SPREE 2025

Context
- ESIC launched Scheme for Promotion of Registration of Employers and Employees (SPREE) 2025 to expand ESI coverage and formalise informal workforce participation.
What is SPREE?
- A special amnesty scheme to register unregistered employers and employees under ESI framework.
- Focuses on contractual, temporary, and unorganised workers lacking formal social security coverage.
Implementing Authority
- Launched by Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC).
- Administered under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India.
Objective
- Promote voluntary compliance and expand social security through formalisation of informal employment.
Key Features
- Digital registration enabled through ESIC portal, Shram Suvidha portal, and MCA portal.
- No retrospective contribution, inspection, or legal action for the pre-registration period.
- Registration treated as valid from the date declared by the employer.
- Removes litigation fears for employers regarding past non-compliance.
- Extends ESI coverage to temporary, contractual, and unorganised sector workers.
- One-time amnesty encourages large-scale participation without penal consequences.
Significance
- Strengthens labour formalisation by integrating informal workers into the organised workforce.
- Expands access to ESI health insurance and social security benefits nationwide.
Tirukkural And Thiruvalluvar

Context
- Prime Minister paid homage to Thiruvalluvar on Thiruvalluvar Day.
- Citizens were urged to read Tirukkural for ethical and social values.
About Thiruvalluvar
- Celebrated Tamil poet–philosopher associated with Sangam or post-Sangam intellectual tradition.
- Revered across South India as a moral teacher and ethical guide.
- Estimated period ranges between 300 BCE and 600 CE in scholarly traditions.
- Popularly associated with Mylapore region of present-day Chennai.
- Emphasised practical morality for individuals, society, and rulers through concise couplets.
- Advocated truth, compassion, self-control, non-violence, and universal humanism.
- Presented ideals of just governance, public welfare, and ethical statecraft.
About Tirukkural
- Classical Tamil text consisting of 1,330 short ethical couplets called kurals.
- Traditionally attributed to Thiruvalluvar as the sole author.
- Structured into three books: Aram, Porul, and Inbam.
- Aram focuses on virtue and moral conduct in personal life.
- Porul deals with governance, economy, leadership, and public administration.
- Inbam addresses love, family life, and emotional relationships.
- Written in concise aphoristic style, easy to memorise and interpret.
- Covers justice, friendship, social harmony, leadership, and civic responsibility.
- Widely regarded as secular and universally applicable moral literature.
- Popularly referred to as the “Tamil Veda” in cultural tradition.
Significance
- Serves as a foundational ethical guide for governance and public integrity.
- Represents a core pillar of Tamil literary and civilisational heritage.
- Recognised as one of the most translated Tamil works globally.
Project Suncatcher

Context
- Google Research proposed Project Suncatcher to explore space-based, solar-powered AI data centres.
What it is
- Concept and research programme to deploy AI datacentres in low-Earth orbit (LEO).
- Uses continuous solar power to run energy-intensive artificial intelligence workloads.
- Launched by: Google Research (Google).
Aim
- Reduce AI energy footprint using uninterrupted space-based solar power.
- Decouple AI growth from terrestrial grids, land use, and water-based cooling systems.
How it Works
- Uses densely clustered satellites, not a sparse global constellation.
- Operates in sun-synchronous orbits to ensure constant sunlight exposure.
- Distributes AI workloads through ultra-high-bandwidth inter-satellite communication links.
- Limits Earth downlinks to input and output data only.
- Employs radiation-tolerant TPUs and specialised thermal systems for vacuum operations.
Key Features
- Always-on solar energy due to continuous sunlight in selected orbital paths.
- Petabit-scale inter-satellite networking for distributed AI training and inference.
- Radiation-hardened compute systems tested for multi-year space operation.
- Minimal dependence on Earth-based bandwidth and infrastructure.
- Modular, scalable constellation architecture with periodic satellite replacement.
Significance
- Provides a sustainable pathway for expanding global AI compute capacity.
- Reduces pressure on terrestrial power grids, water resources, and land availability.
Traditional Indelible Ink

