Nigeria
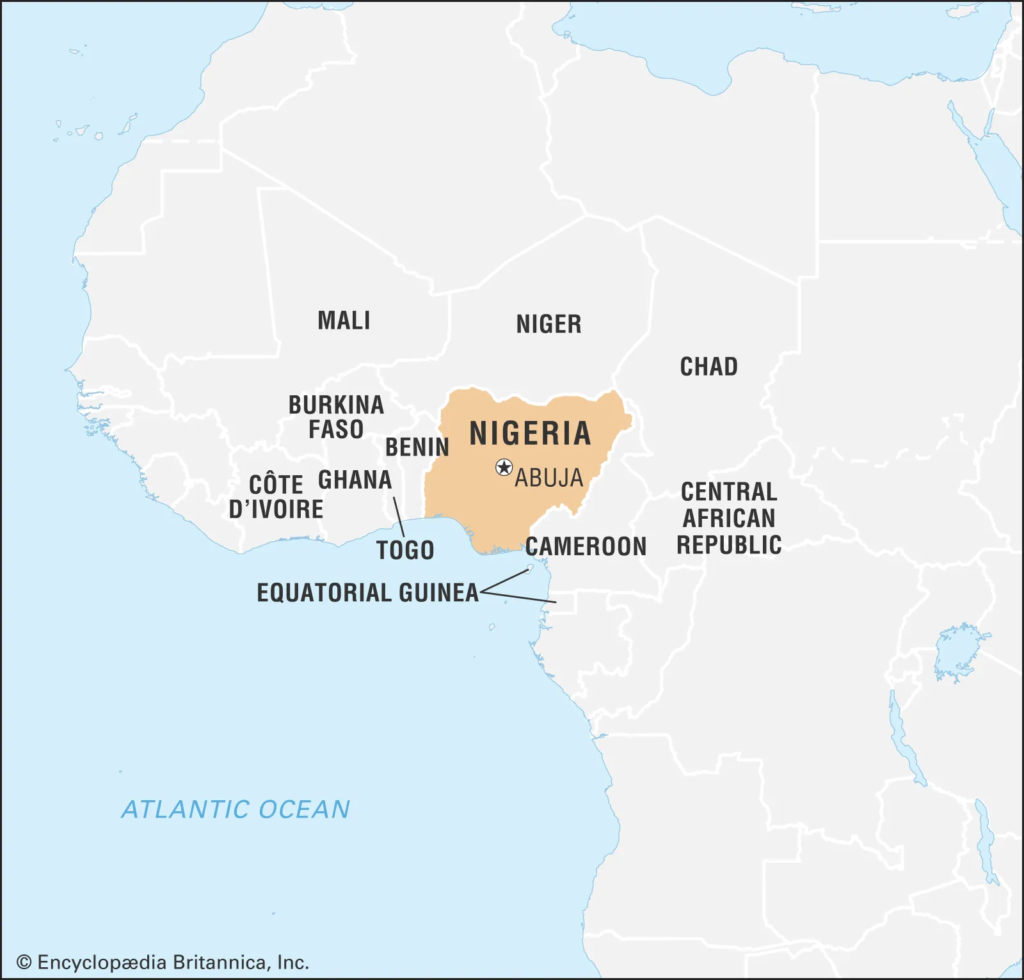
Location
- Nigeria is located on the western coast of Africa along the Atlantic shoreline.
- It lies along the Gulf of Guinea, forming part of West Africa.
Capital
- Abuja serves as Nigeria’s capital city since 1991.
- It replaced Lagos to ensure better administrative centrality.
Neighbouring Countries & Boundaries
- Niger lies to the north of Nigeria.
- Chad is located to the northeast.
- Cameroon borders Nigeria to the east.
- Gulf of Guinea (Atlantic Ocean) lies to the south.
Key Geographical Features
- Rivers & Drainage System
- Niger River forms Nigeria’s principal river system.
- Benue River is the major tributary joining the Niger.
- Their confluence creates fertile agricultural zones.
- Niger Delta forms one of the largest wetlands globally.
- Mountains & Plateaus
- Jos Plateau lies in central Nigeria.
- Plateau region contains extinct volcanic formations.
- Chappal Waddi (2,419 m) is the country’s highest peak.
- It forms part of the Cameroon Highlands.
- Other ranges include Shebshi Mountains.
- Udi–Nsukka Escarpment marks eastern highland terrain.
- Plains & Soil Regions
- Sokoto Plains dominate the northwest region.
- Borno Plains lie in the northeast.
- Central Nigeria has fertile savanna soils.
- Southern regions contain forest-rich tropical soils.
