two persons suspected of being infected by Nipah virus in West Bengal are undergoing treatment, officials said on Monday. The Union Health Ministry responded by deploying a national joint outbreak response team to manage the situation.
Nipah Virus (NiV)
- Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus, spreading from animals to humans, food, and human-to-human contact.
- It is an RNA virus of the Paramyxoviridae family and Henipavirus genus, closely related to the Hendra virus.
- Natural host: Fruit bats (Pteropus genus); virus is present in their urine, faeces, saliva and birthing fluids.
- Intermediate hosts include pigs, dogs, cats, goats, horses and sheep.
- Case fatality rate: 40%–75%, making it one of the deadliest viral infections.
- Disease caused: Encephalitis with fever, headache, drowsiness, disorientation, confusion, coma and death.
- Diagnosis: RT-PCR from body fluids and ELISA-based antibody detection.
- Prevention: No vaccine available for humans or animals.
- WHO status: Listed as a Priority Disease for research and emergency preparedness.
Pax Silica

Context: India will be invited to join “Pax Silica” as incoming U.S. Ambassador Sergio Gor announced on Monday.
Pax Silica Initiative: Overview
- It is a U.S.-led strategic initiative
- Objective: Build a secure, prosperous and innovation-driven silicon supply chain
- Covers the entire value chain:
- Critical minerals
- Energy inputs
- Advanced manufacturing
- Semiconductors
- Artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure
- Logistics and transportation
Core Objectives
- Reduce coercive dependencies in strategic technology supply chains
- Protect materials and capabilities foundational to AI development
- Ensure aligned nations can:
- Develop
- Deploy
- Scale transformative technologies
Countries Participating in Pax Silica
- Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Netherlands, United Kingdom, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Australia
Technology Ecosystem Focus
- Build trusted technology ecosystems including:
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) systems
- Fiber-optic cables
- Data centers
- Foundational AI models
- Technology applications
Swami Vivekananda

Basic Facts
- Original name: Narendranath Datta
- Born on: 12 January 1863
- Birthplace: Kolkata
- 12 January observed as National Youth Day to commemorate his birth anniversary
Spiritual and Organizational Role
- Disciple of Sri Ramakrishna
- After Ramakrishna’s death in 1886, formed a monastic brotherhood
- This brotherhood later became the Ramakrishna Mission
- Lived as a wandering monk across the Indian subcontinent
Key Philosophical Ideas
- Promoted Universal Vedanta
- Advocated religious pluralism
- Popularised idea: “Truth is one, expressed in many ways”
- Emphasised practical spirituality based on:
- Compassion
- Discipline
- Service
- Propagated the Four Yogas:
- Karma Yoga
- Bhakti Yoga
- Jnana Yoga
- Raja Yoga
- Supported rational interpretation of Indian scriptures
Chicago Parliament of Religions, 1893
- Spoke at the World’s Parliament of Religions
- Presented Vedanta as a universal philosophy
- Advocated religious tolerance and pluralism
- Projected India as a civilizational contributor
Major Works
- Raja Yoga
- Karma Yoga
- Lectures from Colombo to Almora
- Interpreting the Gita
Orobanche aegyptiaca (Parasitic Weed)

About
- Orobanche aegyptiaca (locally called Margoja) is a root-parasitic flowering weed that attacks mustard and other crops.
- It attaches to crop roots and extracts water, carbon and nutrients, causing severe yield loss.
- It is native to the Mediterranean–West Asian region and has spread to South Asia, North Africa and parts of Europe.
Distribution and Spread
- It is widespread in mustard-growing areas of Rajasthan and Haryana.
- Seeds remain viable in soil for up to 20 years, enabling repeated infestations.
- It spreads through wind, irrigation water, farm implements and contaminated soil.
Key Biological Features
- Obligate parasite – cannot survive without a host plant.
- Attacks underground before emerging, making early detection difficult.
- Very high reproductive capacity – one plant produces 40–45 flowers, each releasing 4,000–5,000 tiny seeds.
- Moist soil after first irrigation triggers seed germination and root attachment.
Impact on Agriculture
- Causes wilting, yellowing, stunted growth and heavy yield loss in mustard.
- Forces farmers to shift away from mustard cultivation.
- Poses a risk to India’s edible-oil security, as mustard contributes over 4 million tonnes to domestic oil output.
Operation Hawkeye
About the Operation
- Operation Hawkeye is a US-led counter-terror air campaign targeting ISIS bases in Syria.
- It was launched in December 2025 by the United States under President Donald Trump and executed by US Central Command (CENTCOM).
- The operation involved large-scale air and precision strikes across ISIS-held locations.
- It was triggered by an ISIS ambush in Palmyra that killed two US soldiers and one civilian interpreter.
- The aim was to retaliate against ISIS, degrade its networks, prevent regrouping, and protect US and coalition forces.
Key Facts about Syria
-
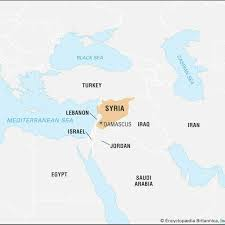
- Syria is a sovereign country in West Asia on the eastern Mediterranean coast.
- It emerged from a 13-year civil war (2011–2024) and is now ruled by an interim government led by President Ahmed al-Sharaa.
- Capital: Damascus.
- Neighbouring countries: Turkey, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon and Israel.
- Physical Geography
- Mediterranean coastline provides strategic naval and trade access.
- Al-Ansariyah Mountains separate the humid coast from the arid interior.
- Anti-Lebanon Range & Mount Hermon form natural borders and water sources.
- Syrian Desert dominates the eastern interior.
- Euphrates River is the main irrigation and hydropower lifeline.
- Orontes River supports fertile western plains and settlements.