What it is
- Permanent marking ink applied on a voter’s finger after voting to prevent repeat voting.
- Introduced in 1962 (Third General Election) as a low-cost anti-impersonation measure.
Manufactured by
- Produced exclusively by Mysore Paints and Varnish Limited, a Karnataka government undertaking.
- Formula developed by National Physical Laboratory (NPL), India, and closely guarded.
Aim
- Prevents multiple voting and impersonation during elections.
- Ensures integrity and credibility of large-scale electoral processes.
Key Features
- Silver nitrate–based formulation that reacts with keratin and light to form a chemical stain.
- Dark, long-lasting mark penetrates skin and nail for high visibility.
- Difficult to remove using soap, water, or common chemicals.
- Standardised application point on left index finger across nail and cuticle.
- Extended visibility period of 3–4 days on skin and 2–4 weeks on nail.
Significance
- Acts as a visible and universally recognised electoral safeguard.
- Strengthens public trust in free and fair elections.
- Demonstrates six decades of proven reliability in Indian democracy.
RBS-15 Missile
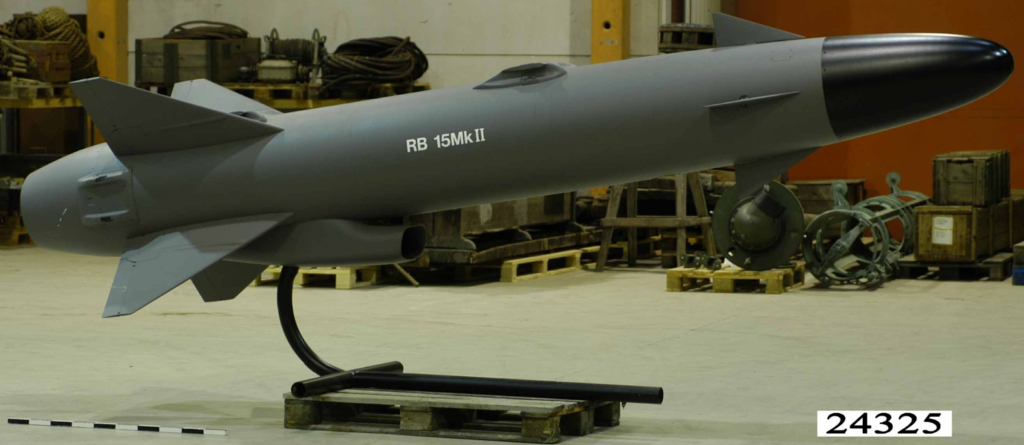

What it is
- RBS-15 is a fire-and-forget, anti-ship missile with surface-to-surface and air-to-surface capability.
- It also possesses land-attack capability for engaging coastal and land-based targets.
- Developed by Saab Bofors Dynamics, Sweden.
Physical Specifications
- Length: 4.35 metres.
- Fuselage diameter: 0.5 metres.
- Wingspan: 1.4 metres.
- Launch weight: 800 kilograms.
- In-flight weight: 650 kilograms.
Performance
- Range: Up to 200 kilometres.
- Speed: Subsonic, approximately Mach 0.9.
- Warhead: 200 kg high-explosive, pre-fragmented blast warhead for maximum target damage.
Guidance and Navigation
- Inertial Navigation System (INS) combined with GPS receiver.
- Radar altimeter for low-altitude flight control.
- Ku-band radar seeker for terminal target acquisition.
Key Features
- Low sea-skimming flight profile with unpredictable evasive manoeuvres.
- Low radar cross-section and infrared signature for reduced detectability.
- Advanced target discrimination and selection capability.
- High resistance to electronic countermeasures, including chaff, jammers, and decoys.
Operational Support System
- Missile Engagement Planning System (MEPS) enables mission planning for multiple combat scenarios.
Vrindavani and Karan Fries Cattle Breeds

Context
- India has registered two high-yielding synthetic cattle breeds: Karan Fries and Vrindavani.
About Karan Fries
- Developed by National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), Karnal, Haryana.
- Crossbreed of indigenous Tharparkar cows and Holstein-Friesian bulls.
- Synthetic breed combining high milk productivity with climatic resilience.
- Produces over 3,500 kilograms of milk in a 10-month lactation period.
- Achieves peak daily milk yield up to 46.5 kilograms under optimal conditions.
About Vrindavani
- Developed by ICAR–Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Bareilly, Uttar Pradesh.
- Synthetic breed created by blending Holstein-Friesian, Brown Swiss, and Jersey.
- Crossed with indigenous Hariana cattle for adaptability and disease resistance.
- Designed to combine high milk yield with suitability to Indian agro-climatic conditions.
Lake Natron