- Climate
- Climate varies from arid conditions in the north.
- Southern Nigeria experiences humid equatorial climate.
- Rainfall increases progressively toward coastal regions.
- Natural Resources
- Nigeria possesses vast petroleum and natural gas reserves.
- Hydrocarbons form the backbone of its national economy.
Agni-3 Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)

Context: India successfully test-fired Agni-3 Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile from Integrated Test Range, Chandipur, Odisha, validating operational readiness.
About Agni-3 Missile
- Agni-3 is an Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile capable of delivering strategic payloads up to 3,000 km.
- Forms a vital component of India’s land-based nuclear deterrent under Agni missile series.
- Developed by
- Developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Operationally deployed under Strategic Forces Command (SFC).
- Aim / Objectives
- Ensure credible minimum nuclear deterrence against long-range adversarial threats.
- Provide reliable land-based second-strike capability.
- Strengthen India’s strategic reach beyond short- and medium-range systems.
Key Features
- Range: Approximately 3,000 km operational strike capability.
- Type: Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM).
- Launch platform: Road-mobile launcher; canisterised versions tested earlier.
- Payload: Capable of carrying conventional or nuclear warheads.
- Guidance system: Advanced inertial navigation ensuring high targeting accuracy.
- Propulsion: Two-stage solid-fuel propulsion configuration.
- Operational validation: 2026 test confirmed all mission parameters.
Scheme To Form Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)

Context: Government launched Central Sector Scheme to form 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) nationwide.
What is the Scheme?
- Central Sector Scheme to promote farmer collectivisation for production and marketing.
- Targets small and marginal farmers’ income enhancement.
- Strengthens processing, aggregation, and value-chain integration.
- Launched in: 29 February 2020
Implementing Agencies (IAs)
- SFAC: Small Farmers’ Agribusiness Consortium.
- NABARD: National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
- NCDC: National Cooperative Development Corporation.
- NAFED: National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India.
Aim
- Build sustainable, income-oriented farming ecosystem.
- Improve access to inputs, credit, technology, and markets.
- Enhance farmers’ bargaining power and price realisation.
Key Features
- Cluster & Commodity Approach
- FPOs formed on produce-cluster basis.
- Aligned with One District One Product (ODOP) strategy.
- Financial Support
- Up to ₹18 lakh per FPO for 3-year handholding.
- Matching equity grant up to ₹15 lakh.
- Equity support capped at ₹2,000 per farmer.
- Credit guarantee up to ₹2 crore project loans.
- Market Linkages
- Forward linkages facilitated by NAFED.
- Integrates farmers with value chains and buyers.
- Capacity Building
- Training through BIRD, Lucknow.
- Support from LINAC, Gurugram.
- Inclusion Focus
- Encourages women farmer participation.
- Covers Aspirational Districts extensively.
Deep Tech Start-ups
Context: The Centre formally defined ‘Deep Tech Start-ups’ through a DPIIT gazette notification.
What are Deep Tech Start-ups?
- Enterprises developing solutions using advanced scientific or engineering knowledge.
- Focus on breakthrough innovation, not incremental digital platforms.
- Characterised by high technical uncertainty and scientific complexity.
- Require long gestation periods and sustained R&D investments.
Organisations Involved
- DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade): Certifying authority for deep tech start-ups.
- ANRF (Anusandhan National Research Foundation): Custodian of ₹1 lakh crore Research, Development & Innovation Fund.
Eligibility Criteria
- Core work must generate new scientific or engineering knowledge.
- Significant expenditure devoted to Research & Development activities.
- Ownership or creation of novel Intellectual Property (IP).
- Commercialisation roadmap for developed technologies mandatory.
- High infrastructure, capital, and scientific risk exposure.
- Long development timelines before market deployment.
- Non-core investments prohibited unless linked to knowledge creation.
- Mandatory certification application to DPIIT required.
Key Features
- Recognition & Regulatory Support
- Extended recognition period up to 20 years.
- Higher turnover eligibility threshold of ₹300 crore.
- Financing Support
- Access to concessional long-term finance.
- Interest rates reported in 2–4% range.
- Loan tenure may extend up to 15 years.
- Governance Mechanism
- Certification overseen by inter-ministerial technical board.
- Ensures scientific authenticity and innovation depth.