Context
- Lake Natron in Tanzania glows blood-red due to volcanic origin and extreme chemical composition.
Location and Geography
- Located in Arusha region of northern Tanzania, near the Kenya border.
- Lies in the Gregory Rift, eastern branch of the East African Rift System.
- Designated as a Ramsar Site of International Importance in 2001.
- Extinct Gelai Volcano, rising 2,942 metres, is visible southeast of the lake.
- Primarily fed by the Ewaso Ng’iro River originating in central Kenya.
- Measures approximately 57 kilometres in length and 22 kilometres in maximum width.
Hydrology and Chemical Features
- The lake has no outlet, causing extremely high evaporation rates throughout the year.
- Evaporation leaves behind natron and trona, increasing salt and mineral concentration.
- Water shows extreme alkalinity, making it one of the world’s harshest aquatic environments.
- The red colour is caused by algae pigments thriving in highly alkaline waters.
Ecological Significance
- Saline conditions make the lake inhospitable for most plants and animal species.
- Surrounding marshes support large breeding populations of flamingos in East Africa.
- Flamingos feed primarily on spirulina, a green algae with red pigmentation.
- Hosts one of the highest concentrations of lesser and greater flamingos regionally.
Chabahar Port
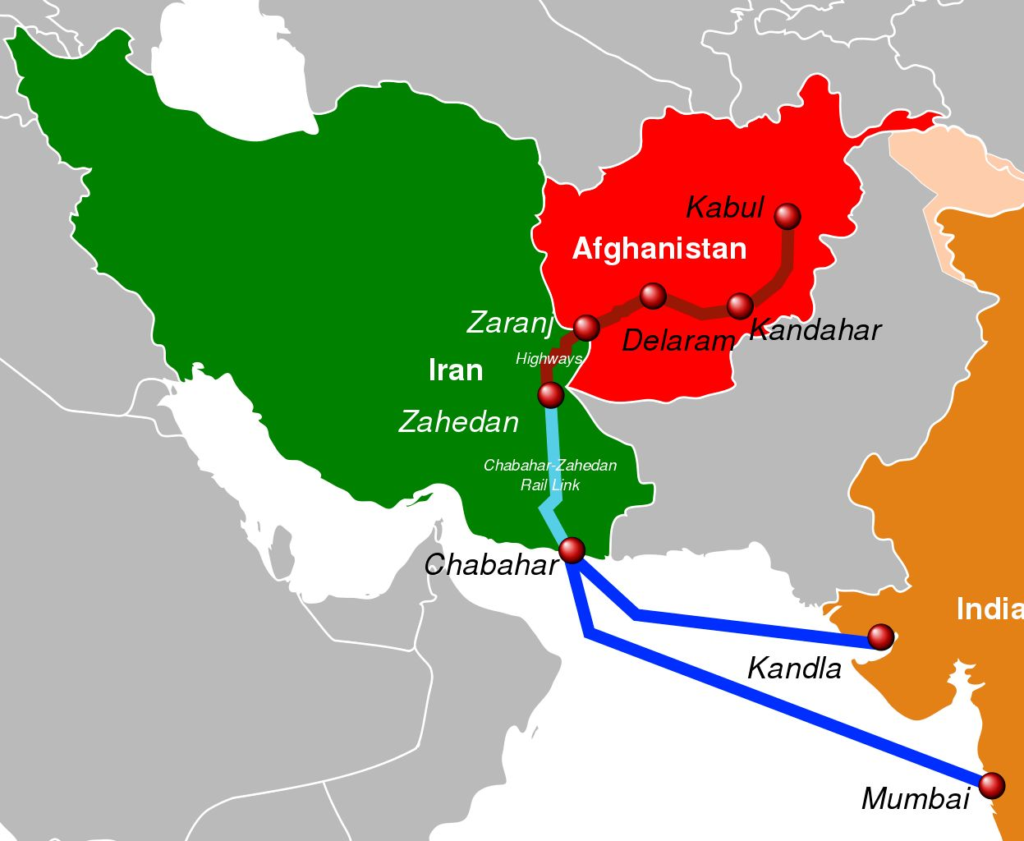
Location and Geography
- Located in Sistan-Baluchistan province, southeastern Iran.
- Situated on the Gulf of Oman at the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz.
- Only Iranian port with direct access to the Indian Ocean.
- Comprises two terminals – Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
Strategic Connectivity
- Geographically close to India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, enhancing regional transit potential.
- Acts as a key node on the International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- INSTC links Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea via Iran, and onward to Russia and Northern Europe.
- Distance:
- Kandla–Chabahar: 550 nautical miles
- Mumbai–Chabahar: 786 nautical miles.
Chabahar Project – Background
- Tripartite agreement signed in May 2016 between India, Iran, and Afghanistan.