Mount Aconcagua
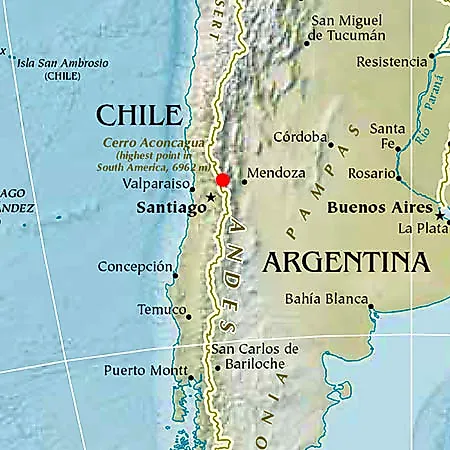
Context: Indian mountaineer Kabak Yano summited Mount Aconcagua during her Seven Summits Expedition.
What is Mount Aconcagua?
- Mount Aconcagua is the highest mountain in South America.
- It is the tallest peak in the Western Hemisphere.
- It is the highest mountain outside Asia.
- Elevation: 22,831 feet (6,959 metres) above sea level.
- Considered a challenging non-technical climb among Seven Summits.
Location
- Located in Argentina, western Mendoza Province.
- Lies close to the Argentina–Chile border.
- Forms part of the Southern Andes mountain range.
Geological Features
- Mountain has a volcanic origin but is not active.
- Formed mainly through tectonic uplift of Andes.
- Contains two peaks — North and South summits.
- Joined by ridge called Cresta del Guanaco.
- Region experiences thin air and extreme winds.
- Sub-zero temperatures create severe climbing conditions.
- Altitude sickness remains a major expedition risk.
Significance
- Geographical Importance
- Highest point in both Southern and Western Hemispheres.
- Mountaineering Importance
- Part of the prestigious Seven Summits challenge.
- Attracts climbers globally despite harsh climate.
- Scientific Importance
- Elevation studied using modern GPS measurements.
- Subject of debate over exact summit height.
Bharat GenAI (Generative Artificial Intelligence) Initiative

Context: The Ministry of Science & Technology informed that Bharat GenAI text models will cover all 22 Scheduled Languages soon.
What is Bharat GenAI?
- BharatGen is India’s first government-supported sovereign foundational AI initiative.
- Develops AI models tailored to Indian languages and societal contexts.
- Focuses on building indigenous Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Designed to reduce dependence on foreign AI ecosystems.
Aim
- To transform AI innovation across India’s linguistic and cultural diversity.
- To enable inclusive digital services in regional languages.
- To support governance, education, and research applications.
Modalities Covered
- Text models through Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Speech systems: Text-to-Speech (TTS) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR).
- Vision-language integrated AI systems.
Language Coverage
- Currently supports 15 Indian languages.
- Includes Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Kannada, Maithili.
- Also Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi.
- Covers Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, and Telugu.
- Target: Coverage of all 22 Scheduled Languages.
Institutional Framework
- Developed under National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Implemented through TIH Foundation for IoT and IoE at IIT Bombay.
- Executed via a network of 25 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIHs).
- Four hubs upgraded as Technology Translational Research Parks (TTRPs).
Pillars of Bharat GenAI
- Technology development.
- Entrepreneurship promotion.
- Human resource development.
- International collaboration.
Key Features
- Multilingual and multimodal AI models.
- Training on Bhartiya datasets.
- Open-source technology architecture.
- Indigenous generative AI research ecosystem.
Bailey Bridge

Context: India recently sent Bailey bridge materials to Sri Lanka for post-Cyclone reconstruction assistance.
What is a Bailey Bridge?
- Bailey Bridge is a modular, prefabricated truss bridge system.
- Components are pre-built and assembled rapidly on-site.
- Designed for quick deployment in emergencies and conflict zones.
Inventor
- Invented by Donald Coleman Bailey, an English civil engineer.
- Developed in 1941 during World War-II.
Key Characteristics
- Modular design enables flexible bridge length.
- Highly portable; parts transported easily.
- Strong load-bearing steel framework.
- Extremely versatile across terrains and conditions.
Design & Construction
- Built using prefabricated steel panels.
- Panels assembled manually without heavy machinery.
- Sections joined to create full bridge span.
- Connected using pins and bolts.
- Forms a truss structure distributing load evenly.
Construction Advantages
- Requires minimal equipment and logistics.
- Rapid installation in disaster-hit areas.
- Suitable where cranes or hoisting machines cannot reach.
- Assembly occupies limited ground space.
Load Capacity
- Designed to carry heavy military and civilian loads.
- Can support tanks and heavy vehicles.
Ideal Usage Areas
- River crossings.
- Mountain valleys.
- Remote or conflict-affected regions.
- Temporary restoration after floods, cyclones, earthquakes.
Significance
- Critical for military logistics and disaster response.
- Enables rapid restoration of connectivity.
- Widely used in humanitarian relief operations.