- Focused on developing the Shahid Beheshti Terminal.
- Recognised as India’s first overseas port development project.
Infrastructure Components
- Development of port terminals and cargo handling facilities.
- Construction of Chabahar–Zahedan railway line to connect with Iran’s national rail network.
Strategic and Economic Significance
- Enables India to bypass Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- Serves as a transit trade hub between India, Iran, and Afghanistan.
- Provides an alternative trade route to traditional Silk Road corridors through China.
- Enhances India’s geopolitical presence in West and Central Asia.
International Relevance
- Supports regional connectivity, trade diversification, and energy corridor development.
- Strengthens India’s role in Eurasian logistics and multilateral transport frameworks.
West Bank
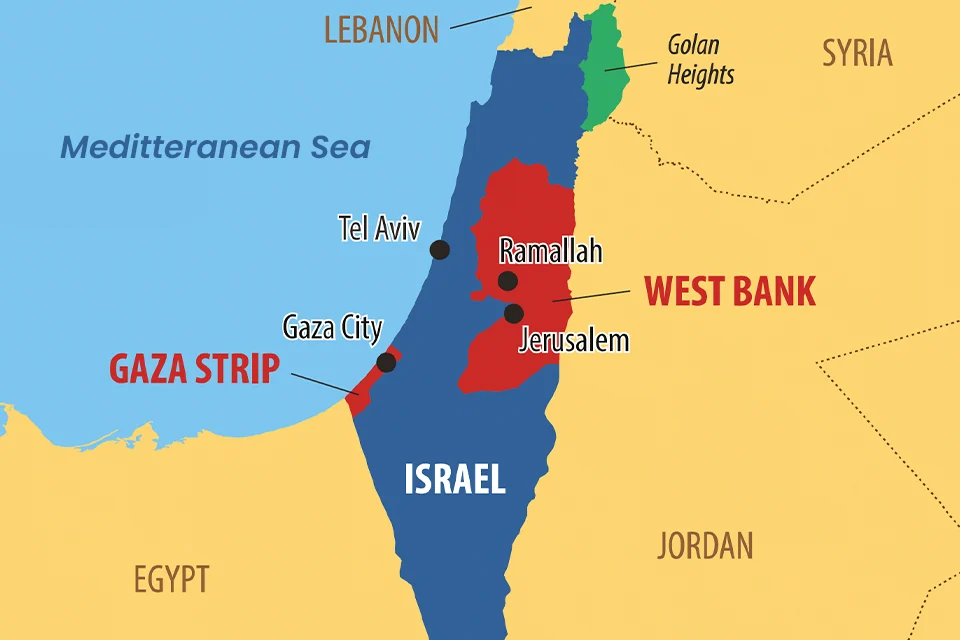
Overview
- The West Bank is a landlocked territory in Western Asia, forming the main part of Palestinian territories.
- It lies near the Mediterranean coast but has no direct sea access.
Geographical Location
- East: Jordan and the Dead Sea.
- North, West, South: Bordered by Israel.
- De facto capital: Ramallah, administrative centre of Palestine.
Historical Background
- Captured by Jordan after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War.
- Occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War in 1967.
- Remains under Israeli occupation since 1967.
Demography and Settlements
- Approximately 2.6 million Palestinians reside in the West Bank.
- Around 130 formal Israeli settlements are present in the territory.
Legal Status of Settlements
- Declared illegal under international law by UN bodies and ICJ.
- Fourth Geneva Convention (1949) prohibits population transfer into occupied territories.
Oslo Accords
- Agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- Oslo I: Signed in 1993, Washington D.C.
- Oslo II: Signed in 1995, Taba, Egypt.
- Key Outcomes of Oslo Accords
- Created the Palestinian National Authority (PNA).
- Granted limited self-governance in parts of West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- Did not establish a sovereign Palestinian state.


